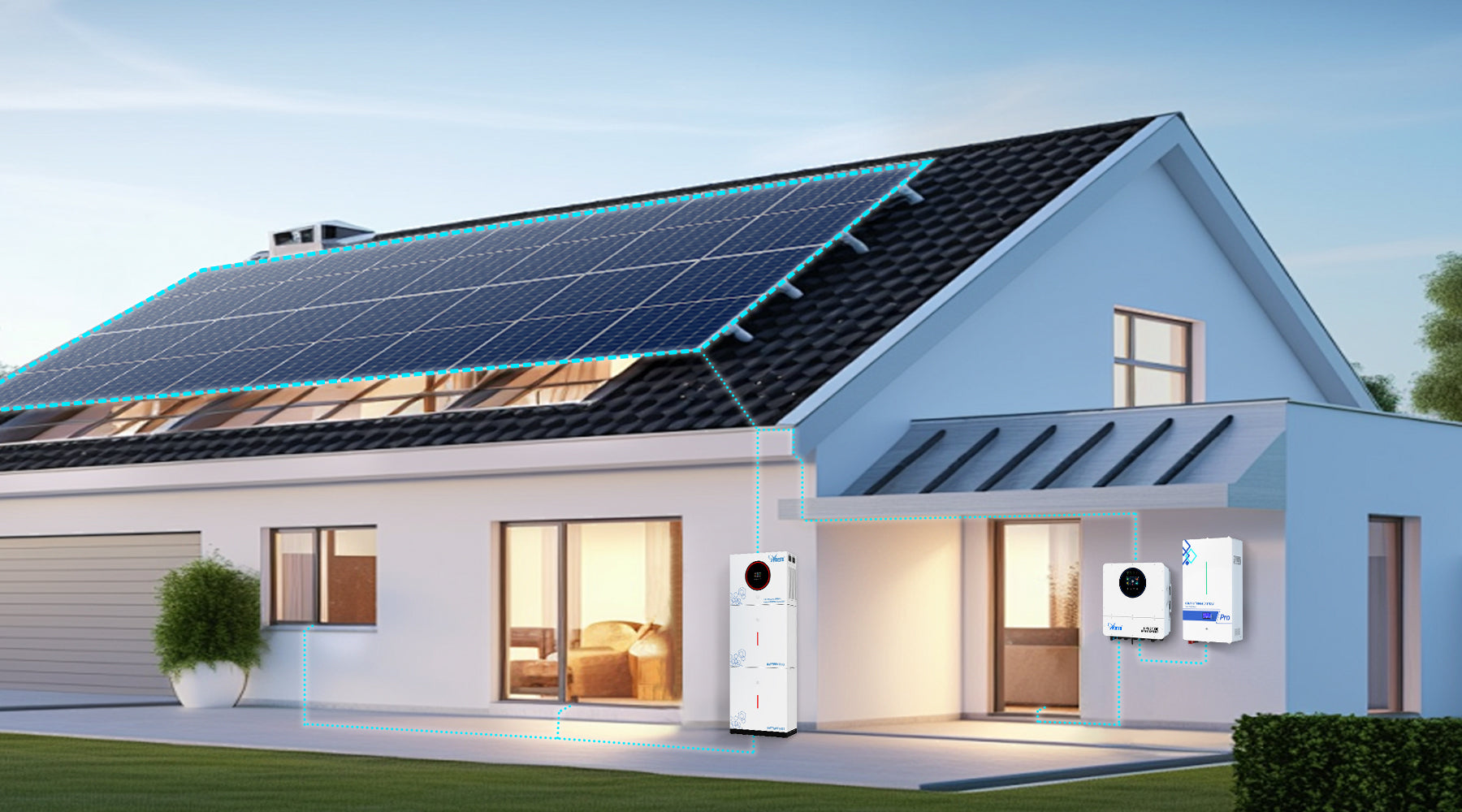
A common question arises for those planning a complete solar energy solution: How do the physical racks on the roof interact with the sophisticated electronics inside the home? The straightforward answer is that roof mount systems are designed to work seamlessly with hybrid inverters and Energy Storage Systems (ESS). They form three distinct but complementary parts of a unified, high-performance energy system.
Think of the roof mounting system as the foundation, the hybrid inverter as the brain, and the ESS as the energy reserve. While the mounting hardware provides the critical structural support for your solar panels, the inverter and battery manage the flow and storage of the energy produced. This article clarifies how these components integrate, what to consider for compatibility, and why this combination is central to achieving energy independence.
