Tin roofs are known for their durability and longevity, making them an excellent foundation for a solar energy system. However, the prospect of retrofitting a roof with solar panels can raise questions about structural integrity and weatherproofing. This case study examines a modern solution: the use of rail-less PV mounts for installing solar panels on existing tin roofs. We will look at the process, the benefits, and the key considerations for a successful installation.
Understanding the Foundation: Tin Roofs and Solar Mounting
Before installing any solar array, it's important to understand the unique characteristics of the roofing material and the mounting options available. Tin roofs, often made of steel or aluminum, offer a stable and long-lasting platform, but their corrugated or standing-seam profiles require specialized mounting hardware.
The Nature of Tin Roofs
Metal roofs, including tin, are lightweight yet strong. They can withstand harsh weather conditions and often last for 50 years or more. Their defined ridges or seams provide predictable and secure attachment points for solar hardware. This avoids the need to guess where structural supports like rafters are located, which can be an issue with other roof types. The key is to use a mounting system that works with the roof's profile without compromising its water-shedding capabilities.
Traditional Railed vs. Modern Rail-Less Systems
The conventional method for mounting solar panels involves a system of long aluminum rails. These rails are attached to the roof and the panels are then clamped onto them. While effective, this approach involves more components and labor. Rail-less PV mounts, on the other hand, attach directly to the roof structure and the panels mount directly onto these smaller, individual blocks. This innovation simplifies the entire process.
| Feature | Traditional Railed System | Rail-Less System |
|---|---|---|
| Key Components | Long aluminum rails, L-feet, clamps | Mounting blocks/clamps, integrated hardware |
| Installation Time | Longer, more assembly required | Faster, fewer parts to handle |
| Material Cost | Generally higher due to more components | Often lower, less aluminum needed |
| Aesthetics | More visible, higher profile | Sleek, low-profile appearance |
| Roof Penetrations | Typically requires more attachment points | Fewer penetrations, often attaching to seams |
The Retrofitting Project: A Step-by-Step Analysis
This case study focuses on a typical residential retrofitting project on a corrugated tin roof. The goal was to install a 7kW solar array efficiently while preserving the roof's integrity and aesthetic.

Initial Assessment and Planning
