The rapid growth of solar energy is a major step forward for clean power. It also brings a new challenge: what happens to millions of photovoltaic (PV) panels when they reach the end of their typical 25- to 30-year lifespan? While recycling is a common answer, a more valuable opportunity often comes first. This analysis uses data to address key questions about the feasibility, benefits, and challenges of solar panel reuse, a critical component of a circular economy for solar.
The Scale of the Opportunity: Understanding End-of-Life Solar Panels
The volume of decommissioned solar panels is set to grow exponentially. Understanding this trend is the first step toward creating effective end-of-life solutions that prioritize value preservation.
How Many Panels Are We Talking About?
Projections from international energy agencies paint a clear picture of a coming wave of used solar panels. According to research on end-of-life management, cumulative PV panel waste is expected to reach between 60 and 78 million tonnes by 2050. It is important to note that “end-of-life” does not mean a panel has stopped working. Often, it simply means the panel has been replaced by a newer, more efficient model or its output has fallen below the level guaranteed by its warranty.
Reuse vs. Recycling: A Data-Driven Comparison
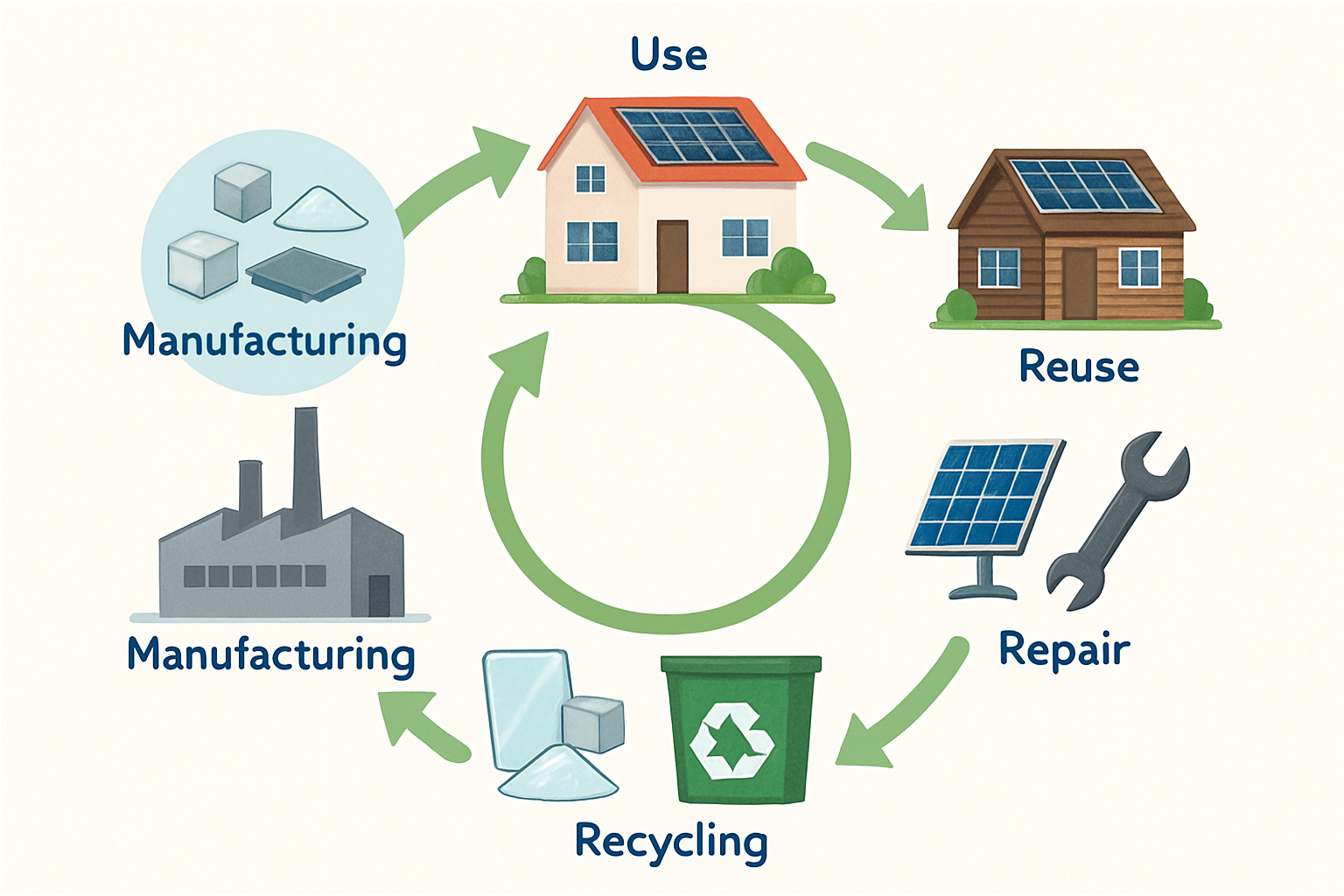
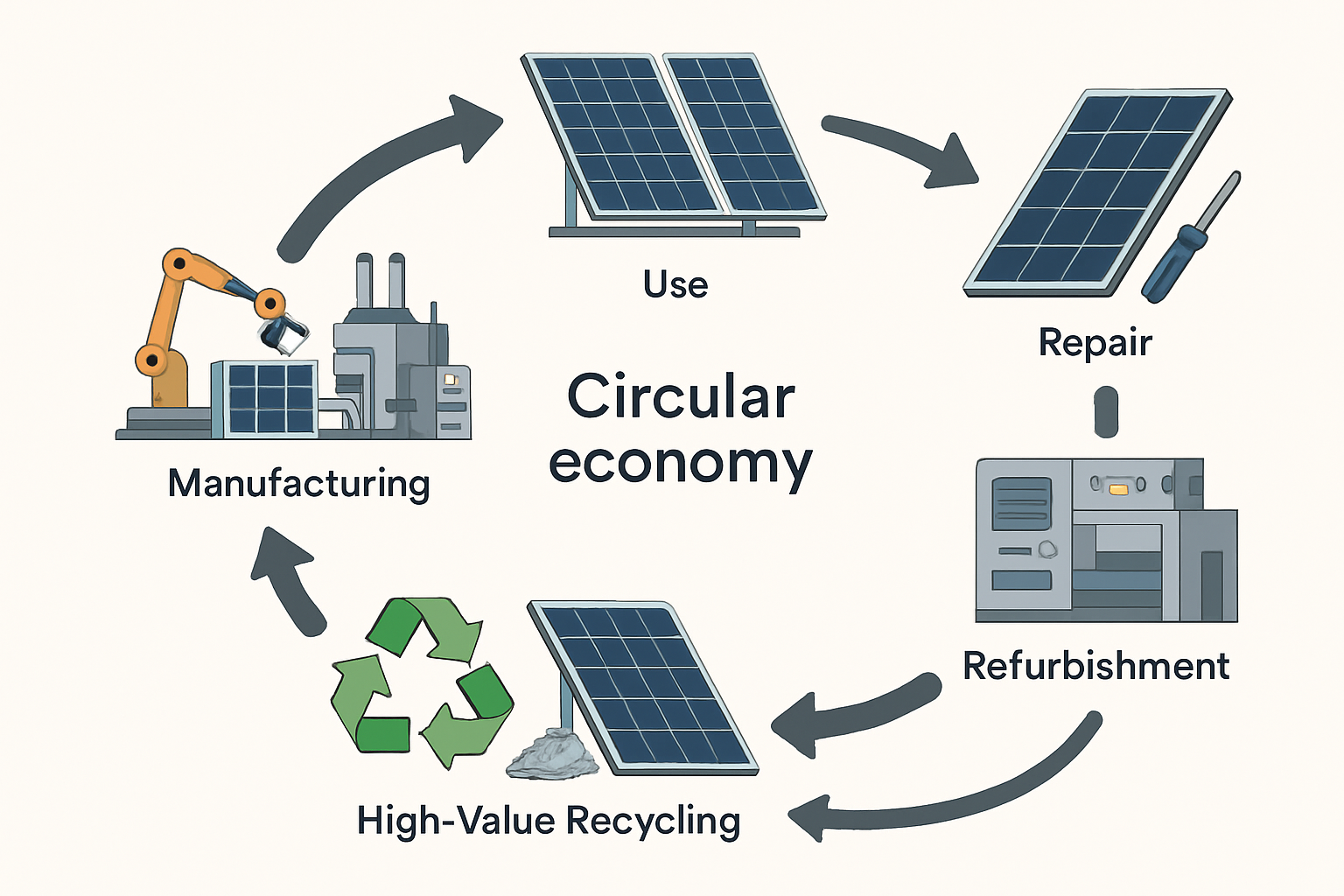
Both reuse and recycling are essential for a sustainable solar industry, but they sit at different levels of the circular economy hierarchy. Reuse is a higher-value option because it preserves the energy and resources embedded in the panel during manufacturing. Recycling breaks the panel down to its constituent materials, a process that itself requires energy. A study by PV Cycle on the challenges and opportunities of PV module reuse highlights that reusing panels can extend their productive life, providing significant environmental and economic benefits.
