Taking control of your home's energy is more accessible than ever. A solar battery storage system allows you to generate, store, and use your own clean electricity. This setup provides a reliable power source during grid outages and can help manage energy costs. This guide offers a clear path to understanding how a complete home solar battery installation comes together, from the essential components to the final commissioning.
Understanding the Core Components
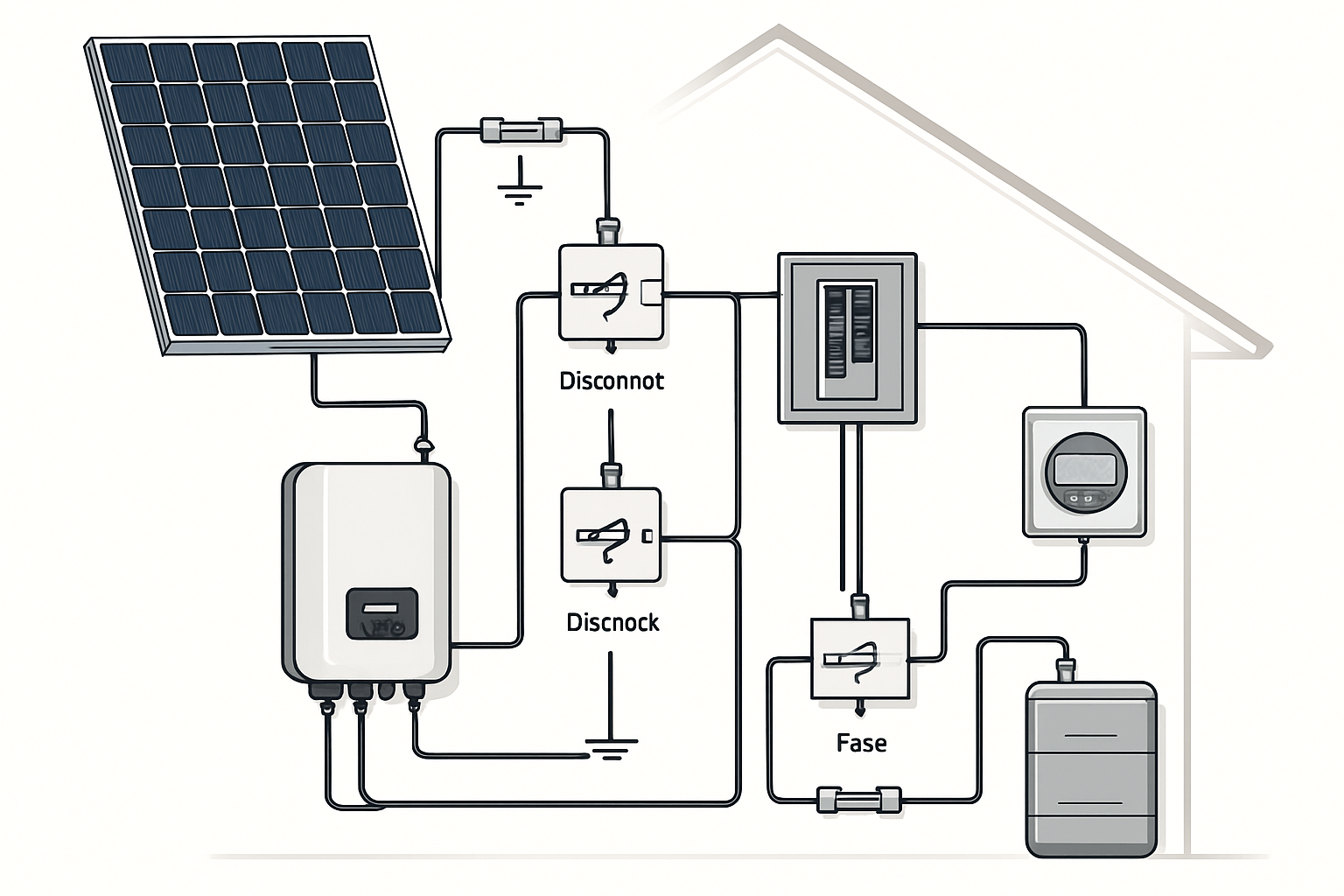
A solar battery storage system is an ecosystem of parts working together. At its core are three main components: the solar panels that capture sunlight, the battery that stores the energy, and an inverter that makes the power usable for your home.
