The idea of energy independence is powerful. Generating your own electricity, free from utility companies and unpredictable grid failures, has a strong appeal. Off-grid solar systems make this possible, but a lot of misinformation can cloud the decision-making process. Separating popular myths from reality is the first step toward building a reliable and effective energy solution.
The Myth of 'Free' and Effortless Energy
One of the most persistent ideas about solar is that once the panels are up, the energy is free and requires no further thought. While solar energy significantly reduces long-term electricity costs, the initial setup and ongoing upkeep are important financial and practical considerations.
'Off-Grid Solar is Free After Installation'
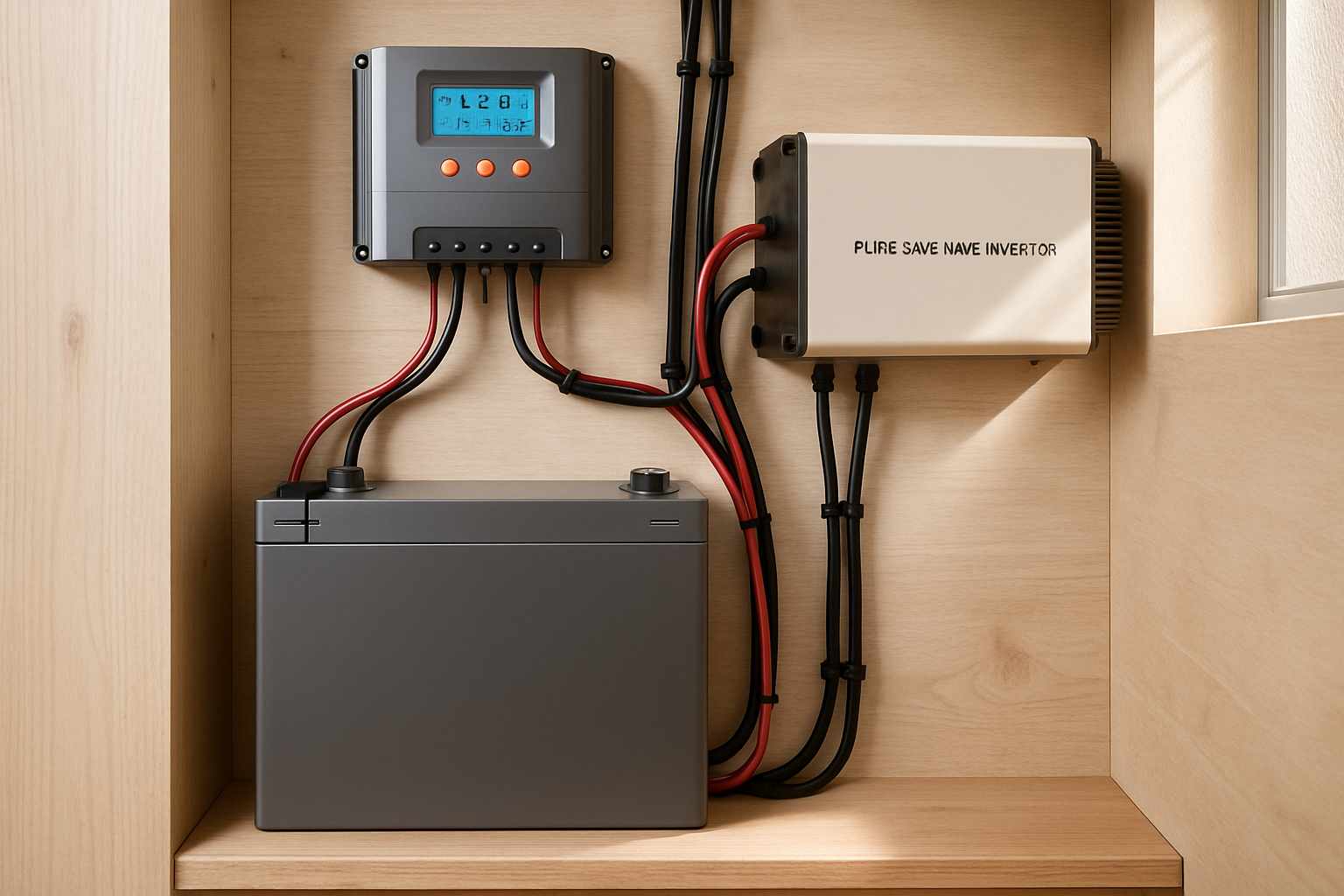
The reality is that an off-grid solar system is a significant upfront investment. This includes not just the solar panels but also inverters, racking, and, most critically, a robust battery bank to store energy. While the cost of solar PV technology has fallen dramatically, these components represent a substantial initial outlay. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global weighted average total installed cost for solar PV has decreased significantly over the last decade, making it more accessible. However, 'free' is not an accurate description. You are essentially pre-paying for decades of electricity. Furthermore, components have finite lifespans. High-quality lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries may last over a decade, but they will eventually need replacement. Inverters and other electronics also have lifespans of 10-15 years, representing future costs.