| Attribute | Solar Panel Reuse | Solar Panel Recycling |
|---|---|---|
| Value Preservation | High (preserves manufactured product) | Medium (recovers raw materials) |
| Energy Savings | High (avoids new manufacturing energy) | Moderate (saves energy over virgin material extraction) |
| Economic Potential | Creates affordable secondary market | Generates revenue from recovered materials |
| Environmental Impact | Lowest impact, extends product life | Low impact, prevents landfilling |
Performance and Reliability of Reused Solar Panels
A primary concern for anyone considering used solar panels is their performance. Data from laboratory tests and field studies show that many panels have significant operational life left, provided they are properly evaluated.

Do Used Panels Still Work Well? Analyzing Degradation Data
Solar panels degrade over time, but at a slow and predictable rate. Most high-quality crystalline silicon panels have a degradation rate of approximately 0.5% per year. This means a 20-year-old panel could still operate at 85-90% of its original nameplate capacity. Actual performance depends on the panel's original build quality, the climate it operated in, and its specific technology. Rigorous testing is the only way to confirm the remaining potential of a used module.
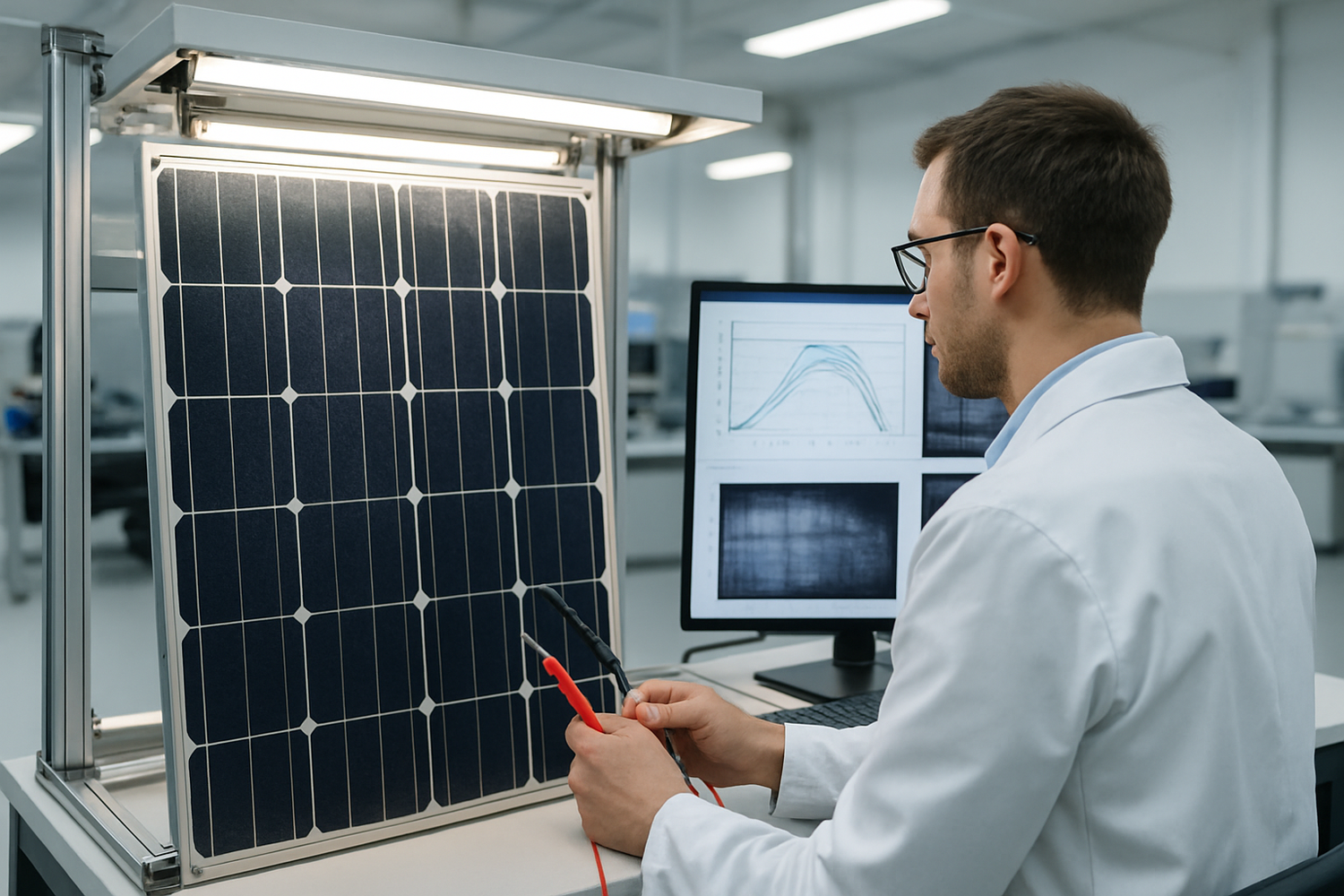
Key Testing and Certification Protocols for Second-Life Modules
To ensure reliability, used panels must undergo a series of tests before they can be safely redeployed. This process creates a trustworthy secondary market.