Understanding the Components of a Modern Solar-Plus-Storage System
A complete solar solution involves more than just panels. It's an ecosystem where each part plays a vital role. The physical structure, power conversion, and energy storage must all function together.
The Role of Roof Mounting Systems
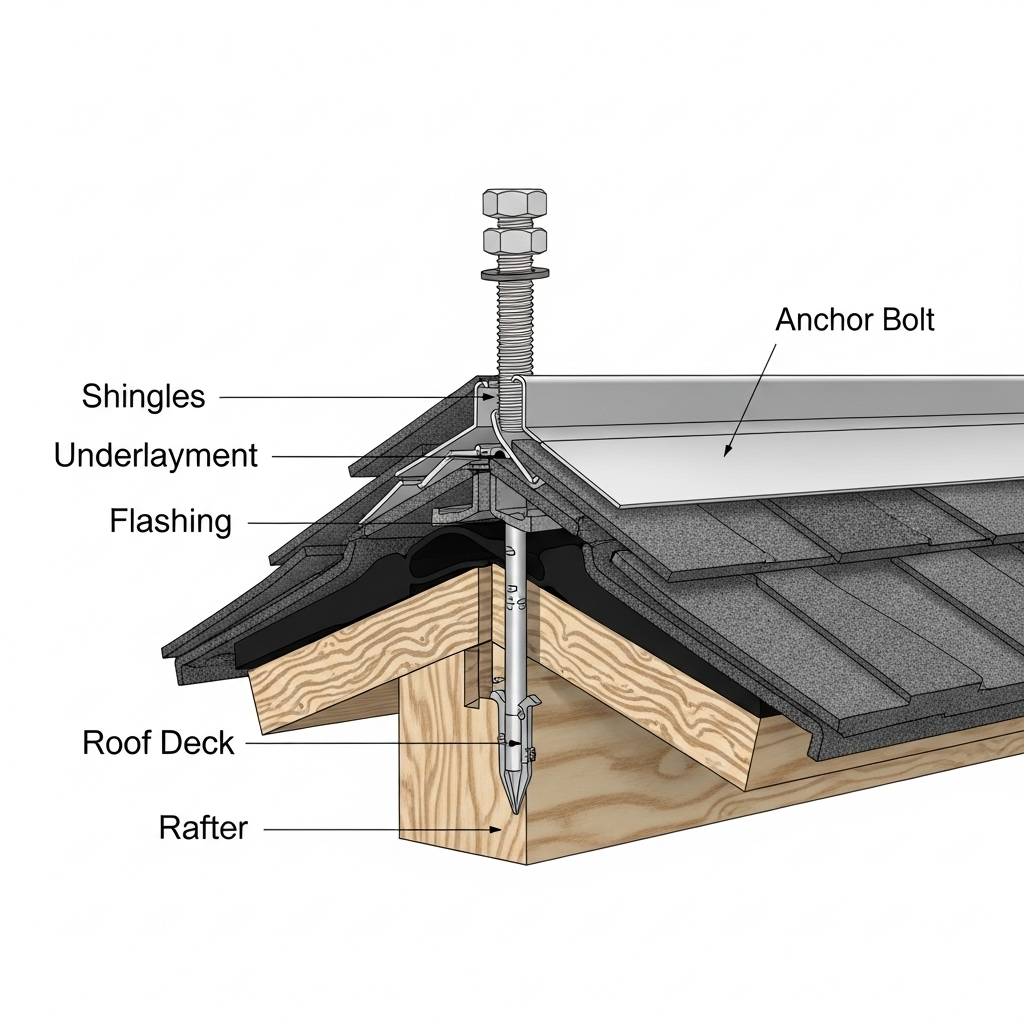
A roof mounting system's primary job is to securely fasten solar panels to your roof. It is an entirely structural component, engineered to withstand environmental forces like wind and snow. Its design is focused on roof integrity, panel security, and durability. The mounting system is electrically passive; it simply provides the platform for the solar array and does not influence the type of inverter or battery you choose.
What are Hybrid Inverters?
