Adding a battery to your solar panel system is a significant step toward energy independence. It allows you to store the excess energy your panels generate during the day and use it at night or during a power outage. When you decide to add a solar battery, the central technical choice you'll face is how to connect it to your system. The two primary methods are Alternating Current (AC) coupling and Direct Current (DC) coupling. This choice impacts efficiency, cost, and installation complexity, especially when adding a battery to an existing solar system.
Understanding the Basics: AC and DC Power in Your Solar System
To grasp the difference between AC and DC coupling, it's helpful to know how electricity flows through your solar installation. The type of electrical current—and how it's converted—is the foundation of this decision.
What is DC Power?
Your solar panels generate Direct Current (DC) electricity. This is a one-way flow of electrical charge. Solar batteries, including modern lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery packs, also store and discharge energy as DC power. This is the native language of solar panels and batteries.
What is AC Power?
Alternating Current (AC) is the type of electricity that powers your home's appliances and is used by the utility grid. AC electricity reverses direction many times per second. A critical component in any solar setup is the inverter, which converts the DC electricity from your panels into usable AC electricity for your home.
The Core of the Choice: Managing Power Conversion
The key difference between AC and DC coupling is where and how many times the solar energy gets converted between DC and AC. Each conversion results in a small amount of energy loss. Minimizing these conversion steps can lead to a more efficient system.
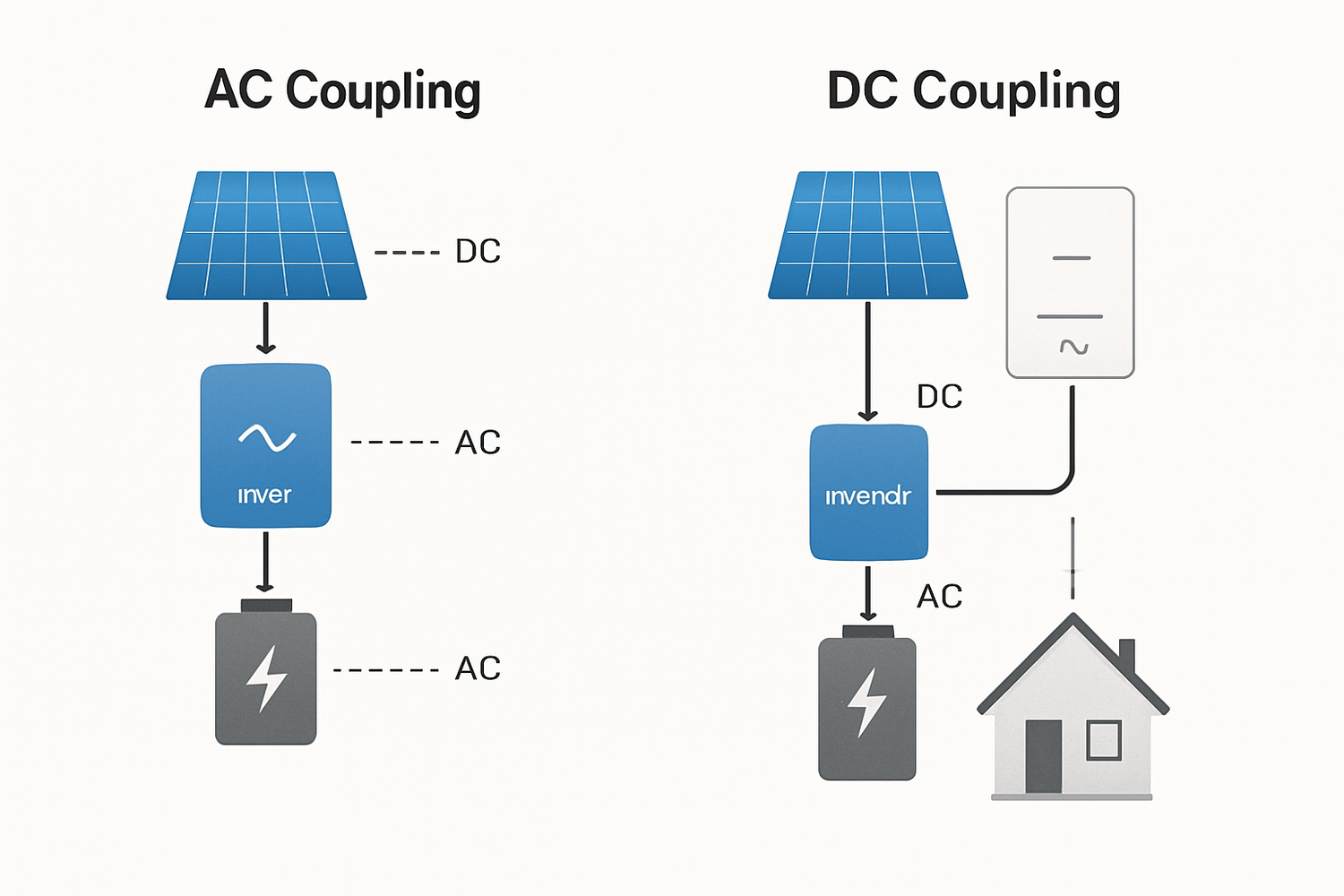
What is DC Coupling?
