Power outages are more than an inconvenience; they disrupt daily life and can compromise safety. A home battery storage system provides a reliable shield, offering energy independence when the grid fails. But selecting the right size is critical. An undersized battery won't meet your needs, while an oversized one is an unnecessary expense. This page offers a clear path to accurate home battery sizing, ensuring you have uninterrupted power when you need it most.
Understanding Your Home's Energy Needs
The first step in any battery capacity calculation is to get a clear picture of your electricity consumption. You need to know what you want to power and how much energy those devices use. A precise assessment prevents you from investing in a system that is too large or too small for your actual requirements.
Conducting an Energy Audit: What to Measure
An energy audit involves listing the appliances you intend to power during an outage and calculating their total consumption. You can find the wattage of most appliances on their labels. For a precise measurement, you can check your utility bills or use an energy monitor to track daily usage. Multiply the wattage by the number of hours you expect to use each device daily to find its total watt-hours (Wh). Adding these up gives you your total daily energy requirement.
Distinguishing Between Essential and Non-Essential Loads
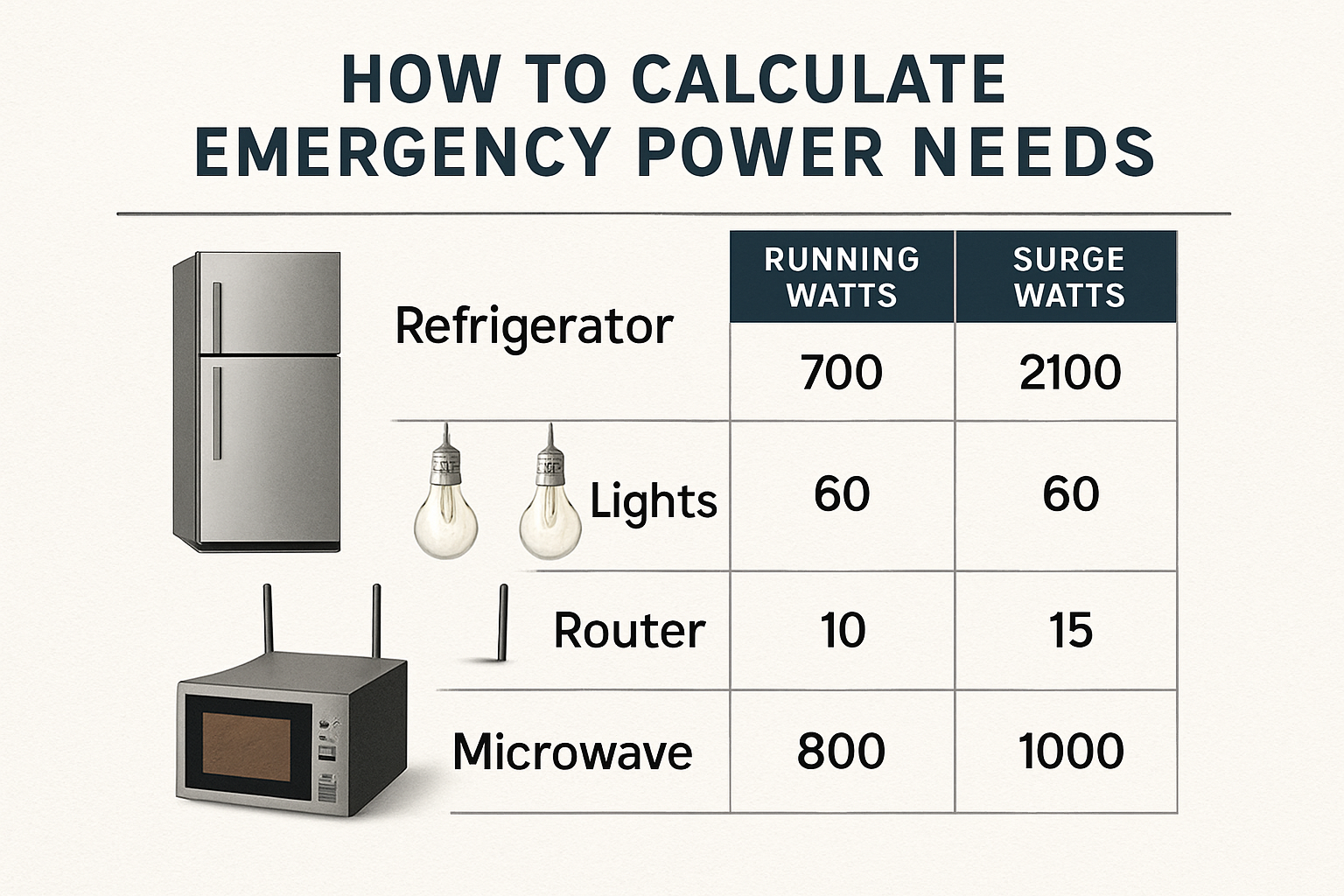
To optimize your emergency power backup, it's practical to separate your home's electrical loads into two categories: essential and non-essential. Essential loads are the critical devices you can't live without during an outage, such as:
- Refrigerator and freezer
- Lighting in key areas
- Medical equipment (e.g., CPAP machine)
- Sump pump
- Internet router and phone chargers
Non-essential loads include high-consumption appliances like air conditioners, electric ovens, and clothes dryers. By focusing on backing up only the essentials, you can select a more cost-effective battery system.
