Powering your RV or campervan on the road requires careful consideration of your electrical system. A critical component in this system is the inverter, which transforms the 12V direct current (DC) from your batteries into the 120V alternating current (AC) that most household appliances use. The choice between a pure sine wave inverter and a modified sine wave inverter significantly impacts the performance and longevity of your devices, influencing your energy independence on every trip.
Pure Sine Wave Inverters: The Preferred Choice for RV Power
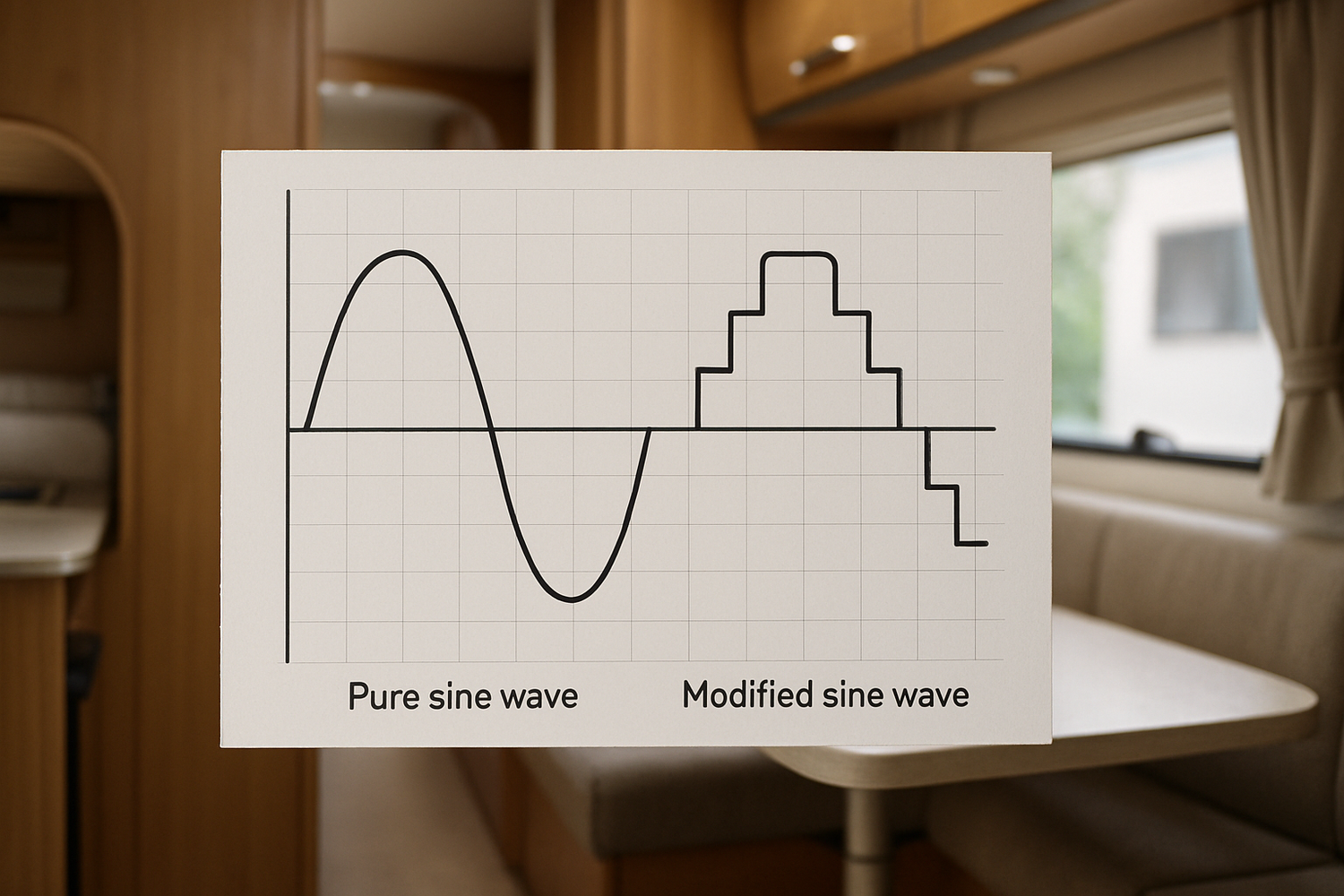
Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth, consistent electrical waveform that closely mimics the AC power you receive from the utility grid at home. This clean and stable output is crucial for many modern electronics and appliances.