'Solar Systems Are Set It and Forget It'
Modern solar energy systems are designed for durability and minimal intervention, but they are not entirely maintenance-free. To ensure optimal performance, you should conduct regular checks. This includes cleaning solar panels to remove dust, pollen, or snow that can hinder efficiency. You will also need to monitor your battery bank’s state of charge and inspect wiring and connections for any signs of wear or corrosion. Neglecting these simple tasks can lead to reduced energy production and can shorten the lifespan of your components.
Misconceptions About Reliability and Performance
Concerns about whether an off-grid system can reliably power a home, especially during poor weather or for demanding appliances, are common. These worries often stem from an underestimation of what a properly designed system can achieve.
'Off-Grid Systems Are Unreliable in Bad Weather'
A well-designed off-grid system is built for resilience. The key is the battery storage system. By calculating your daily energy needs and planning for 'days of autonomy'—the number of consecutive cloudy days your system can sustain your home—you ensure a consistent power supply. A system with three to five days of autonomy can easily handle a week of overcast weather. The reliability hinges on the quality and capacity of your batteries. Advanced options like 12v 100ah LiFePO4 batteries offer deep discharge cycles and a long lifespan, making them an excellent choice for dependable energy storage. For a deeper understanding of how different storage solutions perform, you can review this ultimate reference on solar storage performance, which details key metrics.
'You Can’t Run High-Power Appliances Off-Grid'
This is entirely false. An off-grid solar system can power anything from a refrigerator and well pump to an electric vehicle charger. The limitation is not the technology, but the scale of your system. To run high-power appliances, you need a system with sufficient solar panel capacity to generate the required energy, a large enough battery bank to store it, and a powerful solar inverter to handle high electrical loads. A proper load analysis is the first step to designing a system that meets your specific needs without compromise.
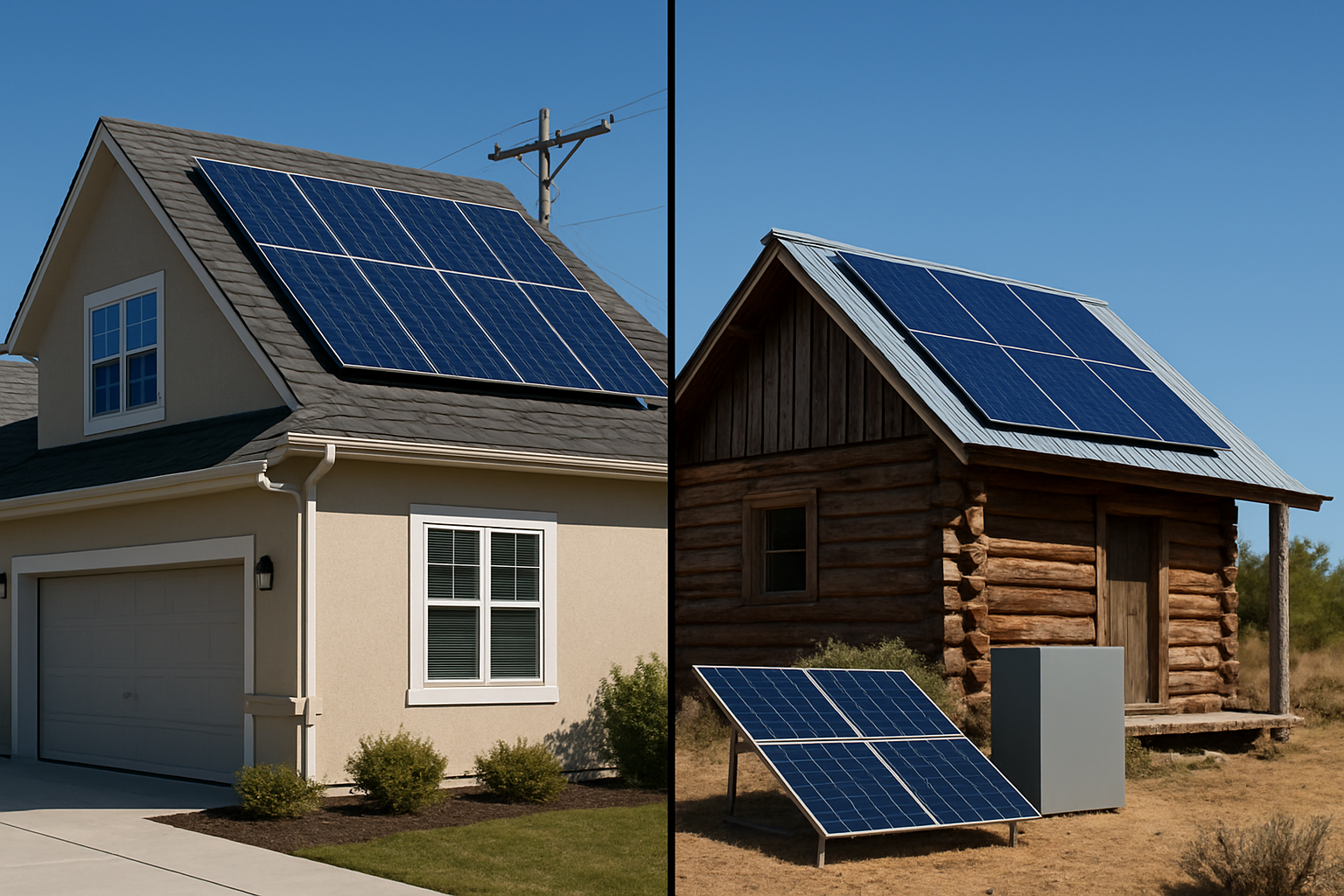
Comparing Off-Grid and Grid-Tied Systems: Common Confusions
The differences between off-grid and grid-tied solar are often misunderstood, leading to incorrect assumptions about cost and functionality. Clarifying these distinctions is essential for choosing the right path for your energy goals.
