The rapid growth of solar energy is a major victory for clean power. But it raises a critical question: what happens to solar panels after their 25 to 30-year lifespan? The answer lies in creating a robust circular economy, a goal that the partnership between PV Cycle and Veolia is turning into a reality. This case study examines their pioneering work in solar panel recycling, a process vital for the long-term sustainability of the solar industry.
The End-of-Life Challenge for Solar Panels
As the first waves of solar installations reach maturity, the volume of decommissioned panels is set to increase dramatically. This presents both a challenge and a significant opportunity. Proactive management of this waste stream is necessary to prevent environmental issues and to capture the value held within these panels.
The Scale of a Growing Waste Stream
According to a report on Solar PV Global Supply Chains by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the world will see tens of millions of tons of decommissioned solar panels by 2050. Simply sending these modules to landfills is not a sustainable option. Panels contain small amounts of materials that, if not handled correctly, could pose environmental risks. More importantly, landfilling wastes valuable resources that required significant energy to produce in the first place.
Why Recycling is a Critical Solution
Solar panel recycling is not just about waste disposal; it's about resource recovery. A typical crystalline silicon panel is rich in materials that can be repurposed. According to Veolia, panels are generally composed of 65-75% glass, 10-15% aluminum, 10% plastic, and 3-5% silicon. The IEA notes that creating a secondary supply of these materials through recycling enhances supply chain security and reduces the environmental impact of mining new resources. This is the foundation of a circular economy in the solar sector.

A Landmark Partnership: PV Cycle and Veolia
To address the end-of-life issue at scale, collaboration is key. The partnership between PV Cycle, a producer-focused collection and recycling organization, and Veolia, a global leader in resource management, provides a powerful model for the industry.
Forging an Industrial-Scale Solution
In 2018, Veolia, in partnership with PV Cycle, opened the first plant in Europe entirely dedicated to recycling photovoltaic panels in Rousset, France. This facility was designed to move beyond the basic recovery of glass and aluminum. The goal was to establish a comprehensive process that could dismantle, sort, and recover nearly all components of a solar panel with high efficiency.
The High-Tech Recycling Process
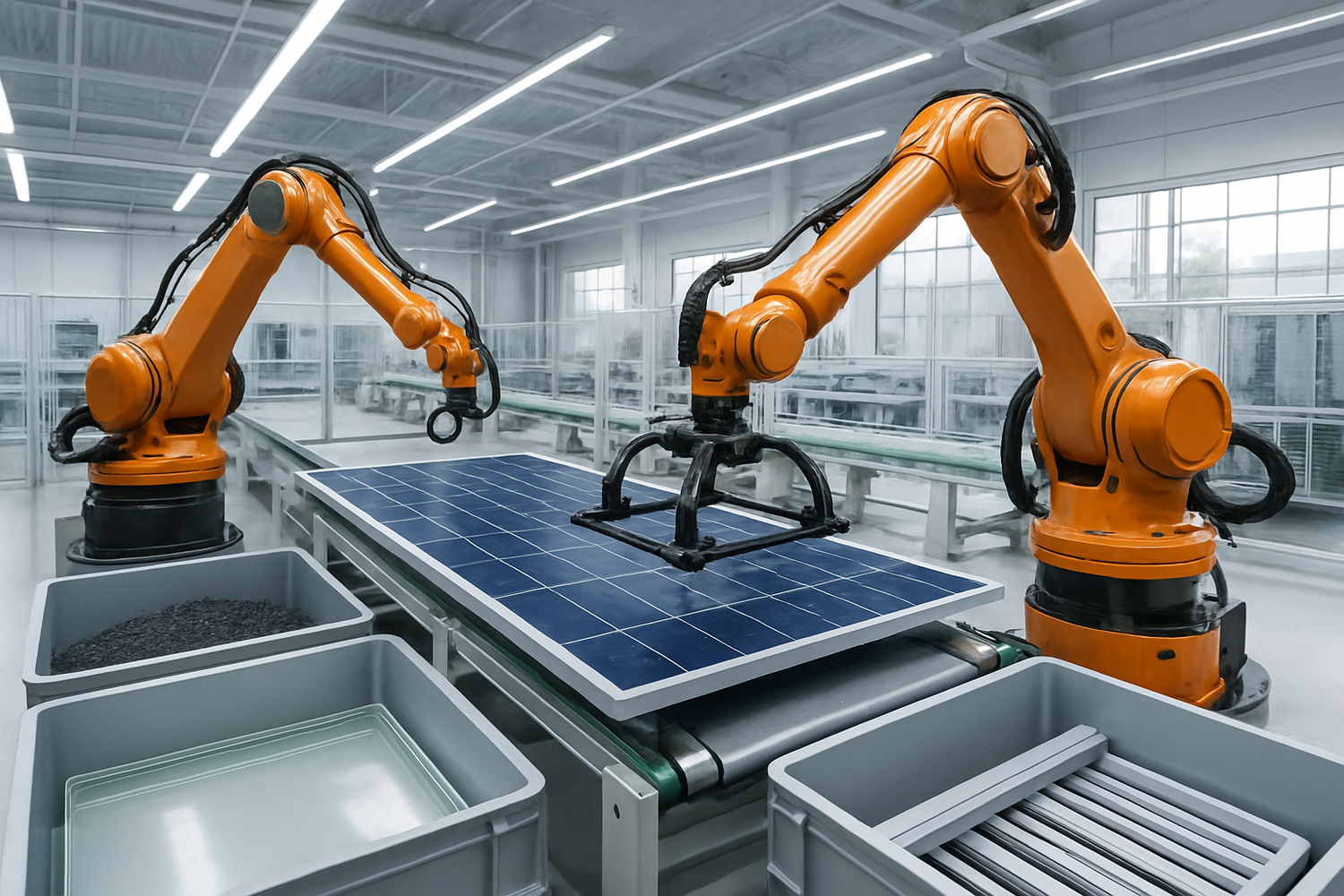
The process at the Rousset plant is a showcase of modern recycling technology. It focuses on maximizing the recovery rate of materials from end-of-life crystalline silicon panels. The plant uses automated robots to safely and efficiently disassemble the panels, separating the aluminum frame and junction box before processing the main laminate. This high-tech approach enables a recovery rate of over 95% of the panel's materials.
From Used Panel to Valuable Raw Material
The success of any recycling program is measured by its ability to turn waste back into high-quality resources for manufacturing. The PV Cycle and Veolia collaboration excels in this area, creating clean material streams that can be reintroduced into various industries.
A Multi-Step Recovery Method
