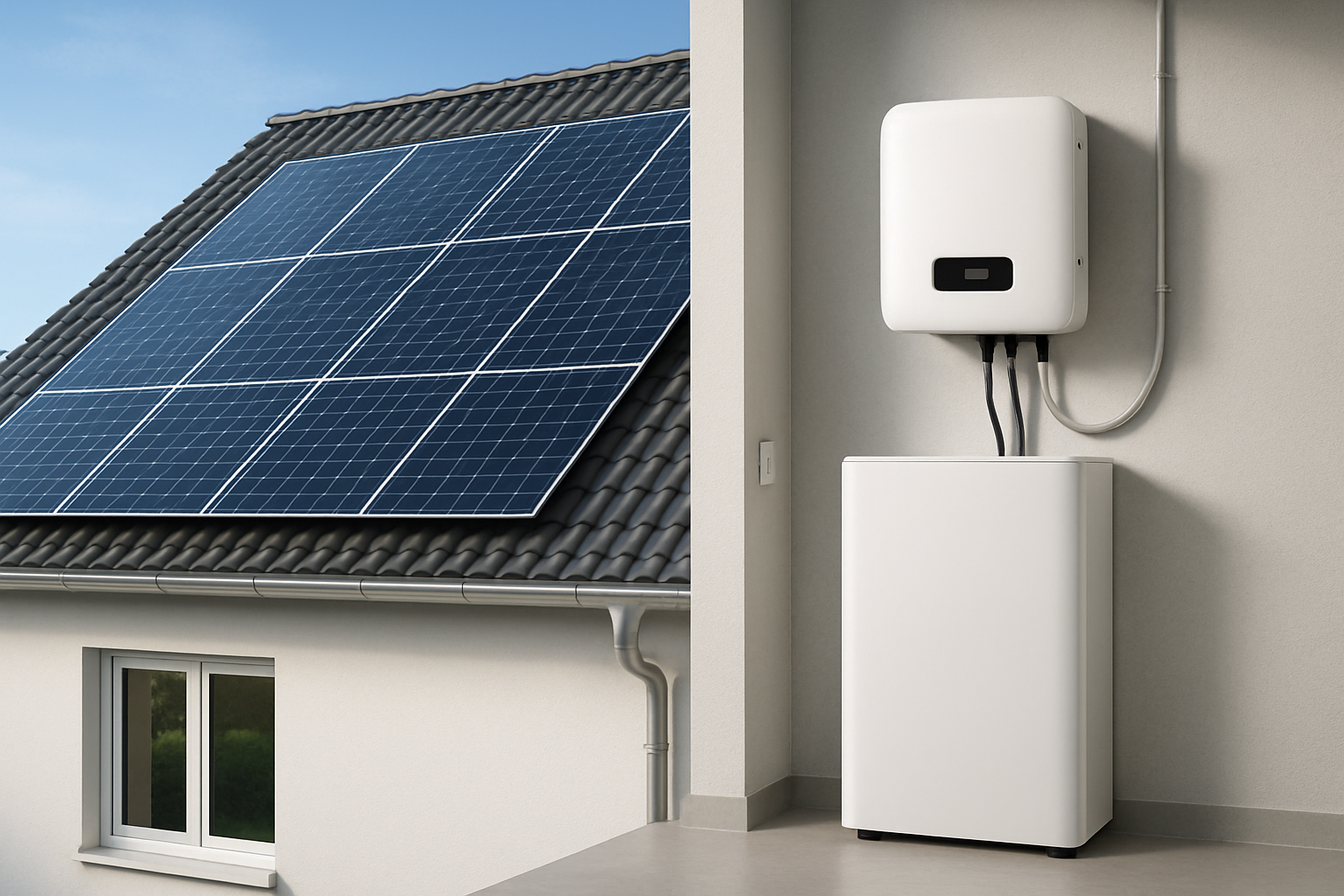
Achieving energy independence is a powerful goal. An off-grid solar kit provides the foundation for self-sufficiency, whether for a remote cabin, a farm, or a home. Understanding the individual off-grid solar kit components is the first step toward building a system that is reliable, efficient, and tailored to your specific needs. Each part plays a distinct role, and their synergy determines the success of your entire energy system.
