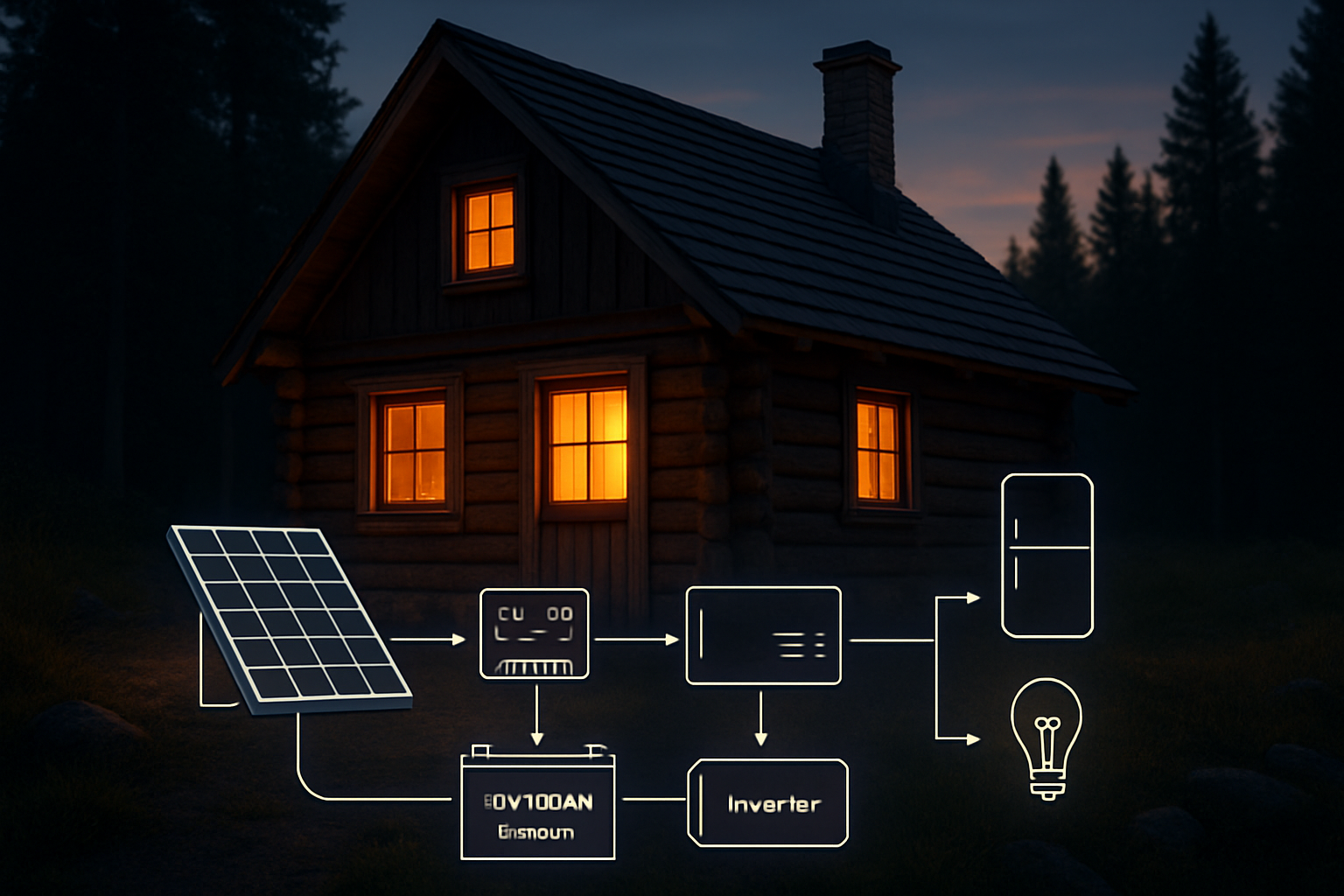
A 100Ah lithium-ion battery is a popular cornerstone for many off-grid solar systems, prized for its balance of capacity, size, and longevity. But determining if it’s the right fit for your specific needs requires a clear understanding of its capabilities and your energy demands. This evaluation will help you decide if a single 100Ah battery is sufficient or if a larger energy storage solution is necessary for your energy independence.
Understanding the Power of a 100Ah Lithium-Ion Battery
Before you can assess its suitability, it’s important to know what '100Ah' truly represents in terms of power. This rating is the key to unlocking how much energy you can store and use in your off-grid solar kit.
What '100Ah' Actually Represents
The term 'Ah' stands for Amp-hours, a unit that measures electric charge. It indicates that the battery can deliver a current of 100 amps for one hour, or 1 amp for 100 hours. To understand the total energy stored, you must convert this to Watt-hours (Wh) by multiplying Amp-hours by the battery's voltage. For a typical 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery, the calculation is:
100 Amp-hours × 12 Volts = 1200 Watt-hours (Wh)
This 1200Wh is the total energy capacity you have available to power your appliances. It’s the most accurate measure of the battery's energy reservoir.
The LiFePO4 Advantage: Usable Capacity
A significant benefit of a 100Ah lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery, a common type of lithium-ion battery for solar, is its high usable capacity. Unlike traditional lead-acid batteries that should only be discharged to about 50% to avoid damage, a LiFePO4 battery can be safely discharged by 80-100%. This means a 100Ah lithium battery provides nearly double the usable energy of a 100Ah lead-acid battery, giving you access to almost the full 1200Wh. Furthermore, LiFePO4 technology offers a longer cycle life and higher efficiency, making it a reliable choice for solar kit components.