How Pure Sine Wave Technology Works
A pure sine wave inverter converts DC power from your 12V RV battery into AC power. Unlike simpler inverter types, pure sine wave models employ advanced circuitry to generate a true sinusoidal waveform. This process ensures a continuous and uniform flow of electricity, which is vital for sensitive equipment.
Benefits for Your RV Appliances
Using a 12V RV pure sine inverter offers several compelling advantages:
- Broad Compatibility: Pure sine wave inverters can power virtually any AC device, including sensitive electronics such as laptops, medical equipment (like CPAP machines), modern LED televisions, and appliances with variable-speed motors (e.g., refrigerators and microwaves).
- Enhanced Efficiency: These inverters are highly efficient, often converting over 90% of DC power to AC power with minimal loss. This efficiency helps conserve your battery power and reduces heat generation in both the inverter and connected devices.
- Reduced Interference: The clean output minimizes electrical noise and harmonic distortion, preventing buzzing sounds in audio equipment and ensuring clear signals for communication devices.
- Extended Appliance Lifespan: Providing stable, high-quality power helps appliances operate more smoothly and quietly, reducing wear and tear and potentially extending their operational life.
For RV solar power systems, a pure sine wave inverter ensures that the energy harvested from your solar panels and stored in your lithium batteries is converted into high-quality AC power, maximizing the effectiveness and reliability of your setup.
Modified Sine Wave Inverters: A Practical Alternative
Modified sine wave inverters represent a more budget-friendly option. They produce a stepped or blocky waveform, which is a rough approximation of a true sine wave.
Understanding Modified Sine Wave Output
Instead of a smooth curve, a modified sine wave inverter generates power by switching its output voltage between positive, negative, and zero in discrete steps. This simpler design makes them less expensive to manufacture.
When Modified Sine Wave Inverters Are Suitable
Modified sine wave inverters can adequately power many basic, less sensitive devices. These include:
- Resistive loads like incandescent light bulbs.
- Simple heating elements.
- Basic phone chargers.
- Older TVs and tube-based monitors.
- Some low-power tools without complex electronics.
However, their limitations become apparent with more sophisticated equipment.

The higher harmonic distortion in modified sine wave output can cause issues. For instance, some audio devices may produce a buzzing sound. Furthermore, devices with motors or sensitive electronic controls, such as laser printers, digital clocks, and certain medical equipment, may not operate correctly or efficiently, potentially leading to overheating or damage over time. Modified sine wave inverters are also less efficient, typically converting 70-80% of DC to AC, meaning more energy loss as heat.
Direct Comparison: Pure Sine vs. Modified Sine
Understanding the core differences between these two inverter types is key to making an informed decision for your RV power system.
Performance and Efficiency
Pure sine wave inverters consistently outperform modified sine wave models in terms of power quality and efficiency. Their smooth output ensures that appliances receive power identical to what they would get from a standard wall outlet. This leads to optimal performance and reduced energy waste. According to research, pure sine wave inverters often exceed 90% efficiency, while modified sine wave inverters typically range from 70% to 80%.
Cost and Application Considerations
The initial cost is a significant differentiator. Modified sine wave inverters are generally more affordable due to their simpler design and fewer components. A pure sine wave inverter, with its more complex circuitry and higher-quality components, comes at a higher price point. However, the long-term cost-effectiveness often favors pure sine wave inverters due to their ability to prevent damage to sensitive electronics and their higher operational efficiency.