Solar Panels: The Power Generators
Solar panels are the starting point of your energy independence. Composed of photovoltaic (PV) cells, they convert sunlight directly into direct current (DC) electricity. When selecting panels, you'll encounter different technologies, primarily monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Monocrystalline panels are known for higher efficiency and a sleek black appearance, while polycrystalline panels are a more budget-friendly option. The key is to choose panels with sufficient wattage to meet your daily energy needs and effectively charge your battery bank.
The Inverter: The Brain of the System
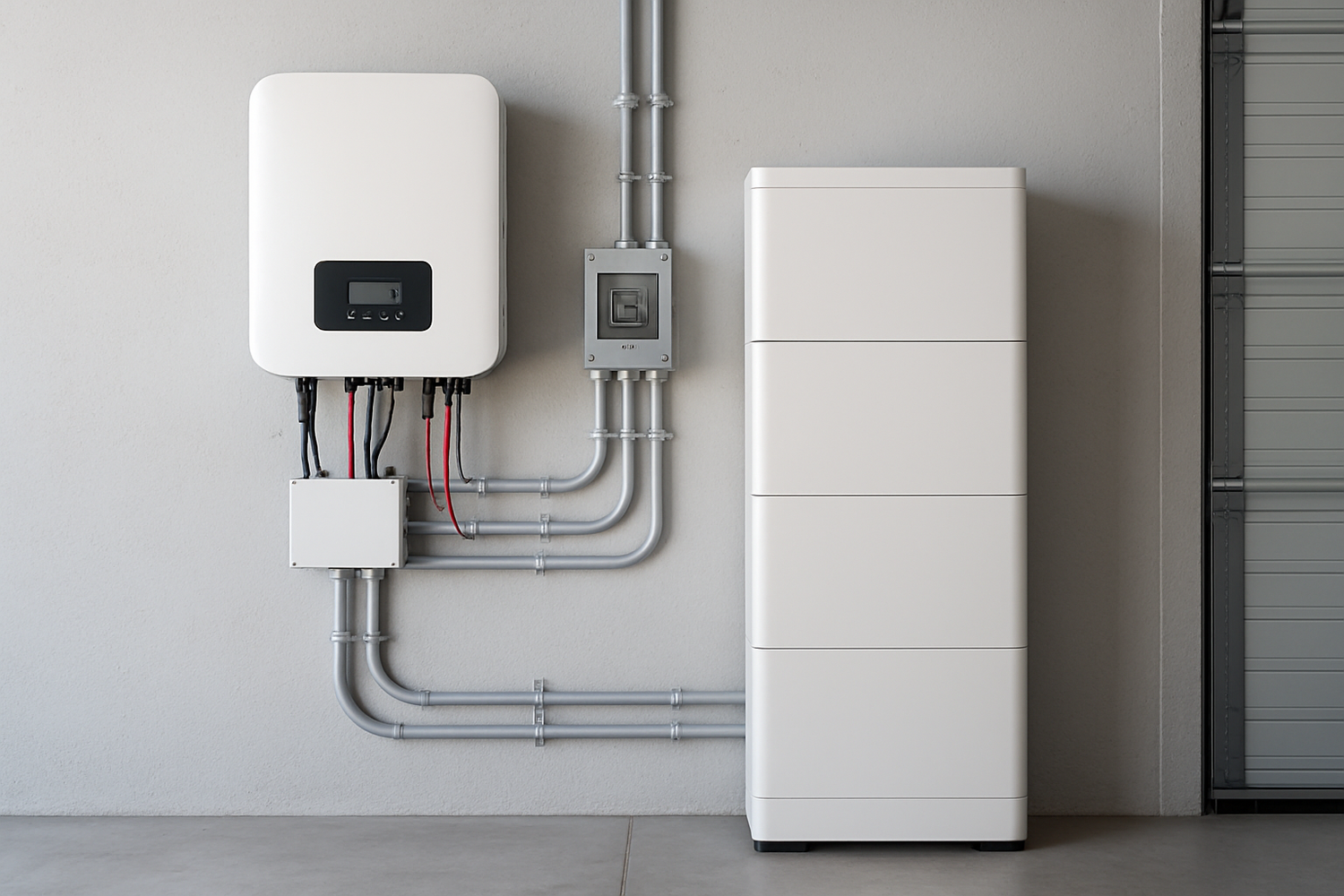
The inverter is a critical component that converts the DC electricity from your solar panels and battery into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the standard for household appliances. For a battery backup system, a hybrid inverter is the ideal choice. These advanced inverters can intelligently manage power from the solar panels, the battery, and the grid simultaneously. This capability is central to creating a seamless energy storage solution, allowing you to prioritize self-consumption of solar power, store excess energy, and draw from the grid only when necessary. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), inverters, along with wiring and protection devices, are crucial parts of the "balance of system" (BOS) that ensures proper operation.