- Visual Inspection: Technicians check for physical defects like cracks, delamination, yellowing (EVA discoloration), or damaged junction boxes.
- Flash Testing: This test measures the panel's current-voltage (I-V) curve under standard test conditions. It determines the actual maximum power output, which can be compared to its original specifications.
- Electroluminescence (EL) Imaging: EL testing functions like an X-ray for solar panels, revealing microcracks, faulty solder joints, and other defects invisible to the naked eye. This is crucial for assessing long-term durability.
The Market for Reused Solar Panels: A Data Snapshot
A growing secondary market is developing for used solar panels, driven by demand for affordable and reliable energy solutions across various sectors.
Who Buys Used Solar Panels?
The demand for second-life solar panels is diverse. Key markets include off-grid systems for remote homes or agricultural applications, where cost is a primary driver. They are also used in community solar projects in developing economies, providing access to electricity where it was previously unavailable. Budget-conscious homeowners and DIY enthusiasts also represent a growing segment of the market, using these panels for smaller-scale projects.
Economic Viability: A Cost-Benefit Analysis
The primary advantage of used solar panels is their lower cost per watt. While prices vary based on age, condition, and brand, certified used panels can often be purchased for 30-60% less than new ones. This cost saving can significantly reduce the upfront investment for a solar installation, making solar energy accessible to a wider audience. As the Solar PV Global Supply Chains report from the IEA notes, creating robust end-of-life management systems is part of building a resilient and sustainable industry.
| Item | New Solar Panels | Certified Used Solar Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per Watt | $0.50 - $0.70 | $0.15 - $0.35 |
| Warranty | 25-30 years (performance) | 1-5 years (variable) |
| Best For | Grid-tied residential, commercial | Off-grid, DIY projects, budget-conscious installations |
Disclaimer: The cost figures presented are illustrative and can vary based on market conditions, location, and supplier. This information does not constitute investment advice.
A Sustainable Future Built on Circularity
Solar panel reuse is more than just a waste management strategy; it is a vital component of a circular economy. By prioritizing reuse, the solar industry can reduce its environmental footprint, conserve valuable resources, and make clean energy more accessible globally. Data-driven testing and certification are the foundation of this effort, building the trust and transparency needed to scale the secondary market. With supportive policies and industry collaboration, we can ensure that solar panels continue to generate value long after their first life cycle, powering a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions about Solar Panel Reuse
Is it safe to use old solar panels?
Yes, provided they undergo professional testing and certification. Reputable refurbishers verify the panels' electrical safety, check for physical damage, and provide performance data like flash test results. This ensures they are safe and reliable for redeployment.
How much power do used solar panels lose over time?
High-quality panels typically have a performance warranty guaranteeing at least 80% of their original output after 25 years. Real-world data shows an average annual degradation rate of about 0.5% to 0.8%, meaning a 15-year-old panel may still produce over 90% of its initial power.
Can I get a warranty on reused solar panels?
Warranties on used panels vary by supplier. Some refurbishers offer limited warranties, often ranging from 1 to 5 years, covering workmanship and a specific power output threshold. These are shorter than warranties for new panels but provide a level of assurance.
What is the difference between reuse and recycling?
Reuse involves testing, certifying, and then redeploying a functional solar panel in a new installation, extending its useful life. Recycling is a material recovery process where the panel is deconstructed to reclaim its raw components, such as glass, aluminum, silicon, and silver.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.