This article breaks down the four core groups of components: the power generation hardware, the energy storage bank, the power management electronics, and the balance of system parts that tie everything together. Gaining a clear picture of these elements will help you make informed decisions for your energy future.
Solar Panels: Capturing the Sun's Energy
The most visible parts of any solar power setup are the solar panels. Their job is simple yet critical: to capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. This process, known as the photovoltaic effect, is the starting point for all the power your system will generate and store.
Types of Solar Panels
When selecting panels, you'll primarily encounter two types: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. While both serve the same function, they have key differences in performance and cost. The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that falling module prices have been a major driver of solar adoption worldwide, making both technologies more accessible than ever. Monocrystalline panels are made from a single, pure silicon crystal, giving them a uniform black appearance. Polycrystalline panels are made from multiple silicon fragments melted together, resulting in a blue, speckled look.
| Feature | Monocrystalline Panels | Polycrystalline Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher (typically 18-23%) | Slightly Lower (typically 15-20%) |
| Performance | Performs better in high heat and low-light conditions | Slightly less efficient in high-heat conditions |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More budget-friendly |
| Appearance | Uniform black color | Blue, marbled appearance |
Sizing Your Solar Array
Correctly sizing your solar array is crucial. You need enough panel wattage to run your appliances during the day and fully charge your battery bank. To calculate this, you'll divide your total daily energy needs (in watt-hours) by the number of peak sun hours your location receives. This will give you the minimum wattage for your solar array. It's often wise to oversize the array slightly to account for cloudy days and system inefficiencies.
Battery Storage: Powering Your Life After Sunset
The heart of any off-grid system is the battery bank. Solar panels only generate power when the sun is shining, so you need a reliable way to store that energy for use at night, on cloudy days, or during periods of high demand. This is where high-quality deep-cycle batteries become indispensable.
The Role of Deep-Cycle Batteries
Unlike the starter battery in your car, which provides a large burst of power for a short time, deep-cycle batteries are designed to provide a steady amount of power over a long period. They are built to be regularly discharged and recharged, making them the only suitable choice for solar power components.
Choosing the Right Battery Chemistry: LiFePO4 vs. Lead-Acid
The most critical decision for your battery storage for an off-grid system is the chemistry. For years, lead-acid batteries (like AGM) were the standard. Today, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries offer superior performance, safety, and lifespan, making them the premier choice for reliable energy storage. A key metric is the Depth of Discharge (DoD), which is the percentage of the battery's capacity that can be safely used. LiFePO4 batteries can be safely discharged to 80-90%, while lead-acid batteries should only be discharged to 50% to avoid damage. This means a LiFePO4 battery provides significantly more usable energy for the same rated capacity.
From our experience building robust energy solutions, the long-term value of LiFePO4 technology is clear. For more details on this comparison, LiFePO4 vs AGM: Which Deep Cycle Battery is Best for Solar? provides an in-depth analysis.
| Feature | LiFePO4 Battery | AGM Lead-Acid Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Life | 5,000+ cycles | 300-800 cycles |
| Usable Capacity (DoD) | 80-90% | 50% recommended |
| Efficiency | ~95% or higher | ~80-85% |
| Safety | Stable chemistry, no off-gassing, built-in BMS | Can release hydrogen gas, risk of acid leaks |
| Maintenance | None required | Requires periodic checks |
Sizing Your Battery Bank
Battery bank sizing depends on your daily energy consumption and your desired "days of autonomy"—the number of days you want your system to run without any solar input. A common goal for off-grid systems is 2-3 days of autonomy. To calculate your required capacity, multiply your daily watt-hour usage by your desired days of autonomy, then adjust for the battery's DoD. For guidance on specific applications, you can review articles like How to Size a 12V 100Ah Lithium Battery for Your Cabin. Avoiding common errors is also key; explore 5 Common Mistakes in Sizing Your Lithium Battery Storage to prevent costly miscalculations.