The Core of Battery Sizing: Key Metrics and Calculations
With your energy audit complete, you can move on to the technical specifications. Understanding the key metrics of battery storage will empower you to make an informed decision. These figures determine both how much energy a battery can store and how much power it can deliver at any moment.
Kilowatt-hours (kWh): The Measure of Energy Capacity
The most important metric for sizing is the battery's capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This number tells you the total amount of energy the battery can store. For example, a 10 kWh battery can deliver 1 kilowatt of power continuously for 10 hours. Your daily energy requirement, calculated during your audit, directly translates to the kWh capacity you need. The average American household uses about 30 kWh per day, so a 10 kWh battery can power essential appliances for a significant portion of the day.
Kilowatts (kW): The Power Rating Explained
While kWh measures energy, kilowatts (kW) measure power—the rate at which energy is delivered. A battery's power rating determines how many appliances it can run simultaneously. It has two ratings: continuous power and peak power. Continuous power is the steady output the battery can provide, while peak power is a short burst needed to start large appliances like a refrigerator or well pump. Ensure the battery's power rating can handle the combined wattage of all the essential devices you might run at the same time.
A Practical Calculation Example
To calculate your required battery capacity, sum the daily energy consumption of your essential loads. Let's create a sample calculation for a 24-hour outage.
| Appliance | Power (Watts) | Daily Hours of Use | Daily Energy (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 200 W | 8 hours (cycling) | 1600 Wh |
| LED Lights (5) | 50 W | 6 hours | 300 Wh |
| Internet Router | 10 W | 24 hours | 240 Wh |
| Laptop Charging | 65 W | 4 hours | 260 Wh |
| Medical Device | 50 W | 8 hours | 400 Wh |
| Total | 2800 Wh or 2.8 kWh |
In this scenario, a battery with at least 3 kWh of usable capacity would be needed. It is wise to add a buffer of 20-25% for inefficiencies and unexpected needs, bringing the target size to around 3.5-4 kWh for a single day of backup.
Selecting the Right Battery Technology and Features
Not all batteries are created equal. The underlying chemistry and features of a battery system directly impact its safety, lifespan, and efficiency. For residential use, certain technologies have emerged as clear leaders.
Why LiFePO4 is a Leading Choice for Home Storage
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have become a preferred technology for home energy storage due to their exceptional safety and longevity. Unlike other lithium-ion chemistries, LiFePO4 is thermally stable and far less prone to overheating. This inherent stability is a critical safety feature for a system installed in your home. Furthermore, LiFePO4 batteries offer a much longer cycle life, often capable of enduring over 6,000 charge-discharge cycles, which translates to a lifespan of 15 years or more. Their composition is also more environmentally friendly, as they do not contain cobalt.
Depth of Discharge (DoD) and Round-Trip Efficiency
Depth of Discharge (DoD) refers to the percentage of a battery's total capacity that can be safely used. A higher DoD means you can use more of the stored energy. LiFePO4 batteries typically feature a high DoD, often 90-100%, compared to older technologies. Round-trip efficiency measures how much energy is lost during the charge and discharge cycle. High-quality systems achieve over 95% efficiency, ensuring minimal energy waste. For a deeper look into these metrics, the ultimate reference on solar storage performance provides valuable data on how these factors impact long-term value.
Scalability: Planning for Future Growth
Your energy needs may change over time. You might add an electric vehicle or other large appliances. Choosing a modular and scalable energy storage system allows you to add more battery capacity later. This flexibility ensures your investment remains valuable as your lifestyle evolves, without needing to replace the entire system.
Final Considerations for Your Power System
Sizing your battery correctly is the most important step, but a few final considerations will ensure your system delivers reliable, uninterrupted power for years to come. Thinking about how the battery integrates with other components and planning for long-term needs will complete your energy independence strategy.
Integrating with Solar Panels
Pairing your home battery with solar panels creates a truly self-sufficient energy solution. Solar panels can recharge your battery during the day, providing continuous power through multi-day outages. As noted in a report from the International Energy Agency, Next Generation Wind and Solar Power, installing battery storage with solar PV systems is an effective way to increase self-consumption and manage energy flows. When sizing a battery for a solar-powered home, you'll need to balance the battery's capacity with your solar array's daily production to ensure it can be fully recharged.
A Step Toward Energy Security
Choosing the right size for your home battery is a deliberate process of matching your specific energy needs with the right technology. By conducting a thorough energy audit, understanding the key metrics of kWh and kW, and selecting a high-quality system, you build a foundation for true energy security. This preparation ensures that when the grid goes down, your home remains a comfortable and powered sanctuary. It's a significant step toward managing your own energy future with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long will a 10kWh battery last in a power outage?
A 10 kWh battery can typically power the essential appliances in an average home, such as a refrigerator, lights, and internet, for 12 to 24 hours. However, this duration depends entirely on your energy consumption. If you avoid using high-power devices like air conditioners or electric stoves, you can extend the backup time significantly.
Can I add more batteries to my system later?
Yes, if you choose a scalable or modular battery system. Many modern energy storage solutions are designed to be expanded. This allows you to start with a capacity that meets your current needs and budget, and then add more batteries in the future if your energy consumption increases.
What is the difference between AC-coupled and DC-coupled battery systems?
The difference lies in how the battery connects to your solar energy system. A DC-coupled system connects the battery directly to the solar panels before the power is converted to AC for your home. This is generally more efficient for new solar-plus-storage installations. An AC-coupled system connects to the AC circuit of your home, making it easier to retrofit a battery to an existing solar panel system.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.