Calculating Your Daily Energy Consumption
The only way to know if a 100Ah battery is enough is to calculate how much energy you use daily. This process, often called an energy audit, involves listing every appliance you intend to power and how long you'll use it.
Create an Appliance Energy Audit
Start by listing all your devices. Note the power consumption (in Watts) for each and estimate the number of hours you'll use it per day. Multiply these two values to find the daily energy consumption in Watt-hours (Wh) for each appliance. Sum these amounts to get your total daily energy requirement.
| Appliance | Power (Watts) | Hours of Use per Day | Daily Energy (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED Lights (x4) | 20W (5W each) | 5 hours | 100 Wh |
| Laptop Charger | 65W | 3 hours | 195 Wh |
| Small Refrigerator | 150W (runs ~8 hrs/day) | 8 hours | 1200 Wh |
| Water Pump | 60W | 0.5 hours | 30 Wh |
| Total Daily Need | 1525 Wh |
Accounting for System Inefficiencies
Energy is lost during the conversion of DC power from the battery to AC power for your appliances. Inverters are not 100% efficient. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), utility-scale battery systems have an average round-trip efficiency of about 82%. For off-grid systems, it's wise to factor in a 15-20% loss. To compensate, divide your total daily energy need by the system's efficiency (e.g., 0.85 for 85% efficiency).
Required Capacity = 1525 Wh / 0.85 ≈ 1794 Wh
In this scenario, a single 12V 100Ah battery with 1200Wh of energy would not be sufficient.
Sizing Your Solar Kit for a 100Ah Battery
If your energy needs are within the capacity of a 100Ah battery, you must correctly size the other solar kit components, particularly your solar panels, to ensure the battery can be reliably recharged.
Matching Solar Panels to Your Battery
To recharge a 1200Wh battery, you need a solar array that can generate enough power in a single day. The amount of power you generate depends on 'peak sun hours'—the number of hours your location receives maximum sunlight. This varies by location and season. Assuming 5 peak sun hours:
Required Solar Panel Wattage = 1200 Wh / 5 hours = 240 Watts
To be safe, it's often recommended to oversize your solar array slightly to account for cloudy days and other inefficiencies. The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that solar PV generation has seen massive growth, underscoring its increasing viability and importance in energy systems worldwide.
Planning for Days of Autonomy
Days of autonomy refers to the number of days your system can run without any sun to recharge the batteries. A single 100Ah battery provides limited autonomy. If you require power through several consecutive cloudy days, you will need to increase your battery bank's capacity. To calculate this, multiply your daily energy needs by the desired number of autonomous days.
Total Capacity = Daily Energy Needs × Days of Autonomy
For example, for 3 days of autonomy with a 1000Wh daily need, you would require 3000Wh of battery storage.
Is a 100Ah Battery Sufficient for Common Applications?
The suitability of a 100Ah lithium-ion battery depends entirely on the application. It excels in some scenarios but falls short in others.
RVs and Mobile Living
For many RVs and vans, a 100Ah lithium battery is an excellent choice. It can comfortably power LED lights, fans, a water pump, and charge electronic devices like phones and laptops. However, it will struggle to run high-draw appliances such as air conditioners, microwaves, or electric heaters for extended periods.
Small Off-Grid Cabins
A 100Ah battery can be adequate for a small, energy-efficient cabin used for weekend trips. It can handle basic lighting, a small refrigerator, and charging ports. For full-time off-grid living, a larger battery bank is almost always necessary to meet higher daily energy demands and provide sufficient autonomy.
Emergency Backup Power
As a backup power source, a 100Ah battery can be very useful. It can keep critical devices running during an outage, such as a modem/router for internet access, some lights, and a small, efficient refrigerator. Its capacity is limited, so it's best for short-term outages or powering only the absolute essentials.
Final Thoughts
A 100Ah lithium-ion battery offers a compact and powerful 1200Wh of energy storage, making it a versatile component for many off-grid solar kits. However, its sufficiency is not a one-size-fits-all answer. The key is a thorough battery capacity calculation based on a detailed energy audit of your appliances. For modest energy needs in an RV or a weekend cabin, it can be a perfect fit. For more demanding applications or full-time off-grid living, it serves better as a starting point for a larger, scalable energy storage system. As noted in an ultimate reference on solar storage performance, understanding metrics like usable capacity and efficiency is fundamental to designing a system that delivers reliable, long-term power.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much power does a 12V 100Ah battery provide?
A 12V 100Ah battery provides 1200 Watt-hours (1.2 kWh) of energy. This is calculated by multiplying its amp-hour rating (100Ah) by its voltage (12V). This means it can theoretically power a 100-watt device for 12 hours.
How long will a 100Ah lithium battery last?
The runtime of a 100Ah battery depends on the power draw of the connected appliances. To calculate the runtime, divide the battery's Watt-hour capacity (1200Wh) by the total wattage of the load. For example, a 50-watt load would last approximately 24 hours (1200Wh / 50W = 24 hours).
Can I connect multiple 100Ah batteries?
Yes, you can connect multiple 100Ah batteries to increase your total energy storage. Connecting them in parallel (positive to positive, negative to negative) increases the Amp-hour capacity while keeping the voltage the same. For instance, two 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel create a 12V 200Ah (2400Wh) battery bank.
What is the main difference between a 100Ah lithium-ion and a 100Ah lead-acid battery?
The primary difference is usable capacity. A 100Ah lithium-ion (specifically LiFePO4) battery offers nearly 100% of its rated capacity, providing close to 100Ah of usable power. A 100Ah lead-acid battery should only be discharged to 50% of its capacity to preserve its lifespan, offering only about 50Ah of usable power. Lithium batteries also have a much longer cycle life and are lighter.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.