Adding a residential solar battery to your home is a significant step toward energy independence. It allows you to store excess solar energy for use at night or during a power outage, giving you control over your power. However, a successful and safe energy storage system installation involves more than just buying a battery. It requires careful planning, adherence to specific codes, and a clear understanding of the technical requirements. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of what you need to know.
Pre-Installation Planning: Sizing and System Design
Before any tools come out, the most critical work is in the planning. Proper system design ensures your home battery meets your energy goals, integrates seamlessly with your property, and provides reliable power for years. This phase is about asking the right questions and making informed decisions.
Calculating Your Energy Needs
The first step is to determine the right size for your battery system. An undersized battery won't provide enough backup power, while an oversized one means you've spent more than necessary. Start by reviewing your utility bills to find your average daily energy consumption, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Then, identify the essential appliances you want to power during an outage, such as your refrigerator, lights, medical equipment, or a well pump. Calculating the total power draw of these critical loads will help define the minimum battery capacity and power output you need. Our scalable energy solutions are designed to match a wide range of energy needs, ensuring you get a system that's just right for your home.
Choosing the Right Battery Chemistry: The LiFePO4 Advantage
Not all batteries are created equal. While lead-acid batteries were once common, modern energy storage systems predominantly use lithium-ion technology. Within this category, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have emerged as the superior choice for residential applications. LiFePO4 technology is known for its exceptional safety, long lifespan, and high efficiency. A key performance metric is the Depth of Discharge (DOD), which indicates how much of the battery's capacity can be used. LiFePO4 batteries offer a high DOD, often 90% or more, meaning you can use more of the stored energy. They are a core component of our reliable and high-performance home energy storage systems. For a detailed breakdown of these metrics, you can review this comprehensive guide on solar storage performance.
System Configuration: AC vs. DC Coupling
Your battery system will be either AC-coupled or DC-coupled, which describes how the battery connects to your solar panel system. Solar panels produce DC (Direct Current) electricity, and your home's appliances use AC (Alternating Current). A solar inverter is required to make this conversion.
- DC-Coupled Systems: The solar energy flows directly from the panels to the battery in DC form. A single hybrid inverter then converts this DC power to AC for your home or sends it to the grid. This configuration is highly efficient because the power is only converted once.
- AC-Coupled Systems: The solar energy is first converted from DC to AC by a solar inverter. To charge the battery, that AC power must be converted back to DC. When the battery discharges, the power is inverted back to AC again. This approach is often ideal for retrofitting a battery to an existing solar installation.
Here is a simple comparison:
| Feature | DC-Coupled System | AC-Coupled System |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher (fewer energy conversions) | Lower (more energy conversions) |
| Best Use Case | New solar and battery installations | Adding a battery to an existing solar system |
| Complexity | Can be more complex to install | Generally easier to retrofit |
The right choice depends on your specific situation. For a deeper dive, consider reading about Grid-Tied vs Off-Grid: Which Battery Install Is for You?
Physical and Electrical Installation Requirements
Once the system is designed, the focus shifts to the physical and electrical aspects of the installation. Adhering to best practices and safety codes is non-negotiable to protect your home and investment.
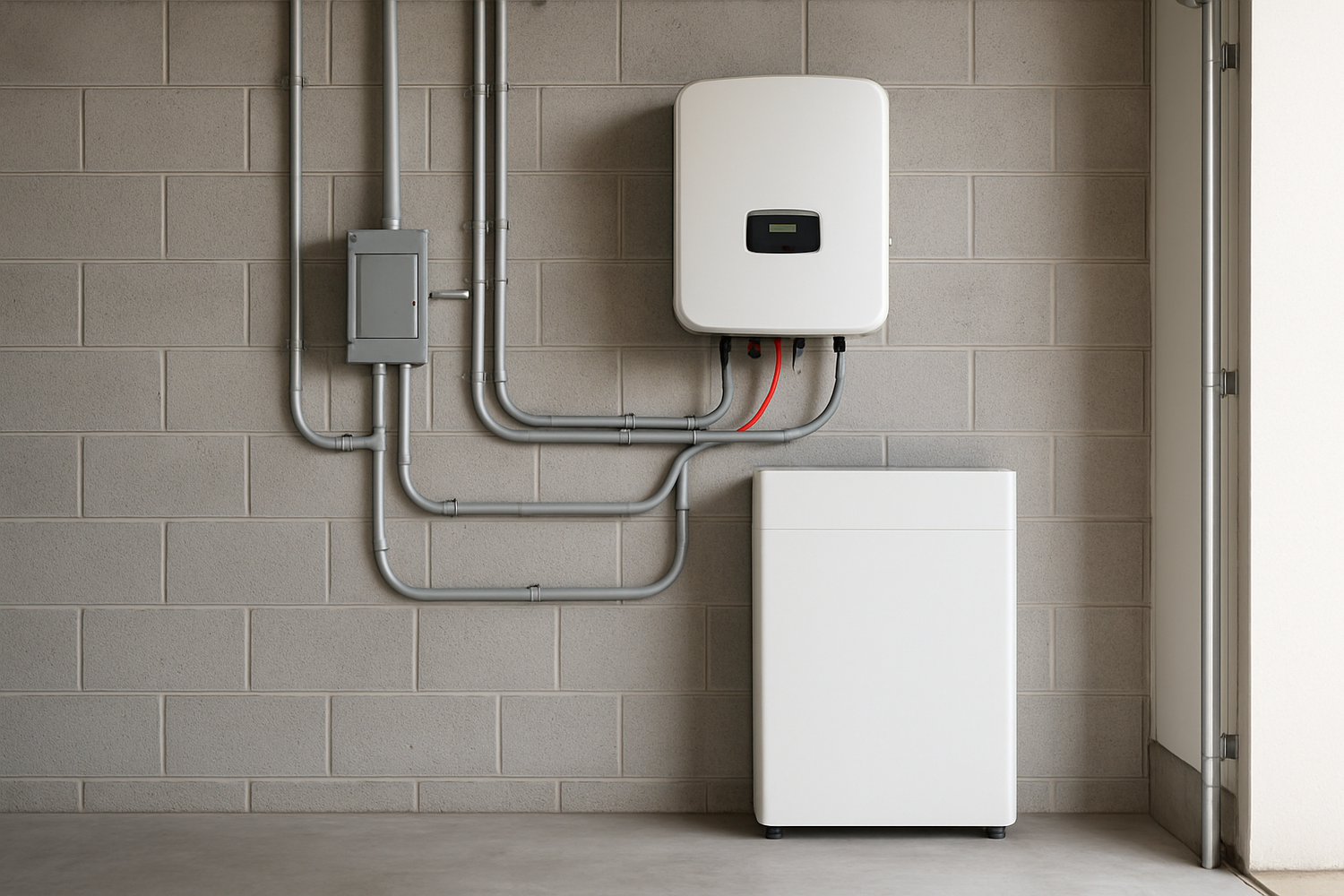
Location, Location, Location: Siting Your Battery System
Where you install your home battery matters significantly for performance and safety. Ideal locations are cool, dry, and well-ventilated. Garages, basements, and utility closets are common choices. Key considerations include:
- Temperature Control: Extreme heat or cold can impact battery life and performance. The location should be protected from direct sunlight and maintain a stable temperature within the manufacturer's specified range.