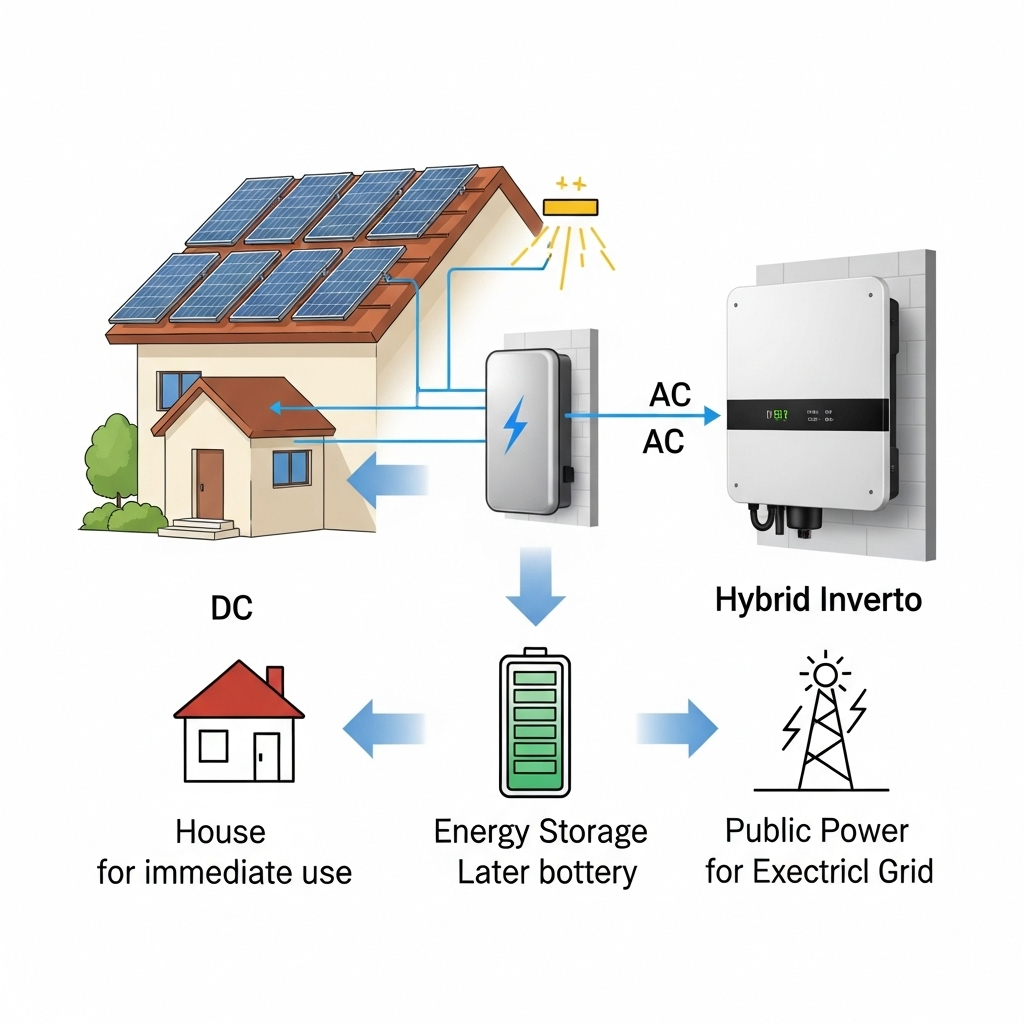
Hybrid inverters are the command center of a modern solar installation. They are far more advanced than traditional grid-tied inverters. A hybrid unit intelligently manages the flow of energy between your solar panels, your home's appliances, the battery system, and the electrical grid. According to the International Energy Agency's Solar Energy Perspectives report, inverters are a critical part of the 'balance of system' (BOS), which includes all components beyond the panels themselves. These devices convert the direct current (DC) electricity from your panels and battery into the alternating current (AC) your home uses.
The Function of an Energy Storage System (ESS)
An Energy Storage System, typically comprised of advanced lithium batteries, acts as your personal energy reservoir. It stores excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during a power outage. This capability is what elevates a standard solar installation into a true energy independence solution, giving you control over your power supply and reducing reliance on the grid.
How Roof Mounts, Inverters, and Storage Work in Harmony
The integration of these three components is a story of physical support meeting intelligent electrical management. The connection is logical and designed for efficiency, with each part performing its function without conflict.
The Physical Connection: From Panel to Inverter
The journey of solar energy begins at the panels. Once secured by the roof mount system, the panels are wired together. This DC electricity travels through specialized, weatherproof wiring that runs from the roof to the location of the hybrid inverter, which is usually in a garage, basement, or utility room. The roof mount's role ends once the panels are secure; it does not participate in the electrical circuit.

The Electrical Integration: The Hybrid Inverter's Central Role
The hybrid inverter is where the system's intelligence lies. It continuously makes decisions based on real-time data:
- During the day: The inverter directs solar power first to meet the home's immediate energy needs.
