
Commercial Marine Power: 12V LiFePO4 Battery Upgrades for Workboats and Fleets
Step-by-step sizing for a 12V LiFePO4 battery bank: calculate daily Wh, set DoD, add margin — secure reliable marine power and proper charger and cable specs.

Upgrading Your RV Power System to a 12V LiFePO4 Battery: A Step-By-Step Guide For Installers
Extend boondocking days with correctly sized 12V LiFePO4 battery packs, charger, and controller upgrades & monitoring. Avoid common RV lithium battery mistakes.
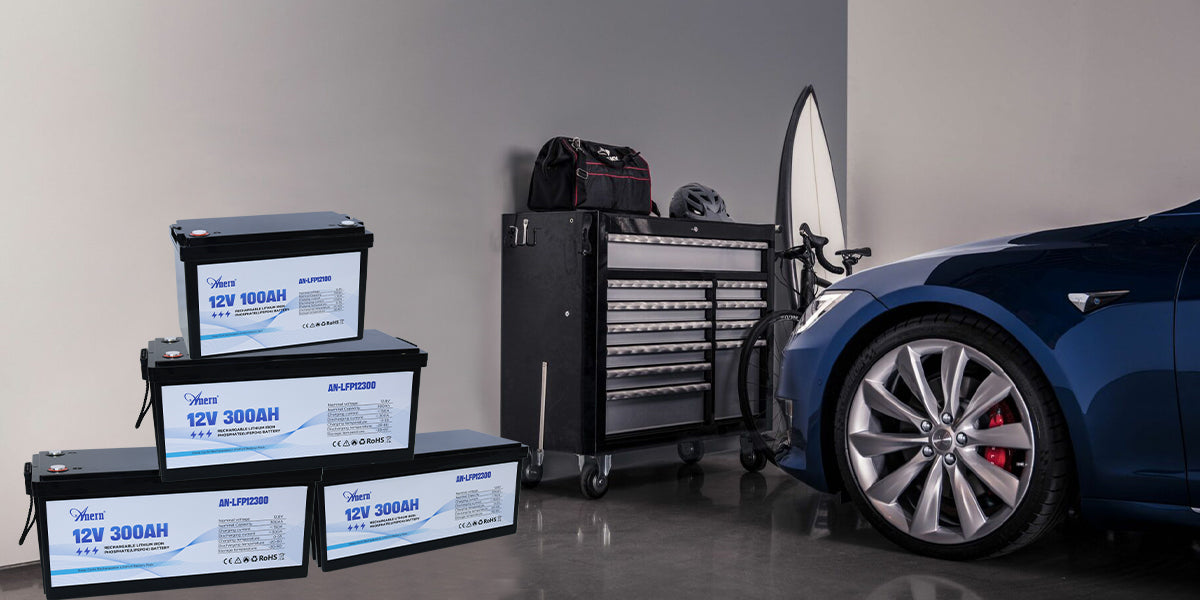

Best Practices for Charging 12V LiFePO4 Batteries in Professional Fleets
Keep your fleet powered: clear 12V LiFePO4 battery charging steps, CC/CV voltages, temp limits and BMS tips to reduce downtime and replacements.

LiFePO4 Battery for Small Manufacturing: The Smart Power Upgrade for Workshops
Stop power surprises in your shop. LiFePO4 battery systems reduce downtime, boost efficiency, and outlast lead-acid—ideal for small workshops needing reliable backup.

LiFePO4 Battery Charging Profiles for Long Life
Stop guessing your LiFePO4 charging profile! Learn the specific voltage and C-rate settings for solar, RV, and backup systems to protect battery life. Click now!
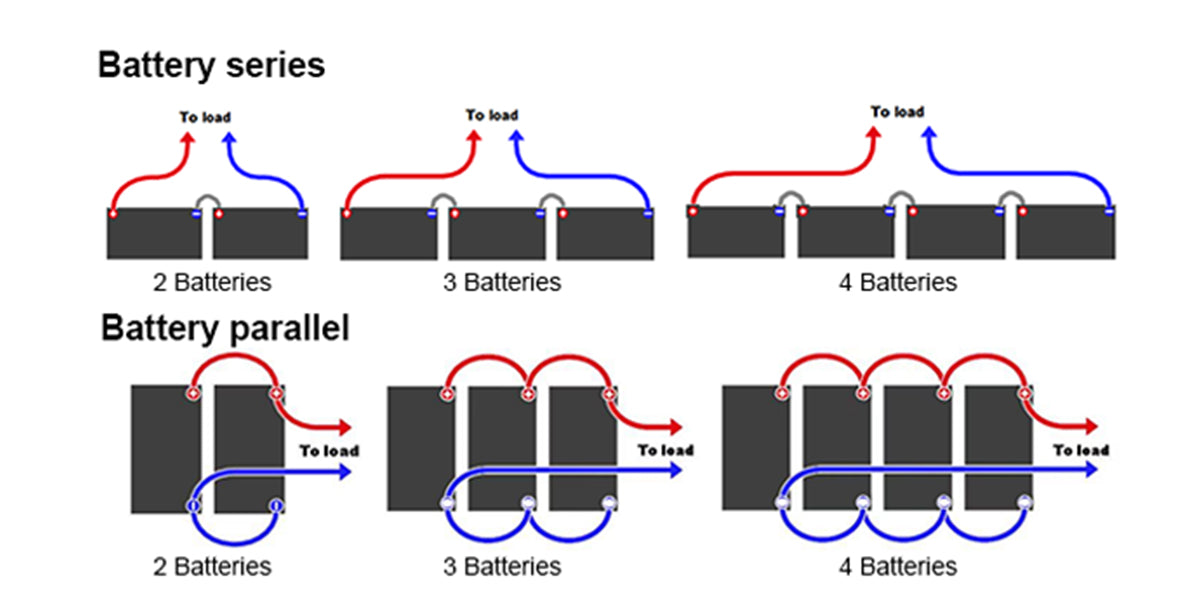
A Guide to Using and Charging Your 12V LiFePO4 Battery in Winter
Transform your off-grid system! This essential 12V LiFePO4 battery winter guide reveals safe LiFePO4 cold charging limits and prevents costly capacity loss now.

Understanding UL, CE and IEC Safety Certifications for Commercial Lithium Batteries
Learn how to evaluate commercial lithium battery safety certifications and protect your energy storage investment with clear, actionable steps.

Lithium-Ion Battery vs Diesel: TCO for Commercial Backup Power
Cut costs and boost reliability with lithium-ion backup power. Learn how battery systems save fuel, maintenance, and improve uptime versus generators.
How to Correctly Size Your Solar Array for a LiFePO4 Battery Bank
Optimize your LiFePO4 solar system to achieve safe charge current, efficient cycling, and full daily recharge with our proven solar array sizing tips.