The first step was a thorough roof inspection. A structural engineer confirmed the roof could handle the additional load of the solar panels. The project team then selected a rail-less mounting system specifically designed for corrugated metal profiles. The layout was planned to maximize sun exposure. As noted in research from the IEA, tilting modules can significantly increase the annual energy received, and the mounting system's design allowed for a slight, optimal tilt. According to the Solar Energy Perspectives report, this optimization is crucial for maximizing energy yield.
The Installation Process
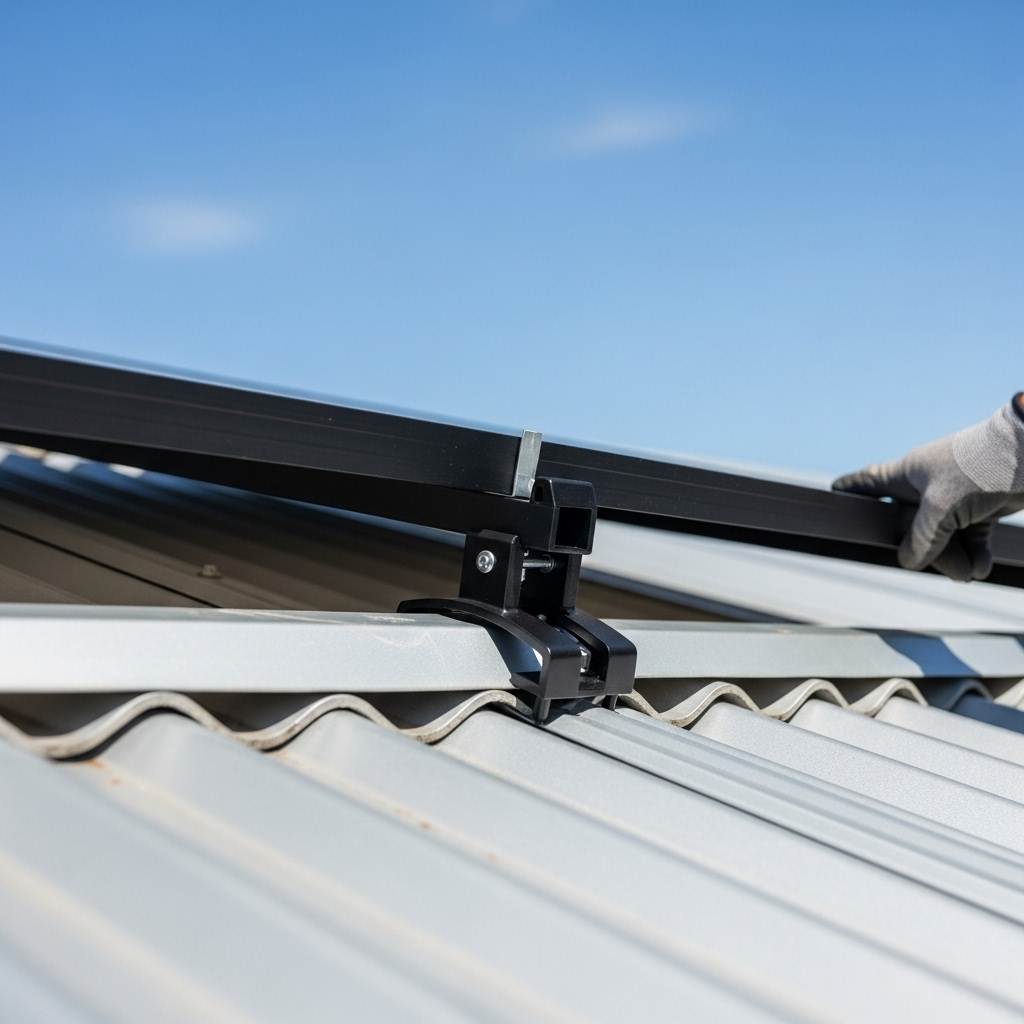
Installation began by cleaning the roof surface. The team then laid out the locations for the mounting blocks, aligning them with the roof's purlins for maximum strength. Each block was attached using specialized screws with EPDM sealing washers to create a waterproof seal. The process involved significantly fewer components than a railed system, which accelerated the work. Once the mounts were secure, the PV modules were placed and locked into position using integrated clamping mechanisms. The final step involved careful wire management, securing cables neatly beneath the panels.
Post-Installation Checks
After the physical installation, every connection was torque-checked to manufacturer specifications to ensure a secure fit. The system was commissioned and began producing power immediately. Initial monitoring showed that the energy output met, and at times exceeded, the projected estimates, partly due to the optimized panel placement and the high efficiency of the modern modules.
Analyzing the Outcomes: Benefits and Key Considerations
The project demonstrated several clear advantages of using rail-less PV mounts for a tin roof retrofit, but also highlighted some important considerations.
The Advantages Realized
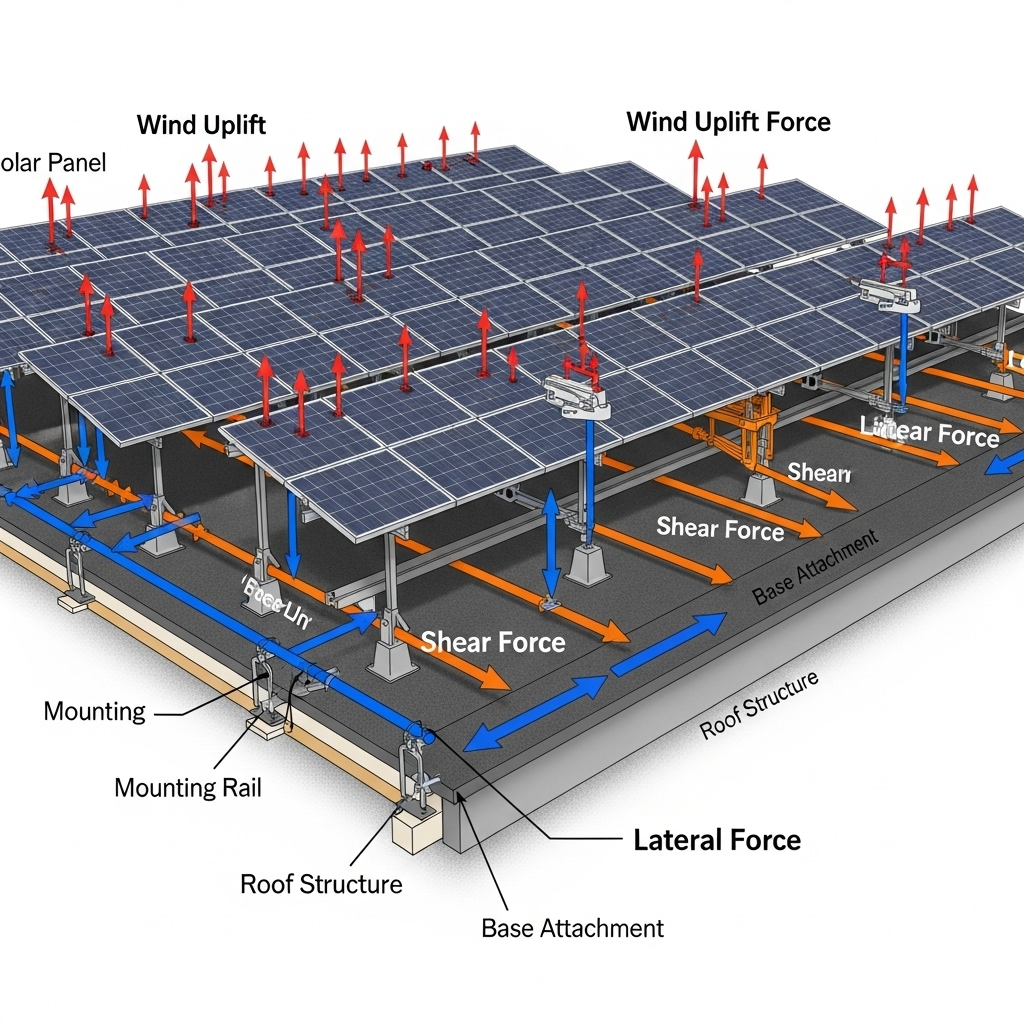
The most immediate benefit was the reduction in installation time and labor costs. With fewer parts to manage and assemble, the team completed the project approximately 30% faster than a comparable railed installation. The material cost was also lower due to the absence of long, heavy rails. From a homeowner's perspective, the aesthetic improvement was significant. The panels sit closer to the roof, creating a sleek, integrated look. Most importantly, the reduced number of roof penetrations directly translates to a lower risk of leaks over the system's lifetime.
Potential Challenges and Mitigation
Success with rail-less systems hinges on careful product selection. Not all systems are compatible with every type of tin roof, so verifying compatibility is the first step. Another critical factor is the skill of the installation team. As the Unlocking the Economic Potential of Rooftop Solar PV in India report highlights, the solar sector requires a trained workforce for proper installation. Installers must be familiar with the specific torque requirements and weatherproofing techniques of the chosen system to prevent issues down the line.
