The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides the foundation for safe electrical design and installation. For solar and energy storage systems, two articles are paramount: NEC 690 for Photovoltaic (PV) Systems and NEC 706 for Energy Storage Systems (ESS). Understanding how these two articles govern the Balance of System (BOS) components is crucial for creating safe, reliable, and compliant projects. The BOS includes all the parts that connect the solar panels and batteries to your home, such as inverters, wiring, and safety devices.
Decoding NEC 690 for Photovoltaic Systems
NEC Article 690 is dedicated entirely to solar electric systems. It covers everything from the PV array itself to the inverters and conductors that deliver power. A well-designed system starts with a solid grasp of these core principles.
Core Requirements for PV Circuits
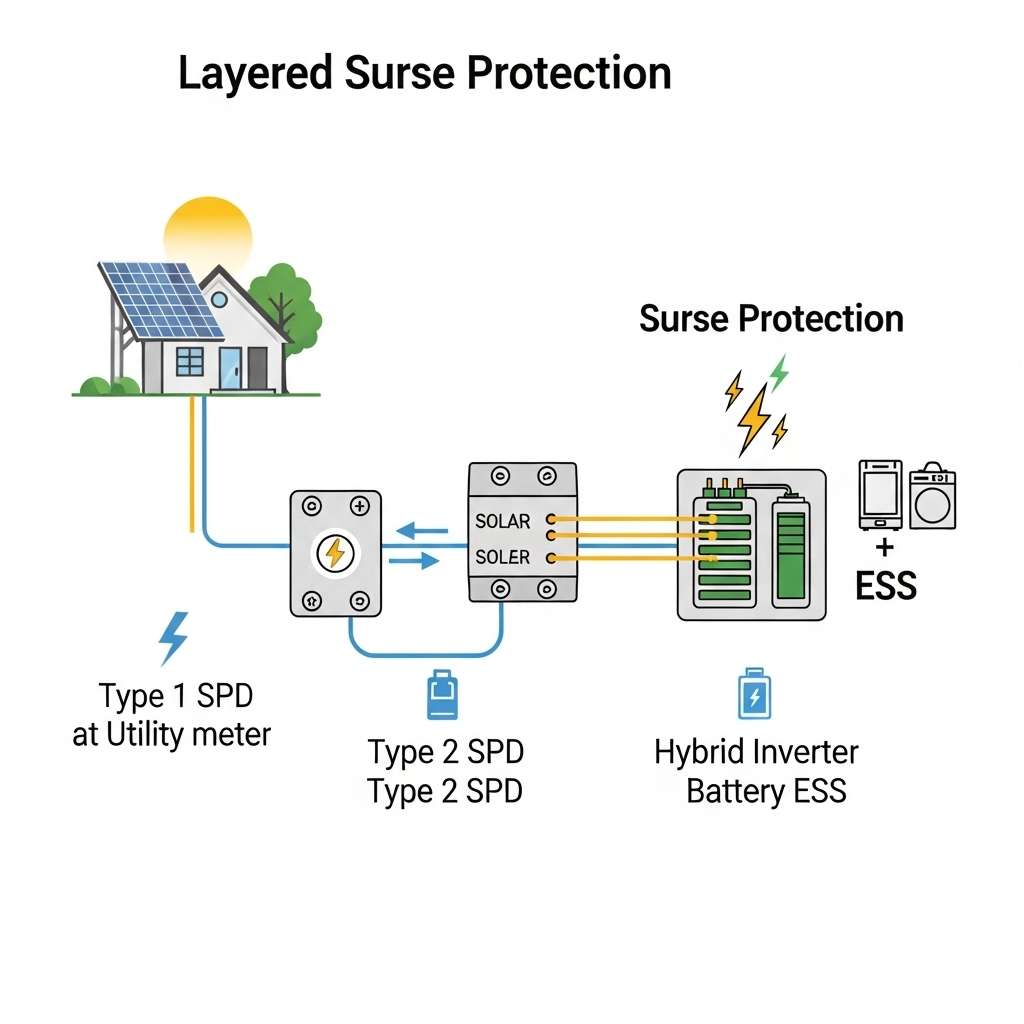
Properly sizing conductors and implementing overcurrent protection are fundamental to PV system safety. Conductors must be sized to handle the maximum possible current under various conditions, accounting for factors like sunlight intensity and temperature. Overcurrent protection devices (OCPDs), such as fuses and circuit breakers, prevent dangerous conditions by interrupting the flow of electricity if a fault occurs. As noted in the IEA's Solar Energy Perspectives report, the BOS, which includes these protection devices and wiring, is essential for the delivery process of solar energy.
