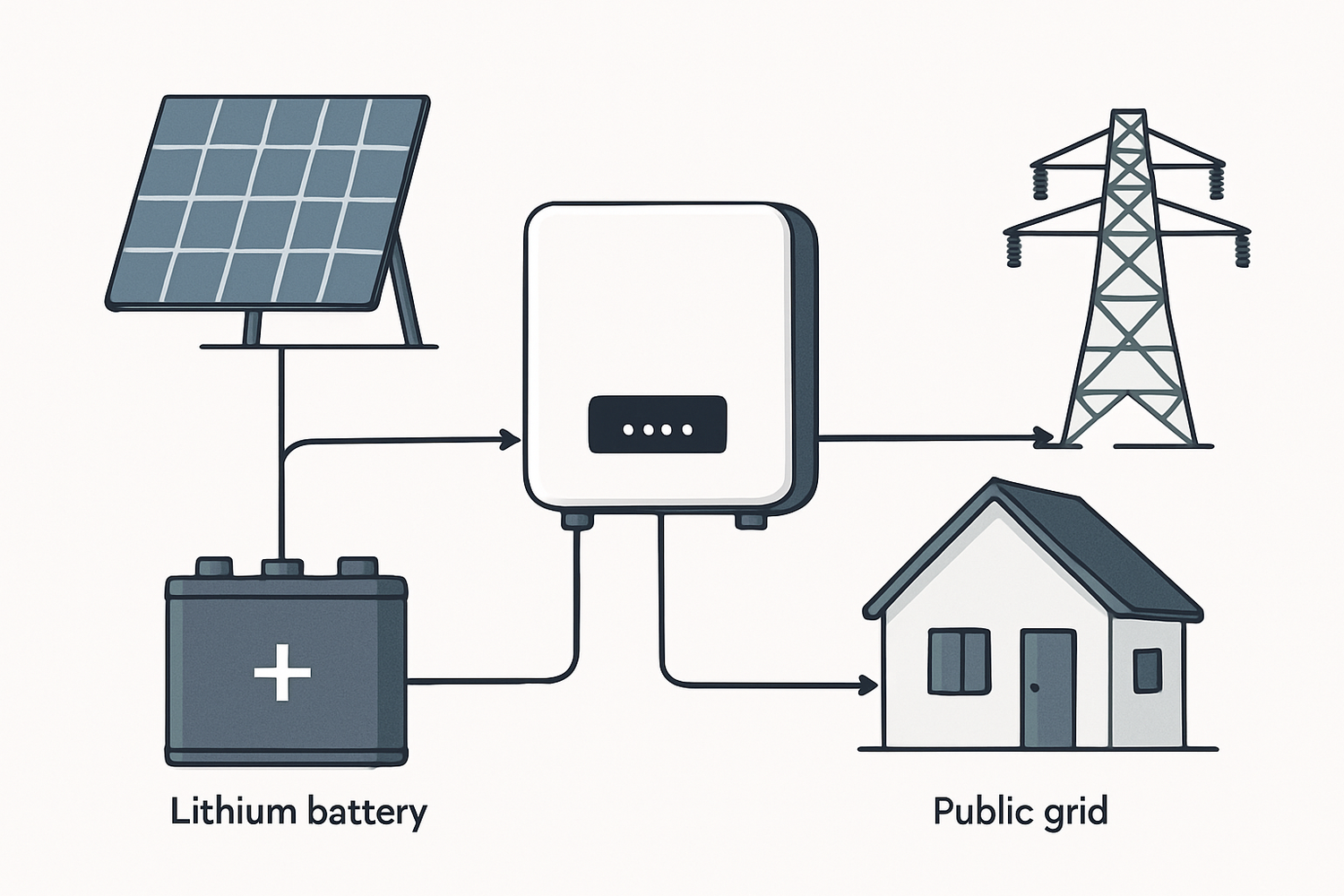
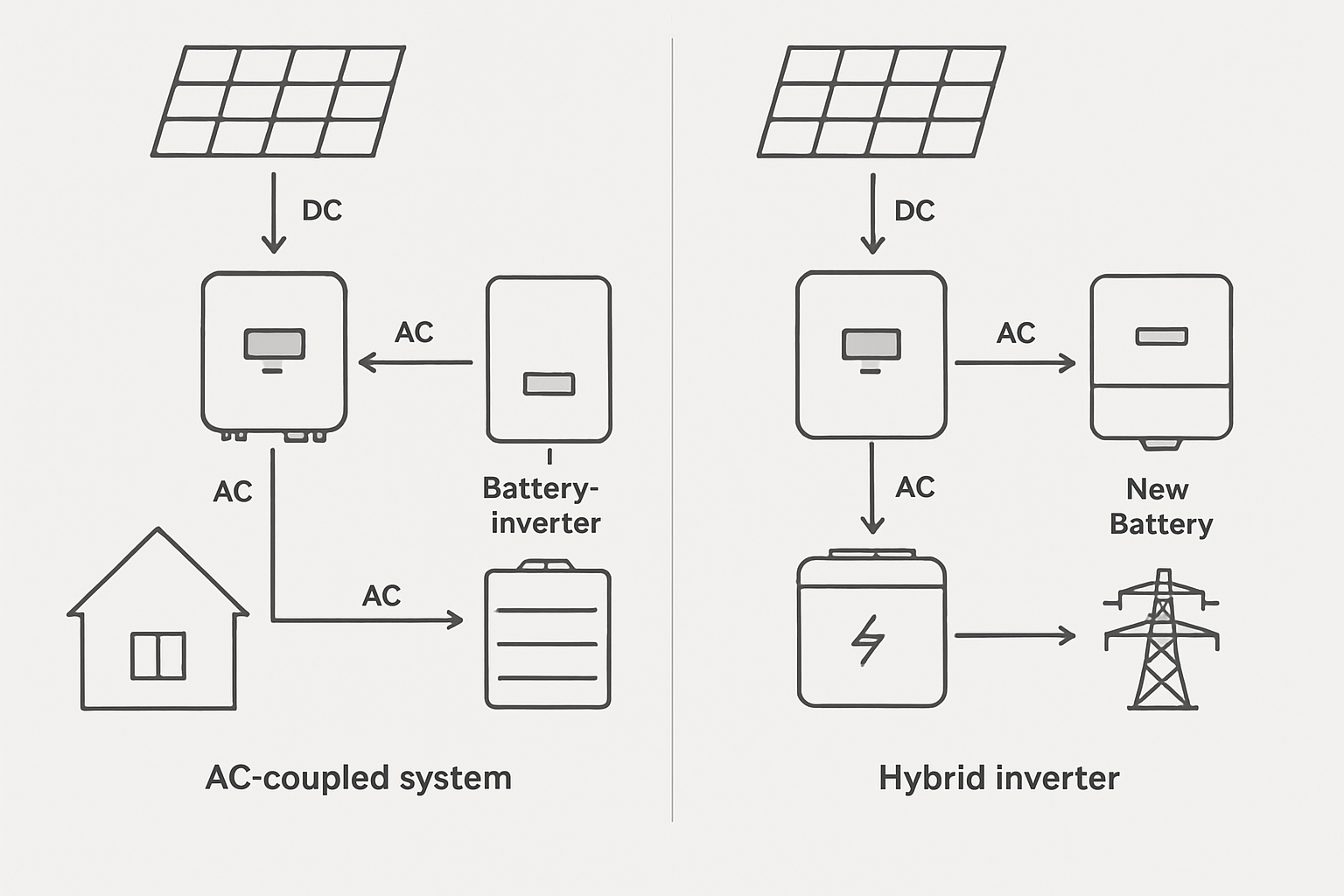
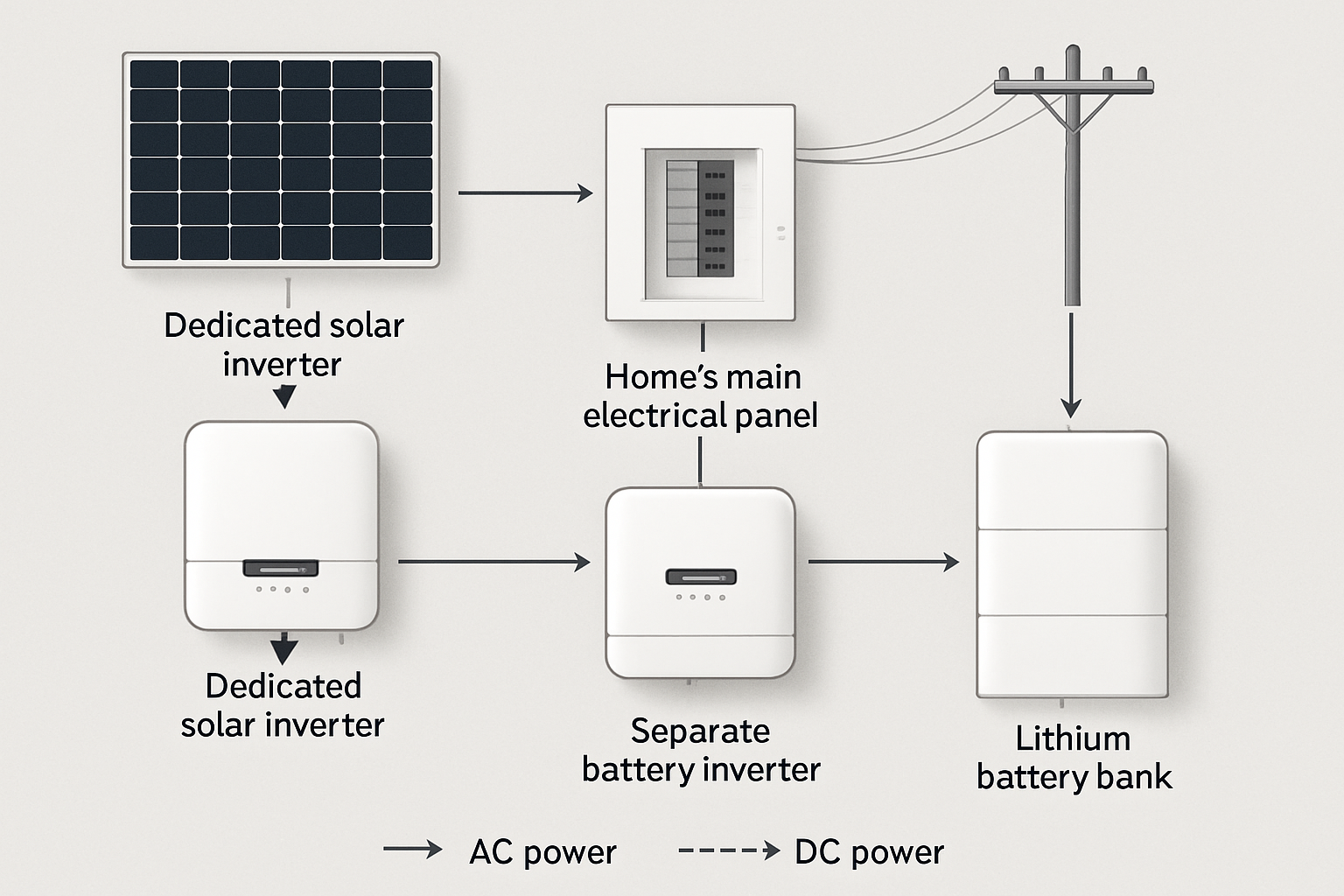
Adding battery storage to an existing solar panel system, a process known as AC coupling, is an effective way to increase energy independence. At the heart of this upgrade is the hybrid inverter, a device that intelligently manages power between your solar array, batteries, home, and the grid. Selecting the right one is critical for the performance and reliability of your entire energy storage system. This checklist provides a clear, step-by-step framework for making a well-informed decision.
Core Technical Specifications to Scrutinize
The datasheet of a hybrid inverter contains vital information. Understanding these numbers will help you match the device to your specific energy needs.
Power Ratings and Sizing
An inverter's power capacity determines how many appliances it can run. Look for two key figures: continuous power output and peak power output. Continuous power is the constant load the inverter can handle, while peak power is a short burst it can supply to start demanding appliances like motors. Ensure both ratings meet your household's requirements, especially for essential loads during an outage. The inverter's charge and discharge rate, measured in kilowatts (kW), also dictates how quickly it can charge your battery from solar or discharge it to power your home.
Battery Compatibility and Chemistry
Not all inverters work with all batteries. It is crucial to verify that the inverter is compatible with your battery's voltage (typically 48V for residential systems) and chemistry. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are a popular choice for their long cycle life and safety. Advanced inverters communicate directly with the battery's Battery Management System (BMS) via protocols like CAN or RS485. This direct communication ensures optimal charging, discharging, and overall system health.
Efficiency Metrics
Inverter efficiency measures how much DC power from the battery is successfully converted to usable AC power. Look for the round-trip efficiency, which accounts for losses in both charging and discharging. A higher percentage means less energy is wasted. High-efficiency inverters contribute to a more effective and economical energy storage solution over the long term.
Grid Interaction and Backup Capabilities
A hybrid inverter's primary advantage is its ability to interact with the grid while also providing backup power. Its capabilities in this area are a major differentiating factor.