The recycling journey involves several sophisticated steps. After initial disassembly, specialized machines shred the panel's laminate. A series of mechanical and chemical treatments then separates the different components. Advanced optical sorting and other techniques isolate glass, silicon, copper, and silver, ensuring each material stream has a high purity level, which is critical for its reuse.
Where Do the Recovered Materials Go?
The materials recovered at the facility are not downcycled into low-grade applications. Instead, they are prepared for re-entry into primary production cycles, contributing directly to the circular economy. This process is detailed in a review of recycling processes for photovoltaic modules, which highlights the importance of creating high-quality secondary raw materials.
| Recovered Material | Purity/Form | Destination Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | Clean Cullet | Glass Manufacturing |
| Aluminum | Refined Ingots | Aluminum Refineries |
| Silicon | Powder/Wafers | Precious Metals / Smelting |
| Copper | Copper Shot | Metal Foundries |
| Plastics | Flakes/Pellets | Energy Recovery (Cement Plants) |
Building a True Circular Economy for Solar
The model established by PV Cycle and Veolia extends beyond a single factory. It provides a blueprint for how the solar industry can take responsibility for its products throughout their entire lifecycle, a concept known as Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR).
Strengthening Supply Chains and Reducing Impact
By creating a reliable source of secondary raw materials, solar panel recycling reduces dependence on volatile global commodity markets and energy-intensive mining operations. As an NREL report on the circular economy for solar points out, this strengthens domestic supply chains and improves the overall sustainability of the industry. It transforms a potential liability—end-of-life waste—into a strategic asset.
The Path Forward
The collaboration between PV Cycle and Veolia demonstrates that solar panel recycling is not a distant future concept; it is a viable, scalable, and necessary practice for today. As the solar industry continues to expand, adopting these circular economy principles will be fundamental to ensuring that this clean energy source is truly sustainable from beginning to end and beyond. This approach doesn't just manage waste; it builds a more resilient and resource-efficient future for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What materials can be recovered from a solar panel?
Modern recycling facilities can recover over 95% of a solar panel's materials. This includes glass, the aluminum frame, silicon, copper from wiring, and even trace amounts of silver. The plastics in the junction box and backsheet are also separated for energy recovery.
Is solar panel recycling economically viable?
The economic viability of solar panel recycling is improving. As the volume of end-of-life panels increases and recycling technologies become more efficient, the value of the recovered raw materials helps offset the processing costs. Policies like the European WEEE Directive also create a regulatory framework that supports the recycling market.
What is the role of consumers in solar panel recycling?
For residential and commercial solar owners, the most important step is to work with certified installers and recycling programs when decommissioning a system. Organizations like PV Cycle provide collection networks to ensure that used panels are sent to appropriate recycling facilities instead of landfills.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.