Here is a comparison:
| Feature | Pure Sine Wave Inverter | Modified Sine Wave Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Output Waveform | Smooth, consistent (like utility grid) | Stepped, blocky approximation |
| Appliance Compatibility | Universal, ideal for sensitive electronics, motors, medical devices | Limited, suitable for basic resistive loads (lights, heaters) |
| Efficiency | High (typically >90%) | Lower (typically 70-80%) |
| Harmonic Distortion | Very low | Higher, can cause interference |
| Device Longevity | Extends appliance lifespan | May shorten lifespan of sensitive devices |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Can cause buzzing in some devices |
Potential Risks and Device Compatibility
Using a modified sine wave inverter with devices designed for pure sine wave power can lead to various problems. These include inefficient operation, overheating, premature failure, and even permanent damage to sensitive components. For example, according to IRENA's “Grid Codes for Renewable Powered Systems” report, power electronic devices like inverters are major sources of harmonic currents. High penetration of variable renewable energy (VRE) can increase harmonic content in the grid unless specific measures are taken. Similarly, the IEEE 519 standard outlines criteria for voltage and current harmonic distortion in electrical systems, with IEEE 1547 or IEEE 2800 standards applying to inverter-based resources (IBR) installations for current distortion limits. These standards highlight the importance of power quality for system stability and equipment integrity.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) “System Integration of Renewables” report also discusses how smart inverters, whose electrical characteristics can be modified through software controls, play a significant role in integrating VRE. This demonstrates the ongoing advancements in inverter technology to ensure stable and clean power delivery.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your RV
Selecting the optimal inverter for your RV or campervan involves a thoughtful assessment of your specific power requirements and priorities.
Assessing Your Power Needs
Begin by listing all the AC appliances and devices you plan to use in your RV. Note their wattage. Summing these wattages will give you an idea of the total power your inverter needs to handle. It is wise to consider both continuous running wattage and surge wattage (the higher power draw some appliances have when starting). For example, a small RV might need a 1,000-watt inverter, while a larger one with more appliances could require a 3,000-watt inverter.
Prioritizing Appliance Safety and Longevity
If your RV setup includes sensitive electronics, medical devices, or appliances with motors, a pure sine wave inverter is the clear choice. It safeguards your valuable equipment from potential damage and ensures they operate at their best. While the initial investment for a pure sine wave inverter is higher, the long-term benefits of reliability, efficiency, and extended appliance lifespan often outweigh the upfront cost. For basic applications with less sensitive loads, a modified sine wave inverter can be a cost-effective solution.
Consider your future power needs as well. If you anticipate adding more sophisticated devices to your RV, investing in a pure sine wave inverter from the start can save you from costly upgrades later. Our expertise in lithium battery manufacturing and solar inverter development means we focus on providing reliable and scalable energy solutions that empower you to achieve true energy independence on your travels.
Empowering Your RV Adventures
The decision between a 12V RV pure sine inverter and a modified sine wave inverter is fundamental to creating a reliable and efficient power system for your mobile adventures. By understanding the distinct characteristics, benefits, and limitations of each type, you can make an informed choice that protects your appliances, optimizes energy usage, and ensures a comfortable, powered experience wherever the road takes you. Prioritize power quality for sensitive devices to truly unlock the full potential of your RV's solar and storage capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need an inverter for my RV solar system?
Yes, an inverter is necessary if you intend to power any AC appliances or devices in your RV. Solar panels generate DC power, while most common RV appliances operate on AC power. The inverter converts this DC power into usable AC electricity.
Will a modified sine wave inverter damage my electronics?
Modified sine wave inverters can potentially damage sensitive electronics, especially those with microprocessors, variable-speed motors, or delicate circuitry. While they might work for basic appliances, using them with items like laptops, medical devices, or modern televisions can lead to inefficient operation, overheating, and a shortened lifespan.
What size inverter do I need for my RV?
The size of the inverter you need depends on the total wattage of all the AC devices you plan to run simultaneously. Add up the continuous wattage of your appliances, and choose an inverter that can handle that combined load, plus a buffer for surge power. It is always a good idea to slightly oversize your inverter to accommodate potential future additions or unexpected power draws.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.