Many owners of grid-tied solar panel systems eventually consider adding battery storage. The goal is to maximize the use of generated solar power, gain protection from outages, and reduce reliance on the grid. This case study examines a real-world scenario where a homeowner upgraded their existing solar installation by adding a battery using an AC coupled configuration with a hybrid inverter. This approach offers a practical and efficient path to energy storage without requiring a complete system overhaul.
The Starting Point: A Standard Grid-Tied Solar System
Understanding the initial setup is key to appreciating the upgrade. We'll look at a typical residential property to illustrate the process and outcomes.
The Homeowner's Energy Profile
The subject of our case study is a family home with a 6kW grid-tied solar PV system. For years, this system reliably reduced their electricity bills by generating power during the day. However, their consumption patterns meant that a significant portion of their solar energy was exported to the grid, especially during midday when the house was empty. In the evenings, when demand was highest, they were still purchasing expensive electricity from their utility provider.
Reasons for Seeking an Upgrade
Several factors motivated the decision to add energy storage. First, rising electricity costs made it financially attractive to use more of their own solar energy. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), residential electricity prices have been on an upward trend, making self-consumption more valuable. Second, the desire for energy resilience during grid outages was a major consideration. Finally, they wanted to reduce their carbon footprint further by minimizing their reliance on grid power, which is often generated from fossil fuels.
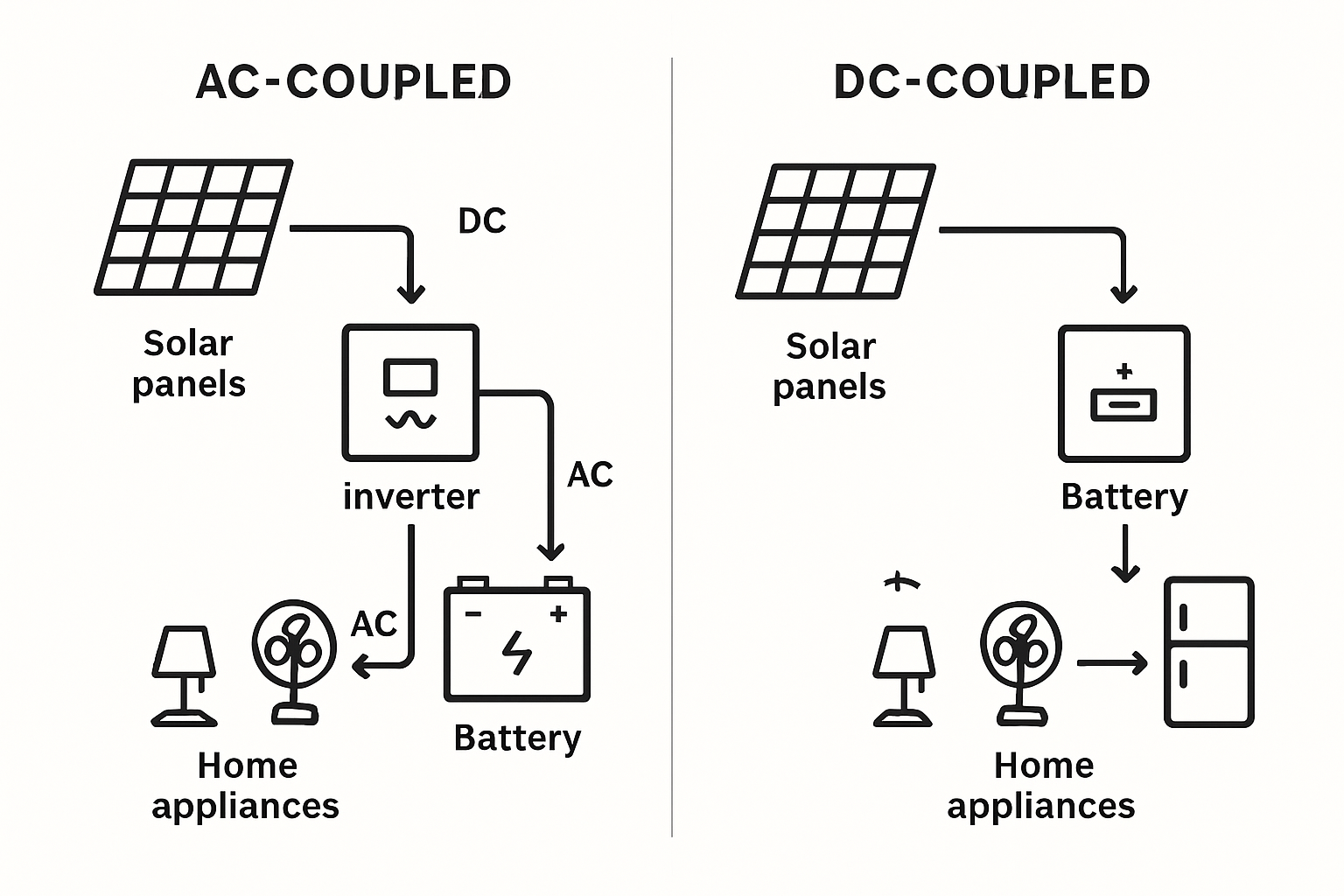
Choosing the Right Path: AC Coupling with a Hybrid Inverter
When adding a battery to an existing solar installation, the primary technical decision is the coupling method: AC or DC. For retrofits, AC coupling is often the most straightforward and cost-effective choice.