- With excess power: Any surplus energy is used to charge the ESS.
- When the battery is full: If the system is grid-tied, the inverter can export the remaining excess power to the utility grid.
- At night or during an outage: The inverter draws stored energy from the ESS to power the home.
This dynamic energy management ensures that solar power is used in the most efficient way possible, maximizing self-consumption and providing a reliable backup.
Why Compatibility is an Electrical Matter, Not Structural
The compatibility between a roof mount and a hybrid system is rarely a concern. Roof mounting hardware is standardized to fit certified solar panels. The critical compatibility checks are electrical. You must ensure that the solar array's voltage and current characteristics are within the operating parameters of your chosen hybrid inverter, and that the inverter is compatible with your ESS. The table below clarifies the distinct roles.
| Component | Primary Function | Key Integration Point |
|---|---|---|
| Roof Mount System | Securely holds solar panels | Physical. Provides a stable platform for the energy source. |
| Solar Panels | Convert sunlight to DC electricity | Electrical. DC output must match the inverter's input specifications. |
| Hybrid Inverter | Manages power flow, converts DC/AC | Electrical Hub. Connects panels, battery, grid, and home loads. |
| Energy Storage System (ESS) | Stores and releases DC electricity | Electrical. Communicates with the inverter for charge/discharge cycles. |
Key Considerations for a Seamless System Integration
Proper planning is essential to ensure all parts of your solar-plus-storage system perform optimally. The focus should be on electrical synergy and correct sizing rather than the physical mounting hardware.
Sizing Your System Correctly
Matching the capacity of your components is crucial. The total power output of your solar panels (measured in kilowatts, kW) should be paired with a hybrid inverter of an appropriate size. An undersized inverter will 'clip' or waste potential energy from the panels on sunny days. Similarly, your battery storage (measured in kilowatt-hours, kWh) should be sufficient to cover your energy needs overnight or during outages. As highlighted in research like the IEA's Solar Energy Perspectives, overall system design is a major factor influencing the total annual energy yield.
Wiring and Balance of System (BOS)
Beyond the main components, the balance of system—which includes wiring, conduits, and safety devices like circuit breakers—is vital. These elements ensure that power is transmitted safely and efficiently. The IEA includes these electrical protection devices as a key part of the BOS, alongside the structural mounts. Using the correct wire gauges and adhering to electrical codes prevents energy loss and ensures system safety.
Performance Monitoring and Management
Modern hybrid systems offer sophisticated monitoring platforms, often accessible via a smartphone app. This allows you to see exactly how your system is performing in real-time. Tracking these metrics is key to maximizing your return on investment. A deeper understanding of key performance indicators, such as those explained in this comprehensive guide on solar storage performance, can help you optimize your system's operation and energy usage patterns.
A Unified Energy Solution
In summary, roof mounting systems are fully compatible with hybrid inverters and energy storage systems. They serve as the essential structural base for the solar panels, which are the fuel source for the entire setup. The real integration happens at the electrical level, orchestrated by the hybrid inverter that manages the energy produced by the panels and stored in the battery. The choice of mounting hardware is dictated by your roof type and local conditions, while the choice of inverter and ESS is determined by your energy goals and electrical requirements. Together, they create a powerful, cohesive system that provides clean, reliable power and a clear path toward energy independence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I add a battery (ESS) to my existing grid-tied solar system with a roof mount?
Yes, this is a common upgrade. It can be done by adding a separate battery inverter (AC coupling) or by replacing your current inverter with a hybrid model. Your existing roof mounting system does not need to be changed as long as it is in good condition.
Does the type of roof mount (e.g., rail-less, ballasted) affect the choice of hybrid inverter?
No. The type of roof mount you use is determined by your roof's material, slope, and structural capacity. It has no impact on the electrical compatibility between your solar panels, hybrid inverter, and ESS.
Are there any special wiring considerations for a roof-mounted system with ESS?
The wiring from the solar array to the hybrid inverter is a standard DC electrical connection. The complexity of the system lies in the connections between the inverter, battery, your main electrical panel, and potentially a dedicated backup loads panel. All wiring must comply with local and national electrical codes for safety.
How does a hybrid system impact the weight on my roof?
The weight on your roof comes from the solar panels and the mounting system itself. The hybrid inverter and the ESS are heavy components that are typically installed on a reinforced wall in a garage or utility room, or on a concrete pad outside. They do not add any load to the roof structure.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.