A home energy storage system is a powerful step toward energy independence. It allows you to store solar energy for use at night or during an outage, giving you control over your power. But the installation process is complex. Errors can lead to poor performance, safety hazards, and unexpected costs. Understanding common pitfalls is the key to a successful and reliable system.
This article details five significant mistakes made during home energy storage system installs. By avoiding them, you can ensure your investment provides lasting value and peace of mind.
1. Underestimating Your Energy Needs
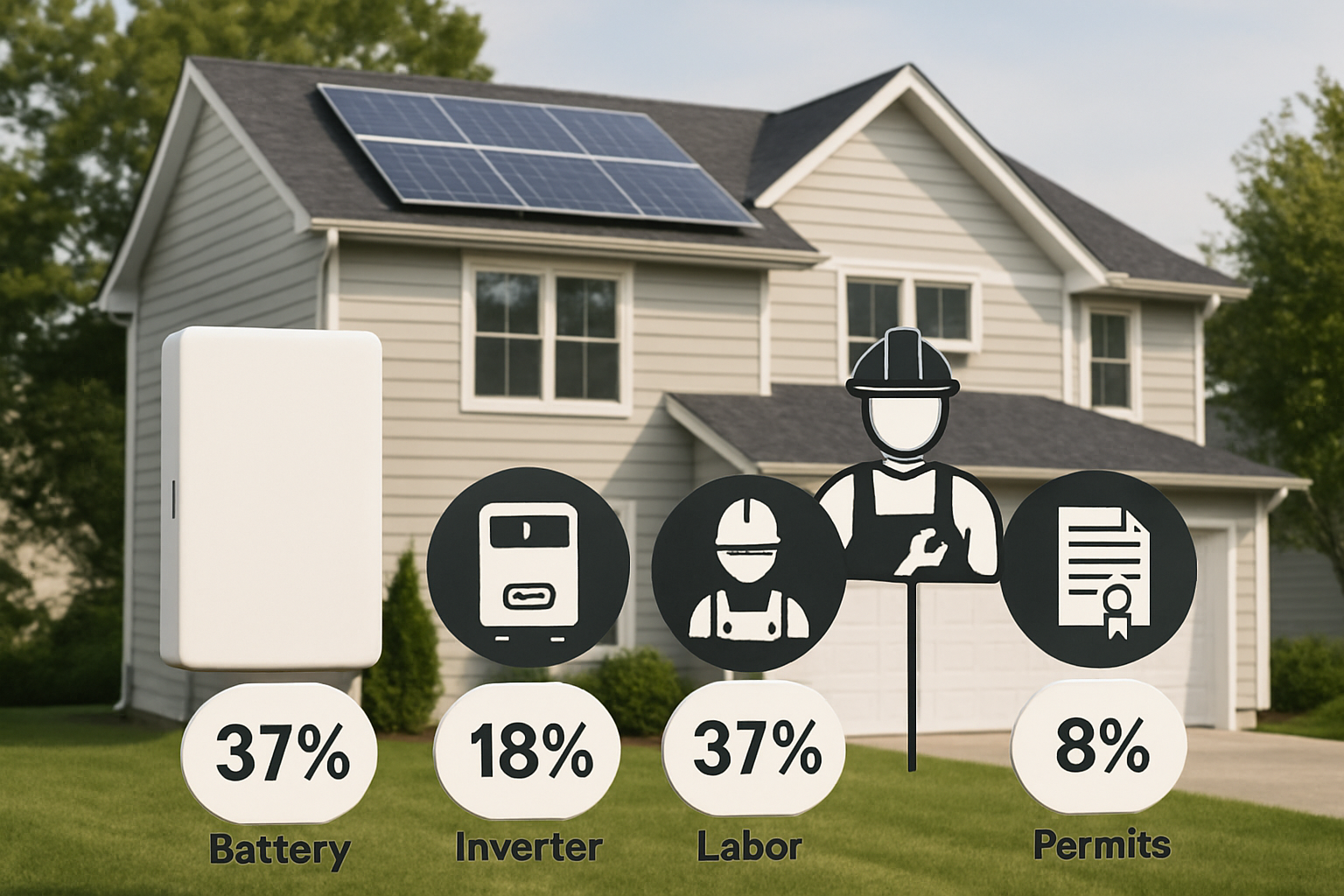
One of the most frequent errors is improper system sizing. A system that is too small will not meet your needs during a power outage, while an oversized system results in unnecessary expense. Getting the size right is fundamental to satisfaction and performance.