The Advantage of AC Coupling for Retrofits
AC coupling involves adding a new battery and a battery-capable inverter to the AC side of the property's electrical system. The original solar panels and their dedicated inverter remain untouched. This modular approach is a key benefit because it avoids the complexity and expense of reconfiguring the existing solar array. The new components work in parallel with the old ones, simplifying installation and minimizing disruption.
How a Hybrid Inverter Streamlines the System
A hybrid inverter is a multi-functional device that can manage power from multiple sources: the solar array (via its original inverter), the battery bank, and the electrical grid. In this AC coupled setup, the hybrid inverter acts as the energy management hub. It directs excess AC power from the solar inverter to charge the lithium battery, pulls power from the battery to supply the home's loads when solar production is low, and manages the connection to the grid for charging or backup.
The Upgrade in Action: Installation and Integration
The physical upgrade was completed with careful planning and component selection, transforming the simple solar producer into a comprehensive home energy storage system.
Component Selection and System Sizing
The upgrade consisted of two main components:
- A 10kWh lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery pack. This capacity was chosen to cover the home's average evening and nighttime energy consumption, ensuring they could operate through peak hours without drawing from the grid. LiFePO4 was selected for its long cycle life and safety profile.
- A 5kW hybrid inverter. The inverter was sized to match the home's peak load and to adequately charge and discharge the 10kWh battery.
The Installation Process
The installation was relatively straightforward. The hybrid inverter was installed next to the main electrical service panel. The LiFePO4 battery was placed in the garage and connected directly to the DC input of the hybrid inverter. The AC output of the hybrid inverter was then wired into the home's main panel. The original solar inverter's AC output, which was already connected to the main panel, did not need to be changed. The entire installation was completed in a single day.
Performance Transformed: Analyzing the Results
After the upgrade, the home's energy dynamics changed dramatically. The benefits were clear in energy consumption patterns, grid independence, and financial savings.
Measurable Gains in Self-Consumption
The most significant improvement was in the home's ability to use its own solar energy. Before the upgrade, the self-consumption rate was approximately 35%. After integrating the AC coupled battery, this figure jumped to over 85%. The excess solar energy previously sent to the grid was now stored for later use. This aligns with the broader goals of energy transition, where storage plays a critical role in maximizing renewable energy utilization, a point emphasized in reports from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). For a deeper dive into performance metrics, the ultimate reference for solar storage performance offers valuable insights into what to measure.
Financial Impact and Return on Investment
The increased self-consumption translated directly into lower electricity bills. The table below illustrates the financial shift. As noted in analysis from the International Energy Agency (IEA), managing electricity demand and supply is crucial for market stability, and home storage contributes to this on a micro level.
| Metric | Before Upgrade (Monthly Average) | After Upgrade (Monthly Average) |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Energy Imported | 450 kWh | 80 kWh |
| Solar Energy Exported | 300 kWh | 50 kWh |
| Electricity Bill | $90 | $16 |
Disclaimer: This is a representative case study. Actual financial returns and performance data can vary based on system size, location, electricity rates, and energy consumption patterns. This information does not constitute financial advice.
A Blueprint for Energy Independence
This case study demonstrates that upgrading an existing solar system with AC coupled storage and a hybrid inverter is a highly effective strategy. It provides a clear path for homeowners to increase their energy independence, secure backup power, and achieve significant long-term savings. By storing solar energy, the system bridges the gap between when power is produced and when it is needed, turning a simple solar installation into a robust, self-sufficient energy solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary benefit of AC coupling for an existing solar system?
The main benefit is ease of installation and compatibility. AC coupling allows you to add a battery and a second inverter without altering the original solar panel array or its inverter, making it an ideal solution for retrofitting.
Can any hybrid inverter be used for an AC coupled storage upgrade?
Not all hybrid inverters are designed for AC coupling. It is crucial to select a hybrid inverter that is specifically rated and designed to be AC coupled. These inverters are built to manage AC power from an existing grid-tied solar inverter and use it to charge a battery.
How does an AC coupled system provide backup power?
During a grid outage, the hybrid inverter can create a local, independent grid for the home. It disconnects from the main utility grid and uses the stored energy in the battery to power essential circuits. The existing solar system can also continue to operate and recharge the battery during the day, provided the hybrid inverter is configured to manage it.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.