In my work designing smart grid solutions, I’m focused on a problem most people don’t see: the potential for a massive traffic jam on our electrical grid. As millions of EVs hit the road, the real challenge isn't just generating more power; it's coordinating when they all decide to drink from the well at the same time. Unmanaged, this could destabilize local grids. The solution we're implementing is built on a common language, a 'Rosetta Stone' for the grid, called IEEE 2030.5. It's the critical link that will turn EVs from a potential problem into one of our greatest grid assets by 2030.
The Challenge I See Every Day: The 5 PM Grid Rush Hour
The core issue is uncoordinated charging. When an entire neighborhood plugs in their cars after work, it creates a massive, sudden spike in demand that can overload the local transformers we rely on. Smart charging is the answer. It allows a utility to gently orchestrate charging sessions—perhaps by shifting your car’s session to 2 AM when power is cheap and plentiful. More advanced systems even enable Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), where your EV can send power back to support the grid. But none of this works without a secure, universal language that the utility, the car, and the charger can all speak. That's the specific job IEEE 2030.5 was built for.
Why I Bet on IEEE 2030.5 for the Future Grid
IEEE 2030.5 isn't just another protocol; it was designed from the ground up for a decentralized grid full of solar panels, batteries, and EVs (what we call Distributed Energy Resources, or DERs). It uses standard internet protocols, which makes it perfect for secure communication over the web.
In practice, it gives grid operators the tools we need to maintain stability:
- Demand Response: This is our blackout prevention tool. We can send a signal asking thousands of EV chargers to temporarily pause or reduce their pull during a heatwave, keeping the lights on for everyone.
- Price Signaling: It allows us to broadcast real-time energy prices. A compliant EV charger can automatically react, charging only when energy is cheapest for the owner.
- Security by Design: In this field, security is paramount. IEEE 2030.5 has mandatory, built-in encryption and authentication (TLS & PKI). This isn't an optional add-on; it's a core feature that prevents bad actors from disrupting the grid.
Its real power, as IRENA highlights in its Innovation Outlook on smart charging, is turning EVs into a flexible resource. That flexibility is built on this kind of standardized communication.
The Protocol Ecosystem: How They Work Together in the Field
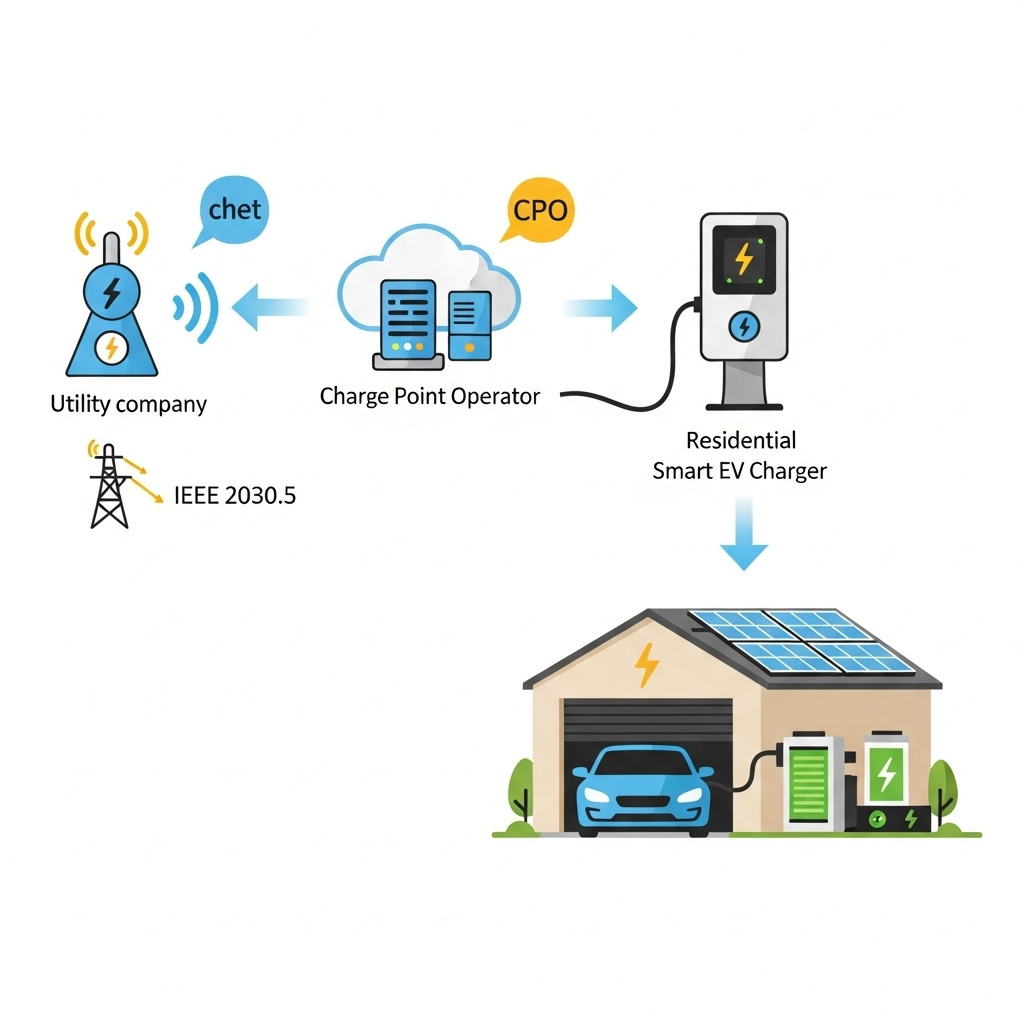
A common point of confusion is how IEEE 2030.5 relates to other protocols like OCPP. They aren't competitors; they're teammates with different roles. Here’s a typical signal flow I would engineer:
A utility's control center sends a demand response event via **IEEE 2030.5** to the cloud platform of a Charge Point Operator (CPO). That CPO's system then sends a specific command, like "limit charging to 4kW," down to an individual charger using **OCPP**. It's a chain of command, where IEEE 2030.5 is the secure bridge from the grid to the charging network.
| Protocol | My Analogy | Primary Job | Who Uses It |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE 2030.5 | Air Traffic Control | Grid-to-DER network communication | Utilities, Grid Operators |
| OCPP | Control Tower to Plane | Charging network-to-charger management | Charge Point Operators |
| OpenADR | Simple Weather Alert | Basic automated demand response signals | Utilities, Building Controls |
The Holy Grail: Paving the Way for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
Looking toward 2030, the ultimate goal is full V2G, where EV fleets act as a massive, distributed power plant. A school bus fleet could charge with solar during the day and help power the grid during the evening peak. This requires a communication standard that can securely manage the bidirectional flow of energy and, crucially, the financial transactions that go with it. With its robust security and rich data model, IEEE 2030.5 is the foundational standard that makes a V2G future possible and safe.
This push for standardization is a powerful catalyst for growth. As the U.S. Department of Energy found with its SunShot initiative, common standards can dramatically accelerate cost reductions and market expansion. The same is happening now for smart charging.
Building the 2030 Grid Today
The transition to an electrified future hinges on intelligent coordination. While consumers see the EVs, those of us in the industry see the immense data and control challenge behind the scenes. IEEE 2030.5 is the essential, secure communication backbone we are building today to ensure that the millions of EVs coming tomorrow will strengthen our grid, not strain it.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.