- Ventilation: Proper airflow is necessary to dissipate any heat generated during charging and discharging.
- Physical Protection: The unit should be protected from physical damage, such as being hit by a vehicle if installed in a garage.
- Accessibility: Ensure there is adequate clearance around the unit for maintenance and inspections as required by code.
For more on this topic, our Siting LiFePO4 Batteries: A Pro Guide to Safety & ROI offers expert guidance.
Electrical Infrastructure and Safety Measures
A home battery installation is a major electrical project that must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local regulations. Key components include the battery itself, an inverter to convert DC/AC power, wiring, and safety devices like circuit breakers and disconnect switches. The system must be properly grounded, and all wiring must be sized correctly to handle the electrical load. Our integrated energy storage systems (ESS) are designed with these requirements in mind, combining the lithium battery, hybrid inverter, and management system into a streamlined package that simplifies installation.
Integrating with Solar Panels
For a residential solar battery system, seamless integration with your solar panels is essential. The battery system must be compatible with the voltage and current characteristics of your solar array. A professional installer will ensure that all components work together efficiently and safely. Proper preparation is key to a successful project, as outlined in our guide on How to Prep for a Flawless Solar Battery Installation.
Navigating Permits, Codes, and Costs
The final phase of requirements involves administrative and financial planning. Understanding the regulatory landscape and the full cost of your project will prevent surprises and ensure a smooth process from start to finish.
Permits and Regulatory Compliance
Nearly all home battery installations require permits from your local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ). This typically involves submitting an application with detailed plans, including a one-line diagram of the electrical system. The permitting process ensures the installation is safe and compliant with local building, electrical, and fire codes. While this can seem daunting, organizations are working to create simplified guidelines to streamline the process for local governments. Working with a certified installer is the best way to navigate this process, as they are familiar with local requirements. To learn more, see our article: Do I Need a Permit for My Home Battery Installation?
Understanding the Full Cost of Installation
The total cost of a home battery project includes more than just the battery itself. The full investment typically ranges from $9,000 to $19,000, depending on system size and complexity. It's important to budget for all components and services.
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Unit | The energy storage device itself. Cost varies by capacity (kWh). | $6,000 - $12,000 |
| Inverter | Converts DC to AC power. May be integrated or separate. | $1,000 - $2,500 |
| Installation Labor | Professional labor for electrical work and mounting. | $1,000 - $2,000 |
| Balance of System (BOS) | Wiring, conduits, breakers, disconnects, and mounting hardware. | $500 - $1,500 |
| Permits & Fees | Fees for local permits and inspections. | $200 - $800 |
For a complete financial picture, explore Beyond the Price Tag: Unpacking Home Battery Install Costs.
Common Installation Pitfalls to Avoid
A successful installation depends on avoiding common mistakes. From our experience, issues often arise from improper system sizing, selecting a poor location, or cutting corners on safety codes. A well-thought-out plan is the best prevention. Using a comprehensive checklist can help you stay on track and ensure no detail is overlooked. We recommend reviewing 5 Big Mistakes in Home Energy Storage System Installs and using Your Home Battery Installation: A 7-Point Checklist to guide your project.
A Final Check on Your Path to Energy Independence
Installing a home battery system is a powerful move towards securing your energy future. By understanding and meeting the requirements for sizing, system design, physical installation, and regulatory compliance, you ensure your system is safe, reliable, and effective. The process requires careful planning and technical expertise, but the rewards—from backup power during outages to greater control over your energy usage—are well worth the effort. By choosing reliable and scalable energy solutions, you are building a more resilient and independent home.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or investment advice. You should consult with a qualified professional for advice tailored to your specific situation.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.