Rapid Shutdown Systems (RSD)
A critical safety feature mandated by NEC 690.12 is the rapid shutdown system. Its purpose is to provide a safe working environment for firefighters by quickly de-energizing the PV array conductors. Within a controlled boundary around the array, conductors must be reduced to safe voltage levels within 30 seconds of RSD initiation. This allows first responders to access a roof without the risk of electrical shock from active solar conductors, a vital safety protocol for any PV installation.
Disconnecting Means and Labeling
Clear and accessible disconnecting means are required to isolate PV equipment for maintenance or emergencies. This includes DC disconnects for the array and AC disconnects at the point of connection to the building's electrical system. Equally important is the detailed labeling specified in NEC 690. These labels provide first responders and qualified electricians with critical information about the system, including shutdown procedures, voltages, and the location of key components. Proper signage is a non-negotiable part of a compliant installation.

Mastering NEC 706 for Energy Storage Systems
With the rise of energy storage, NEC 706 was developed to address the unique safety considerations of battery systems. This article covers everything from installation and disconnecting means to ventilation and commissioning.
ESS Disconnecting Means
Similar to PV systems, an ESS requires a readily accessible disconnect to isolate the battery from all other circuits. This is crucial for performing maintenance or responding to an emergency. The disconnect must be clearly labeled and located as specified by the code. For systems containing multiple batteries, specific rules apply to ensure each unit can be safely isolated. This ensures that the stored energy can be contained and controlled when necessary.
Ventilation and Thermal Management
Proper thermal management is key to the safety and longevity of an ESS. While older battery chemistries like flooded lead-acid often required significant ventilation to disperse explosive hydrogen gas, modern technologies have different needs. For sealed lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, the focus shifts from gas dilution to thermal management—keeping the cells within their optimal temperature range. Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions, as they provide the most accurate guidance for your specific ESS technology, a principle that overrides generalized assumptions about ventilation.
Commissioning and Signage
Before an ESS is put into service, it must be commissioned. This process involves a complete inspection and testing of all components to verify that the system is installed correctly and operates safely according to the manufacturer's specifications. NEC 706 also requires specific signage for the ESS, indicating its location, type, and shutdown procedures. This ensures that anyone interacting with the system has the information they need to do so safely.
The Synergy of NEC 690 and 706: Integrated Systems
In a combined PV and energy storage system, NEC 690 and 706 work together. The Balance of System components are what truly unite these two sets of standards, creating a single, cohesive energy solution.
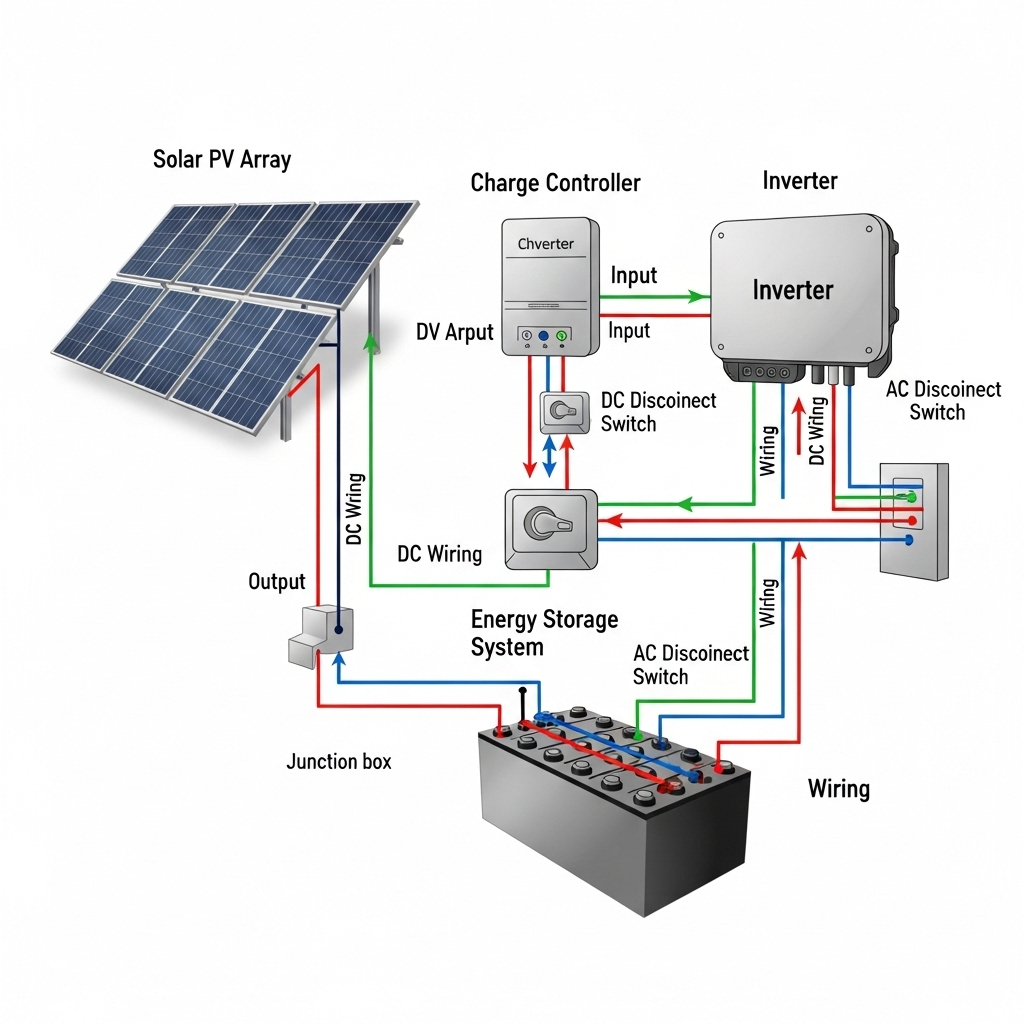
System Interconnection and BOS
BOS components are the bridge between the PV array and the energy storage unit. The inverter, charge controller, wiring, and protection devices must all be selected and installed to handle the flow of energy from the solar panels to the batteries and, ultimately, to the building's loads. A study from the IEA on Next Generation Wind and Solar Power highlights that co-locating solar PV with storage can minimize output variability, making the grid connection more stable and efficient. This synergy is only possible with a properly designed BOS.