The Battery: The Heart of Energy Storage
The battery is what transforms a standard solar panel system into a resilient energy solution. It stores the excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during a power outage. Among the available technologies, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have become the standard for home energy storage. Our focus on LiFePO4 technology stems from its superior safety, long cycle life, and high efficiency. Key metrics to understand are:
- Capacity (kWh): The total amount of energy the battery can store.
- Power Rating (kW): The maximum amount of electricity the battery can deliver at once.
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): The percentage of the battery's capacity that can be safely used. LiFePO4 batteries often have a DoD of 90-100%.
- Cycle Life: The number of charge and discharge cycles a battery can endure before its capacity degrades significantly. LiFePO4 batteries can last for thousands of cycles, often translating to a lifespan of over 10 years.
Choosing the right battery is foundational to your system's performance. For more details on this technology, you can read about how to Unlock Energy Independence with a LiFePO4 Battery Pack and debunk common misconceptions in Solar Storage Myths: The Truth About LiFePO4 Batteries.
Planning Your Home Solar Battery Installation
Proper planning is the most critical phase of a solar battery setup. It ensures your system meets your energy needs, fits your home's characteristics, and provides a return on your investment. A thorough plan prevents costly errors and maximizes performance from day one.
Sizing Your System Correctly
The first step is to conduct a load analysis to understand your energy consumption. You can calculate your average daily energy usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh) by reviewing your past utility bills. This figure is the baseline for determining the size of your battery bank and solar array. For example, if your home uses 30 kWh per day, you'll need a battery with enough usable capacity to cover your needs during non-solar hours or an outage. The solar array must be large enough to power your home during the day while simultaneously charging the battery. The U.S. Department of Energy highlights successful projects where careful modeling determined the optimal size of solar and battery systems for communities, demonstrating the importance of accurate sizing. To learn more about sizing for specific needs, see our articles on if a 100ah Lithium Deep Cycle Battery Is Enough for a Home or when to use a 200ah Lithium Battery.
| Appliance | Power (Watts) | Hours of Use/Day | Energy (Watt-hours/Day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 150 W | 8 hours | 1200 Wh |
| LED Lights (10) | 100 W | 6 hours | 600 Wh |
| Television | 200 W | 4 hours | 800 Wh |
| Laptop | 65 W | 5 hours | 325 Wh |
| Total | - | - | 2925 Wh or 2.925 kWh |
On-Grid, Off-Grid, or Hybrid?
Your connection to the utility grid defines the type of system you'll install.
- On-Grid: A standard solar installation without batteries. It reduces your electricity bill but does not provide power during an outage.
- Off-Grid: Completely disconnected from the utility grid, providing total energy independence. This requires a robust system capable of meeting 100% of your energy needs. We specialize in reliable off-grid solar solutions for homes, farms, and cabins. Explore a real-world example in our Case Study: An Off-Grid Home Solar & Battery Setup.