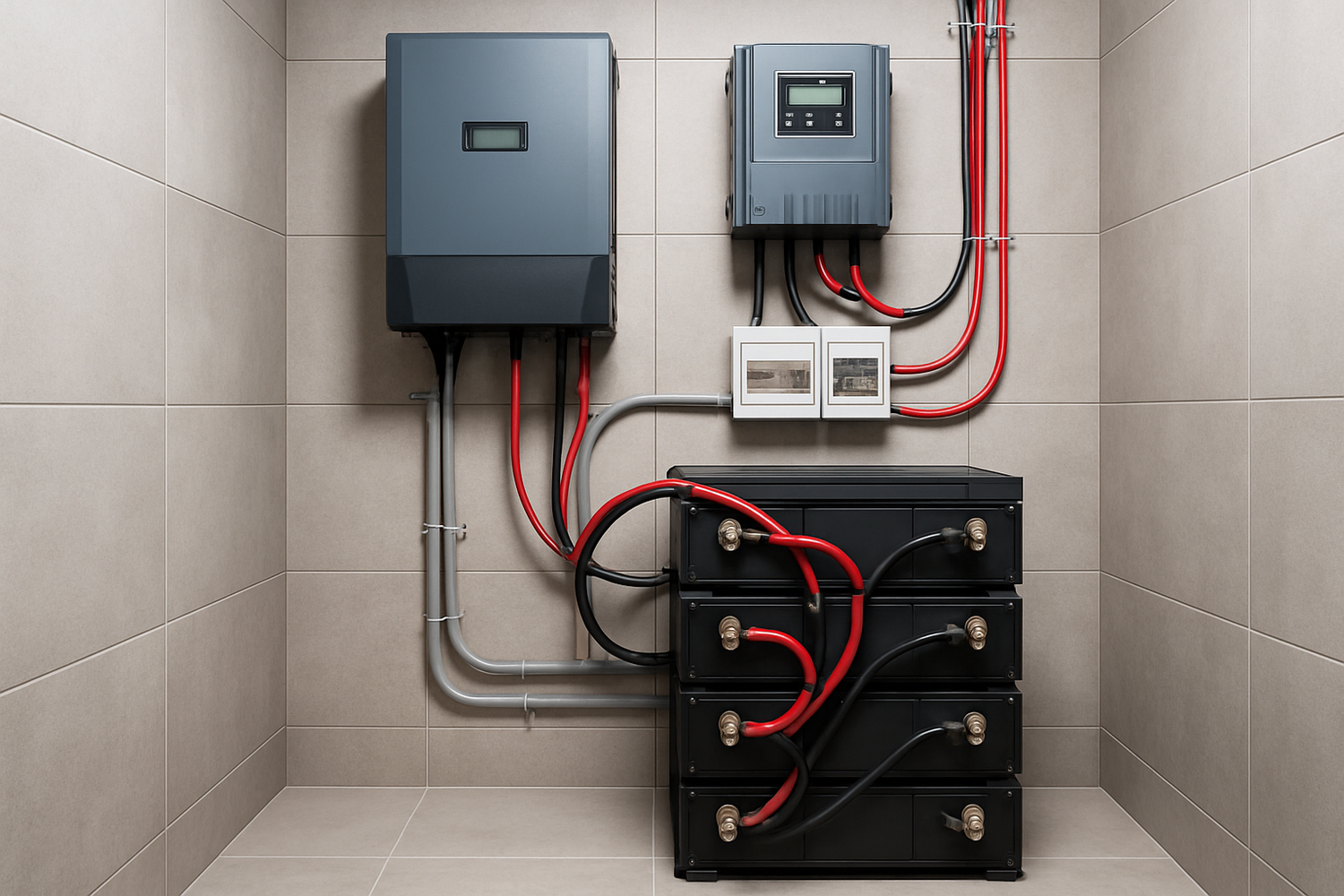
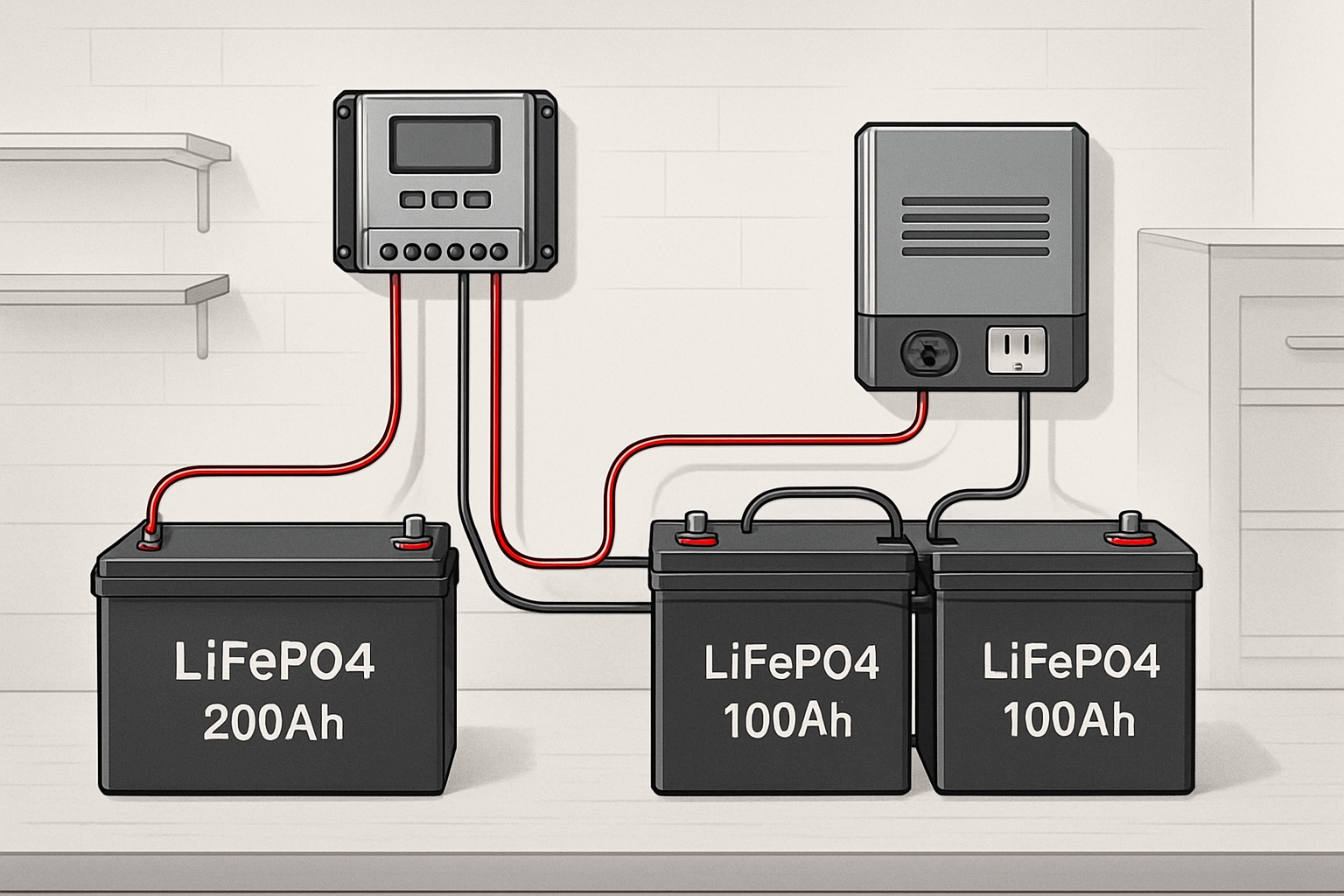
Inverters and Charge Controllers: Managing the Flow of Energy
If the battery is the heart of the system, the inverter and charge controller are the brains. These electronic devices manage the flow of electricity, ensuring that power is delivered safely and efficiently from the panels to the batteries and from the batteries to your appliances.