Sizing Components in Hybrid Systems
In a hybrid system, conductors and overcurrent protection devices must be sized to accommodate power flow in multiple directions. For example, a circuit may carry current from the PV array to the battery, from the battery to the inverter, or from the PV array directly to the inverter. Each scenario must be calculated to ensure the components are never overloaded, which is a key consideration for both NEC 690 and 706 compliance.
Beyond the Code: Performance and Reliability
Meeting NEC requirements is the baseline for safety and compliance, but system design also directly impacts performance and longevity. High-quality components and proper installation are essential for maximizing your energy investment.
The Role of Quality BOS in System Longevity
Choosing robust and reliable BOS components is just as important as selecting high-quality solar panels or batteries. Inverters with high efficiency ratings, properly sized wiring that minimizes voltage drop, and durable safety switches contribute to a system that not only meets code but also performs optimally for decades. Investing in quality BOS components protects the entire system and ensures it operates at its full potential.
Integrating Performance Metrics
A well-designed system should deliver on its performance promises. Key metrics like Round-Trip Efficiency (RTE) and Depth of Discharge (DoD) are critical for evaluating an energy storage system's effectiveness. As explained in the ultimate reference for solar storage performance, a high-quality LiFePO4 battery can achieve an RTE of 95% or more, meaning very little energy is lost during charging and discharging cycles. Achieving these metrics depends on a system designed and installed in alignment with NEC standards, ensuring all components work together seamlessly.
A Foundation for Safe and Powerful Energy Systems
NEC 690 and NEC 706 are not just sets of rules; they are comprehensive frameworks for building safe and effective solar and energy storage systems. By focusing on the critical role of the Balance of System, installers and designers can create integrated solutions that are compliant, reliable, and high-performing. A deep understanding of these codes transforms a collection of components into a powerful tool for achieving energy independence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between NEC 690 and NEC 706?
NEC 690 specifically governs the installation of photovoltaic (PV) systems, covering everything from the solar panels to the inverter. NEC 706 is dedicated to Energy Storage Systems (ESS), addressing the unique safety requirements of batteries and their associated control equipment.
Why is the Balance of System (BOS) so critical for NEC compliance?
The Balance of System (BOS) includes all the components—like wiring, inverters, and disconnects—that connect the major parts of a PV and storage system. These components are where the requirements of NEC 690 and 706 intersect. Proper BOS design is essential for ensuring the entire system functions safely and meets all code requirements.
Does NEC 706 mandate ventilation for all battery types?
No, it does not. Ventilation requirements are technology-dependent. While older, vented battery technologies required ventilation to disperse harmful gases, modern sealed batteries like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) primarily require thermal management to control temperature. The manufacturer's instructions are the ultimate authority on this matter.


Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.