- Hybrid: The most popular option for residential use. A hybrid system is connected to the grid but includes a battery backup. You can store solar energy for later use, power your home during an outage, and still draw from the grid as a final backup. This offers the ultimate combination of resilience and flexibility.
System Voltage: 12V, 24V, or 48V?
The system's DC voltage is another important consideration, particularly for off-grid and DIY setups. While 12V systems are common for smaller applications like RVs, 48V systems are generally more efficient for larger home energy storage systems. Higher voltage allows for smaller, less expensive wires and reduces energy loss over distance. Our guide on 12V vs. 48V LiFePO4 Battery systems can help you decide which is right for your application.
The Installation Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
Disclaimer: A solar battery storage system setup involves high-voltage electricity and should be performed by a qualified and certified professional. This overview is for informational purposes only.
Pre-Installation: Site Assessment and Permitting
Before any equipment is installed, a professional will conduct a thorough site assessment. This includes evaluating your roof's condition, orientation, and any potential shading issues that could impact solar production. The installer will also determine the best location for the battery and inverter, which should be a cool, dry, and well-ventilated space like a garage or utility room. This phase also involves securing necessary permits from your local municipality and approval from your utility company. Proper planning here helps avoid the common pitfalls detailed in 7 Mistakes in a Home Battery Storage System Installation.
Mounting and Wiring the Components
Once permits are approved, the physical installation begins. This involves securely attaching racking to your roof to hold the solar panels. The inverter and battery are then mounted in their designated location. An electrician will connect all the components: wiring the solar panels to the inverter, the inverter to the battery, and the entire system to your home's main electrical panel. The IEA identifies this wiring and electrical protection as a fundamental part of the system's reliability.
Commissioning and Monitoring
The final step is commissioning, where the installer activates the system and verifies that everything is operating correctly. You will be provided with access to a monitoring platform, usually a smartphone app, that allows you to track your system's performance in real-time. You can see how much energy your panels are producing, your home's consumption, the battery's state of charge, and your overall energy savings. For a deep dive into the metrics you should be watching, consult the Ultimate Reference for Solar Storage Performance.
Maximizing Your Investment and Future-Proofing
A solar battery system is a significant investment in your home's future. Understanding the financials, maintenance, and potential for expansion will help you get the most value from your system for years to come.
Understanding the Financials
The total cost of a solar panel battery setup depends on system size, component quality, and local labor rates. However, various incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost. The federal Residential Clean Energy Credit, for example, provides a tax credit for a percentage of the total system cost, including the battery. Many states and local utilities also offer rebates and programs to encourage the adoption of energy storage. To better understand the investment, explore our analysis of What's the True Cost of a Lithium-Ion Solar Battery?.
Maintenance and Longevity
Solar energy systems are known for their reliability and low maintenance requirements. Panels may need occasional cleaning to remove dust or debris that could hinder production. The most significant advantage of modern systems lies in the battery technology. LiFePO4 batteries are maintenance-free, unlike older lead-acid technologies that required regular upkeep. With durable components, a properly installed system can provide clean energy for 25 years or more.
Scalability and Future Trends
Your energy needs may change over time. That's why our energy storage systems are designed to be scalable. You can start with a battery bank that meets your current needs and easily add more capacity in the future. The energy landscape is also evolving. The IEA points to the growing synergy between distributed solar, battery storage, and electric vehicles (EVs), which can act as additional storage capacity. As technology advances, your solar system will be the foundation for a smarter, more integrated home energy ecosystem. Stay ahead of the curve by reading about 2026 Trends: The Future of Home Energy Storage Solutions.
Your Path to Energy Independence
Setting up a solar battery storage system is a clear step toward energy resilience and control. By understanding the core components, planning carefully, and relying on quality installation, you can create a reliable source of power tailored to your home. A well-designed system built with high-performance LiFePO4 batteries and a smart hybrid inverter doesn't just protect you from outages; it empowers you to manage your energy usage and costs effectively. For a complete overview, refer to The Blueprint for a Solar Battery Storage System Setup.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial or legal advice. Consult with a qualified professional before making any investment decisions or undertaking electrical work.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.