Solar Charge Controllers: Protecting Your Batteries
A solar charge controller sits between your solar panels and your battery bank. Its primary job is to regulate the voltage and current coming from the panels to prevent overcharging the batteries, which can cause permanent damage. There are two main types:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): A simpler, less expensive technology that acts like a switch, connecting the panels directly to the batteries.
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking): A more advanced and efficient technology that converts the higher voltage from the panels down to the battery voltage. This process allows the controller to capture significantly more power. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, MPPT controllers can boost power harvesting by up to 30% compared to PWM controllers, especially in cold weather or low-light conditions.
Power Inverters: Converting DC to AC Power
Your batteries store power as DC, but most household appliances run on alternating current (AC). The power inverter's job is to convert DC electricity from the battery bank into usable AC power. There are two main types of inverters:
- Modified Sine Wave: An older, less expensive technology that produces a blocky, stepped waveform. It can run simple appliances but may cause issues or damage to sensitive electronics like computers, modern TVs, and devices with motors.
- Pure Sine Wave: This type of inverter produces a smooth, clean electrical signal that is identical to or better than the power from the utility grid. It is compatible with all AC appliances and ensures they run efficiently and without risk of damage. For any serious off-grid system, a pure sine wave inverter is the recommended choice. Ensuring your inverter is properly matched with your battery is crucial for performance, a topic covered in Unlock Your Kit’s Power: Match Your Inverter & LiFePO4 Battery.
The All-in-One Solution: Hybrid Inverters and ESS
Modern off-grid system parts often come in integrated packages. A hybrid inverter combines a solar inverter, a battery charger, and a charge controller into a single unit. Going a step further, an Energy Storage System (ESS) integrates these components with a high-performance LiFePO4 battery. This approach simplifies installation, improves efficiency, and ensures all components are perfectly matched for optimal performance. These integrated systems represent the future of reliable, scalable home energy solutions, as detailed in The 2025 Buyer's Guide to Solar Energy Storage Systems.
Wiring, Fusing, and Mounting: The Unseen Essentials
While panels, batteries, and inverters get most of the attention, the "balance of system" (BOS) components are what safely connect everything. These parts include wiring, fuses, circuit breakers, and mounting hardware. Skimping on these items can create safety hazards and reduce system efficiency.
- Wiring and Cabling: Using the correct wire gauge (thickness) is essential to minimize power loss and prevent overheating.
- Fuses and Breakers: These safety devices protect your equipment and wiring from overcurrent situations, preventing potential fires and equipment damage.
- Racking and Mounting: This hardware secures your solar panels to your roof or the ground, ensuring they are stable and positioned for optimal sun exposure.
For a complete overview of how these parts fit together, refer to A Beginner's Guide to Off-Grid Solar System Components.
Building a Reliable and Scalable Off-Grid System
Constructing a dependable off-grid solar system is about more than just buying parts; it's about selecting quality components that work together seamlessly. From the efficiency of your solar panels to the cycle life of your LiFePO4 batteries and the clean output of your pure sine wave inverter, every choice impacts your energy independence. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) has consistently shown that renewable technologies are increasingly cost-effective, making now an excellent time to invest in a durable system.
Our focus on developing high-performance lithium batteries and integrated energy storage systems is driven by the goal of providing reliable and scalable solutions. By understanding each component in your off-grid solar kit, you are empowered to build a system that will deliver clean, consistent power for years to come, truly freeing you from the grid.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute legal or financial advice. Installing an electrical system involves risks, and it is highly recommended to consult with a qualified professional. Always follow local codes and safety guidelines.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.