Calculating Load Requirements
Before selecting a battery, you must analyze your household's energy consumption. Review your past utility bills to find your average daily energy use in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Next, identify your 'critical loads'—the essential appliances you need to run during an outage, such as refrigerators, lights, and medical devices. Calculating the power requirements for these items will help determine the minimum battery capacity you need.
| Appliance | Power Rating (Watts) | Daily Use (Hours) | Daily Energy (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 200 W | 8 | 1600 Wh |
| LED Lights (5) | 50 W | 6 | 300 Wh |
| Internet Router & Modem | 15 W | 24 | 360 Wh |
| Total Essential Load | 2260 Wh (2.26 kWh) |
Planning for Future Growth
Your energy needs may change. Are you planning to buy an electric vehicle (EV) or add a new major appliance? It is wise to select a scalable system that allows for future expansion. Choosing a modular design lets you add more battery capacity later without replacing the entire system.
2. Bypassing Local Regulations and Permits
Skipping the permitting process is a serious mistake. Local and national codes exist to ensure safety and proper functionality. A non-compliant installation can result in fines, an order to remove the system, or even denial of a homeowner's insurance claim in case of an incident.
Navigating Electrical Codes
Installations must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC), particularly Article 706, which covers Energy Storage Systems (ESS). These codes specify requirements for wiring, disconnects, and overcurrent protection to prevent electrical hazards. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, standardized permitting processes not only ensure safety but can also significantly reduce installation costs.
The Permitting Process
The permitting process typically involves submitting detailed plans of your system to your local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) for approval. After installation, an inspector will verify that the system was built according to the approved plans and meets all code requirements before it can be legally operated. While it can seem like a lengthy step, it is a critical checkpoint for safety and quality.
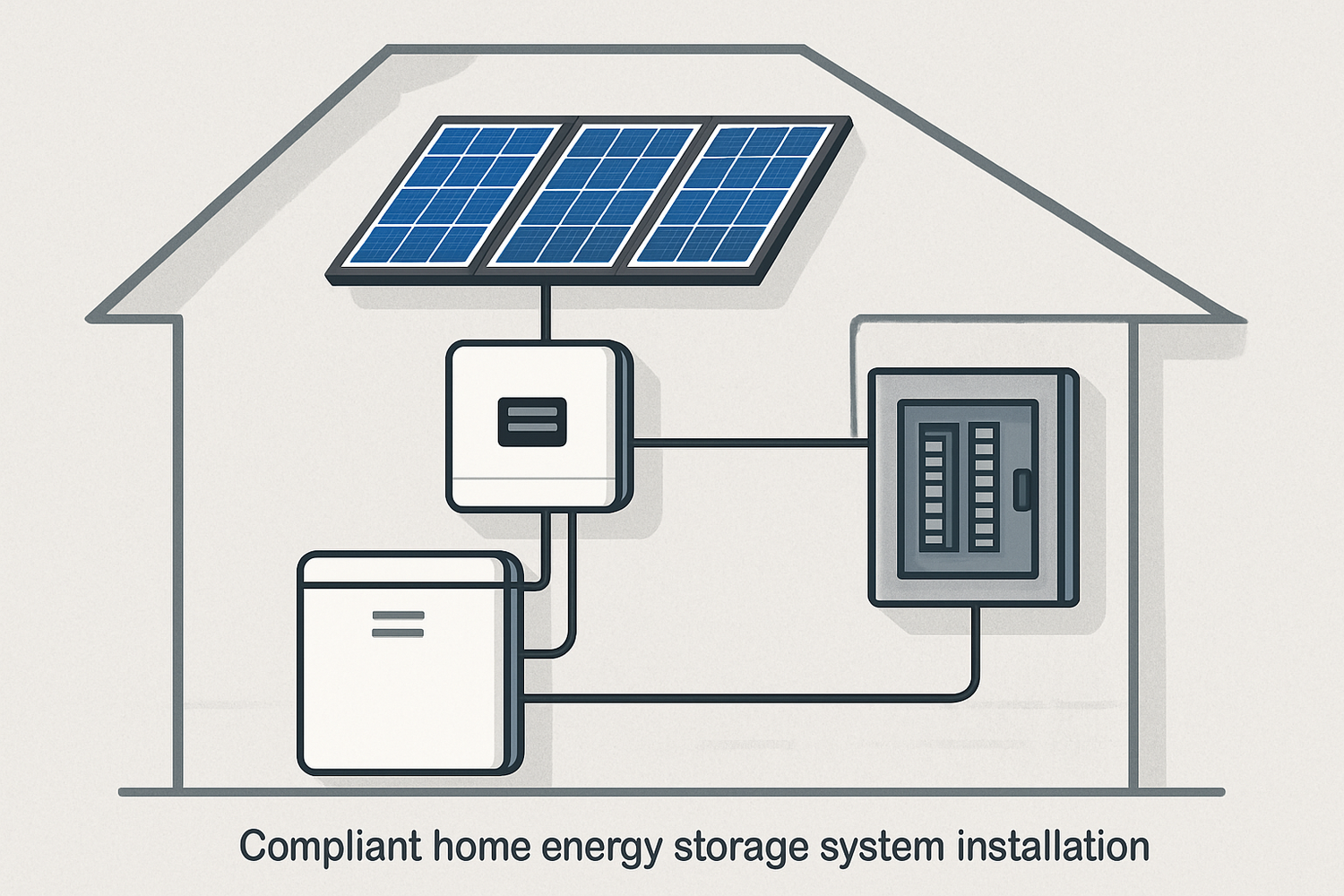
3. Creating a Mismatch of Components
A home energy storage system is an ecosystem of parts, including the battery, inverter, and solar panels. These components must be compatible to work efficiently and safely. Ignoring compatibility can lead to system malfunctions and voided warranties.
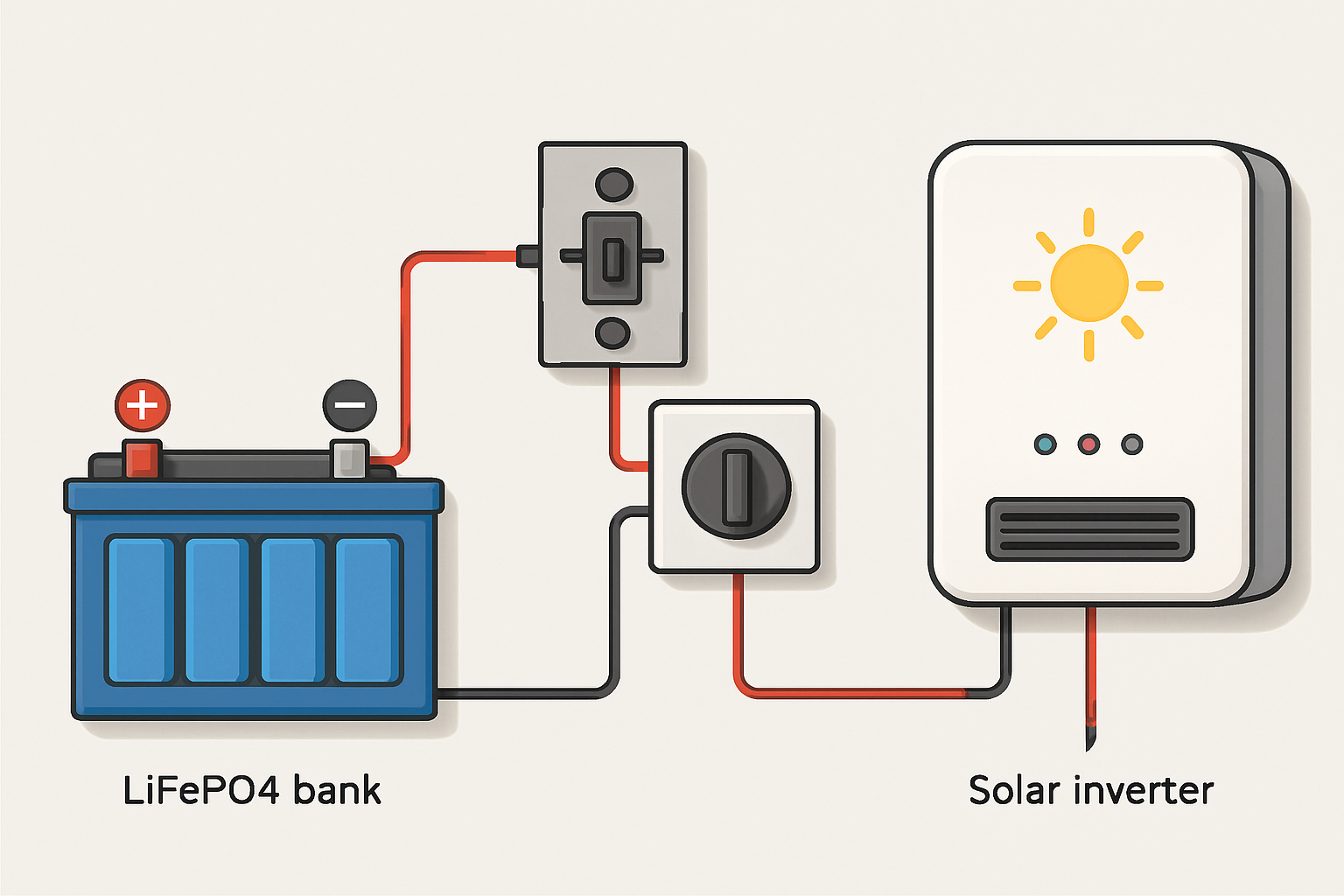
Battery and Inverter Synergy
The inverter converts the battery's direct current (DC) power to alternating current (AC) power for your home. The battery and inverter must be compatible in terms of voltage and communication protocols. A hybrid inverter is often a good choice as it is designed to manage power flow from solar panels, batteries, and the grid in a single unit. A mismatch can prevent the system from operating or even damage the components.