'Off-Grid is Always Cheaper Than Staying on the Grid'
While going off-grid eliminates your monthly electricity bill, it doesn't always result in lower overall costs. The upfront investment for a fully independent off-grid system, particularly the large battery bank required, is much higher than for a standard grid-tied system. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), residential electricity prices have been rising, which strengthens the financial case for solar. However, a true cost comparison must account for the initial system price, maintenance, and eventual component replacement against decades of projected utility payments.
| Factor | Grid-Tied Solar System | Off-Grid Solar System |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | Moderate (No batteries required) | High (Requires large battery bank) |
| Monthly Bill | Reduced or eliminated | Eliminated |
| Grid Reliability | Dependent on utility grid | Independent of utility grid |
| Backup Power | No (unless a hybrid system with batteries) | Yes (core function) |
| Long-Term Costs | Potential grid fees, inverter replacement | Battery and inverter replacement |
'All Solar Systems Provide Backup Power During an Outage'
This is a critical and often misunderstood point. Standard grid-tied solar systems are legally required to shut down during a power outage. This is a safety measure to prevent them from sending electricity back into the grid and endangering utility workers making repairs. Only off-grid systems or grid-tied systems with an integrated battery storage solution (often called hybrid systems) can provide backup power when the grid goes down.
The Reality of Sizing and Installation
Correctly sizing and installing your system are foundational to its success. Missteps in this phase can lead to underperformance, frustration, and unexpected costs.
'A One-Size-Fits-All Kit Will Work for My Home'
Pre-packaged solar kits can be a good starting point, but they rarely meet the unique energy needs of a household perfectly. A successful off-grid system requires a custom design based on a detailed energy audit. Factors like your daily electricity consumption, the number of peak sun hours in your specific location, and your desired level of energy security all dictate the proper size of your solar array, battery bank, and inverter. The U.S. Department of Energy provides resources and solar maps that can help in this planning phase.
'DIY Installation is Easy and Saves a Lot of Money'
While a do-it-yourself approach can save on labor costs, it is not without risks. Installing a solar energy system involves working with high-voltage electricity, which can be dangerous without proper knowledge and safety precautions. Incorrect wiring can reduce system efficiency, damage expensive components, or create a fire hazard. For larger, more complex systems, hiring a certified professional is often the wisest choice to ensure safety, performance, and compliance with any local regulations.
Making an Informed Decision
Transitioning to an off-grid solar lifestyle offers unparalleled energy independence and stability. However, this path requires a clear understanding of the investment, responsibilities, and technology involved. By moving past the common myths, you can accurately assess the costs and benefits. A well-planned, properly sized system built with high-quality components will provide reliable, clean energy for years to come, turning the dream of energy self-sufficiency into a practical reality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many batteries do I need for an off-grid system?
The number of batteries depends on two main factors: your average daily energy consumption (measured in kilowatt-hours) and the number of 'days of autonomy' you want. To determine this accurately, you must first perform a detailed load calculation to understand your daily power needs. Then, you decide how many consecutive cloudy days you want your system to be able to power your home without any solar input.
Can an off-grid solar system increase my property value?
In many cases, yes. A professionally installed, high-quality off-grid solar system can be a significant selling point, especially for properties in remote areas or regions with unreliable power grids. It offers the tangible benefit of energy independence and eliminates electricity bills, which is attractive to many buyers. The exact increase in value can vary based on the local real estate market and the size and quality of the system.
What is the lifespan of an off-grid solar system?
The lifespan varies by component. Solar panels are the most durable, typically warrantied for 25 to 30 years and often lasting longer. A quality solar inverter may last 10 to 15 years before needing replacement. The lifespan of the battery bank depends heavily on the technology; traditional lead-acid batteries might last 3-7 years, while modern lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries can last for 10 years or more and deliver thousands of charge cycles.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.