Maximizing Your Investment with Energy Storage
A solar installation is just the first step toward energy independence. To get the most value from the clean energy your system produces, integrating it with an energy storage solution is essential. This allows you to store excess solar power generated during the day for use at night or during power outages.
Pairing Your PV System with the Right Battery
The effectiveness of a solar-plus-storage system depends on how well the components work together. High-performance lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are a reliable and safe choice for residential energy storage. They offer a long cycle life and excellent thermal stability. To make an informed decision, it's helpful to review a comprehensive guide on the topic. For example, you can find a detailed breakdown of metrics and considerations in this ultimate reference for solar storage performance, which can help you select a battery that aligns with your energy goals.
A Forward-Thinking Approach to Solar
This case study confirms that retrofitting tin roofs with rail-less PV mounts is a highly effective strategy. It offers a faster, more cost-effective, and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional methods without compromising on safety or performance. By carefully planning the project and pairing the solar array with a suitable energy storage system, property owners can create a robust and reliable solution for their long-term energy needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do rail-less mounts cause leaks on tin roofs?
When installed correctly, rail-less mounts do not cause leaks. They use specialized hardware with integrated EPDM rubber gaskets that create a durable, watertight seal around each penetration point. The key is to follow the manufacturer's installation instructions precisely and ensure all fasteners are torqued to the correct specification.
Are rail-less systems as strong as traditional racks?
Yes. Rail-less mounting systems are engineered to meet the same rigorous industry standards for wind and snow loads as traditional railed systems. They achieve their strength by attaching directly to the structural elements of the roof, such as purlins or rafters, ensuring a secure and durable foundation for the solar panels.
Can I install a rail-less system myself?
While a DIY installation is possible for those with significant roofing and electrical experience, it is generally recommended to hire a professional. A certified installer ensures the system is mounted safely, meets all local building codes, and is eligible for warranties. Improper installation can lead to roof damage, poor system performance, or safety hazards.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.