Integrating with Solar Panels
When adding batteries to an existing solar PV system, compatibility is equally important. The type of solar inverter you have will determine the best way to add storage. As the International Energy Agency (IEA) notes in its report 'Next Generation Wind and Solar Power', installing battery storage with solar PV effectively increases self-consumption by storing excess energy produced during the day. This reduces the amount of power sent back to the grid, maximizing the value of your solar investment.
4. Neglecting Location and Environmental Factors
Where you install your battery system has a major impact on its performance, lifespan, and safety. Batteries are sensitive to their environment, and poor placement is a common and costly error.
Temperature and Ventilation
Most batteries, including modern Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) types, have an optimal operating temperature range. Installing a battery in a location with extreme heat or cold, like a non-insulated garage in a harsh climate, can reduce its efficiency and shorten its life. Proper ventilation is also necessary to dissipate heat generated during charging and discharging. Understanding key metrics is crucial, as explained in this comprehensive guide on solar storage performance, which covers how factors like temperature affect battery health.
Physical Safety and Accessibility
The NEC and local fire codes have specific requirements for the placement of battery systems, including clearance from living areas and flammable materials. The system should be installed in an accessible location for routine maintenance and emergency servicing. It must be secured on a level, stable surface capable of supporting its weight.
5. Forgetting About Long-Term Management
The installer's job may end when the system is switched on, but your role as the system owner is just beginning. Overlooking monitoring and maintenance can lead to undetected problems that reduce your system's effectiveness over time.
The Role of a Battery Management System (BMS)
A quality battery comes with an integrated BMS. This crucial component acts as the brain of the battery, protecting it from overcharging, deep discharging, and temperature extremes. The BMS ensures the battery operates safely and helps maximize its lifespan by keeping the internal cells balanced.
Setting Up Remote Monitoring
Modern energy storage systems come with monitoring software that allows you to track your energy production, consumption, and battery status from a smartphone or computer. Regularly checking this data helps you understand your energy habits and can alert you to potential issues, such as a sudden drop in performance, before they become serious problems.
Achieving a Successful Installation
A home energy storage installation is a valuable upgrade to your home, offering resilience and control. By avoiding these five common mistakes—improper sizing, skipping permits, using incompatible parts, poor placement, and neglecting monitoring—you can ensure your system is safe, reliable, and efficient. Careful planning and working with qualified professionals are the cornerstones of a successful project that will deliver clean energy for years to come.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute professional electrical or financial advice. Always consult with a qualified installer and a financial advisor for your specific situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a home battery last?
The lifespan of a home battery depends on its chemistry, usage, and operating conditions. LiFePO4 batteries are known for their long life, often rated for 10 to 15 years or more and capable of delivering several thousand charge-discharge cycles.
Can I install a home battery system myself?
While some smaller, portable systems are designed for DIY setup, a whole-home energy storage system involves high voltages and complex wiring connected to your home's main electrical panel. For safety and compliance with electrical codes, this work should be performed by a licensed and certified professional installer.
How much maintenance does a battery system require?
Modern residential energy storage systems, especially those using LiFePO4 technology, are designed to be low-maintenance. They do not require regular fluid checks like older lead-acid batteries. Maintenance typically involves keeping the unit and its ventilation clear of debris and periodically checking system monitoring software for any fault alerts.


Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.