Grid-Tied and Off-Grid Functionality
An essential feature for backup power is 'grid-forming' capability. While standard grid-tied inverters ('grid-following') shut down during a grid outage for safety, a grid-forming inverter can create its own stable, independent grid to power your home. Also, check the transfer time—the speed at which the inverter switches to battery power during an outage. A fast transfer time, often called uninterruptible power supply (UPS) functionality, is important for keeping sensitive electronics running without interruption. For grid connection, the inverter must be certified to safety standards like UL 1741.
Advanced Grid Services
Modern hybrid inverters can do more than just provide backup. They can be programmed for peak shaving (using battery power to avoid high utility rates) and load shifting (charging batteries when electricity is cheap and discharging when it's expensive). Some inverters can also participate in Virtual Power Plants (VPPs). As the International Energy Agency (IEA) notes, VPPs aggregate distributed energy resources to support grid stability. These features can provide additional financial returns on your investment.
Usability and System Integration
The best hardware can be let down by poor software or difficult installation. Pay attention to the user experience and physical design.
Monitoring and Control Systems
A quality hybrid inverter should come with a user-friendly monitoring platform, accessible via a web browser or mobile app. This software should provide real-time data on solar production, battery state of charge, home consumption, and grid import/export. The ability to receive remote firmware updates is also valuable, as it ensures the inverter can adapt to new technologies and grid requirements without a service call.
Physical Characteristics and Installation
Consider the inverter's physical footprint, weight, and cooling system. Fanless, passively cooled inverters operate silently, which is a benefit for residential installations. The Ingress Protection (IP) rating indicates its resistance to dust and water; a higher rating like IP65 is suitable for outdoor installations. Finally, review the warranty period and the availability of technical support, as these are indicators of the manufacturer's confidence in their product.
A Practical Checklist in Action
Choosing an inverter involves balancing these technical criteria with your budget and energy goals. The following table summarizes the key decision points.
| Feature | Why It Matters | Ideal Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Power | Determines the constant load the inverter can support. | Sized to match or exceed your home's typical energy consumption. |
| Peak Power | Ability to start high-demand appliances. | Sufficient to handle the startup surge of your largest motors (e.g., well pumps, AC units). |
| Battery Voltage | Must match your battery bank for compatibility. | Typically 48V for modern residential systems. |
| Chemistry Support | Ensures safe and efficient battery operation. | Compatibility with LiFePO4 and communication with its BMS. |
| Round-Trip Efficiency | Minimizes energy loss during charging and discharging. | 94% or higher. |
| Transfer Time | Ensures uninterrupted power for sensitive electronics. | Less than 20 milliseconds for UPS-level performance. |
| Grid-Forming Capability | Essential for providing power during a grid outage. | Clearly stated support for off-grid or microgrid operation. |
| IP Rating | Determines where the inverter can be safely installed. | IP65 for outdoor installations; IP20 or higher for indoor. |
| Warranty | Indicates product reliability and manufacturer support. | 10 years or more. |
Understanding these specifications is crucial. For a deeper dive into how these factors influence overall system output, the data presented in the Ultimate Reference for Solar Storage Performance provides valuable benchmarks on efficiency and battery cycle life.
Final Considerations
Selecting the right hybrid inverter is a foundational step in building a resilient and efficient AC-coupled energy storage system. By methodically working through this checklist—evaluating technical specifications, grid capabilities, and usability features—you can choose a device that not only meets your immediate backup power needs but also provides long-term value through energy savings and grid independence. This choice is an investment in a more stable and sustainable energy future for your home.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. It does not constitute financial or legal advice. Consult with a qualified professional before making any investment decisions or system installations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can any hybrid inverter be used for AC coupling?
Not all hybrid inverters are designed for AC coupling. This is a specific feature that allows the inverter to manage power from an existing grid-tied solar inverter. Always check the product specifications for 'AC coupling' or 'retrofit' capabilities to ensure it's suitable for upgrading an existing solar installation.
How do I size a hybrid inverter for my existing solar system?
In an AC-coupled system, the hybrid inverter is sized primarily based on the battery and the loads you want to back up, not the solar array. Its power rating should match or exceed your battery's continuous charge/discharge rate and be sufficient to handle your home's critical loads during a power outage.
What is the difference between a hybrid inverter and a standard solar inverter?
A standard solar inverter's only job is to convert DC power from solar panels into AC power for your home. A hybrid inverter is a more advanced device that acts as a central energy manager. It can handle power flows between solar panels, a battery bank, your home's loads, and the electrical grid, including the critical function of charging and discharging batteries.


Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.