In a DC-coupled system, the energy flows more directly between the components that use DC power. It is an efficient and streamlined architecture, often favored for new installations.
How DC Coupling Works
With DC coupling, the DC power from your solar panels is sent to a charge controller, which then feeds the DC power directly into your battery. All of this happens before the power is ever converted to AC. A single, specialized inverter, known as a hybrid inverter, manages the power flow from the panels, the battery, and the grid. It converts DC power from either the panels or the battery into AC power for your home as needed.
Advantages of DC Coupling
The primary benefit of DC coupling is higher efficiency. Because the solar energy goes straight to the battery in its native DC form, there are fewer energy conversions. DC-coupled systems can achieve a round-trip efficiency of up to 98%, meaning very little energy is lost in the process of storing and retrieving it. This setup is also effective at capturing 'clipped' energy—power generated by panels that exceeds the inverter's capacity. Instead of being wasted, this excess DC energy can charge the battery.
Disadvantages of DC Coupling
The main drawback of DC coupling is its complexity when retrofitting. If you already have a solar system, you will likely need to replace your existing solar inverter with a more expensive hybrid inverter that can manage both the panels and the battery. This makes it a more invasive and often costlier option for existing setups.
What is AC Coupling?
AC coupling essentially treats the solar array and the battery system as two separate, independent units. This modular approach provides flexibility and is the go-to method for upgrading existing solar installations.
How AC Coupling Works
In an AC-coupled setup, your existing solar panels and solar inverter continue to function as they always have, converting DC power to AC power for your home. To add a battery, a second inverter—a battery inverter—is installed along with the battery. Excess AC power from the solar inverter is directed to the battery inverter, which converts it back to DC to charge the battery. When your home needs power from the battery, the battery inverter converts the battery's DC power back into AC.
Advantages of AC Coupling
The most significant advantage of AC coupling is its simplicity for retrofits. It can be added to virtually any existing grid-tied solar system without modifying the current solar installation. This modularity also means the solar and battery systems operate independently; a fault in one system won't necessarily disable the other. You also gain flexibility, as the battery and its inverter can be sized without being constrained by the existing solar inverter.
Disadvantages of AC Coupling
The main trade-off with AC coupling is lower round-trip efficiency. The multiple power conversions (DC to AC from the panels, then AC to DC for battery storage, and finally DC to AC for use in the home) result in more energy loss. The round-trip efficiency of an AC-coupled system is typically between 90-94%. While this difference may seem small, it can add up over the lifetime of the system.
Head-to-Head Comparison: AC Coupling vs. DC Coupling
Choosing the right solar battery integration method depends on your specific situation. Your priorities regarding efficiency, cost, and your current system setup will guide your decision.
| Feature | AC Coupling | DC Coupling |
|---|---|---|
| Best Use Case | Adding a battery to an existing solar system (Retrofit) | New solar and battery installations |
| Round-Trip Efficiency | Good (Approx. 90-94%) | Excellent (Up to 98%) |
| Retrofit Complexity | Low, works with existing solar inverter | High, often requires replacing the solar inverter |
| Cost (New Install) | Potentially higher (two inverters) | Potentially lower (one hybrid inverter) |
| Cost (Retrofit) | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| System Design | Modular, two separate inverters | Integrated, one hybrid inverter |
Which is Better for an Existing Solar System?
For homeowners who already have solar panels, AC coupling is almost always the more practical and cost-effective solution. The ability to add a battery with a separate inverter without redesigning the existing solar array makes the installation process much simpler and less expensive.
Which is Better for a New Installation?
If you are installing a solar panel and battery system at the same time, a DC-coupled system is often the preferred choice. Its higher efficiency and potentially lower initial equipment cost (one inverter instead of two) make it an attractive option for a brand-new, fully integrated system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Ultimately, both AC and DC coupling are effective ways to add battery storage. The best path forward depends on your starting point. If you have an existing solar system, AC coupling offers a straightforward upgrade path. If you are starting from scratch, the superior efficiency of DC coupling is a compelling advantage. For a deeper analysis of how different system components contribute to overall effectiveness, the Ultimate Reference to Solar Storage Performance provides helpful insights into maximizing your investment. As noted in a U.S. Department of Energy report on improving interconnection, integrating storage is key to building a more resilient grid. Consulting with a qualified solar installer is the best way to evaluate your specific needs and determine the most suitable solution.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. It is not financial or legal advice. Please consult with a qualified professional before making any investment or installation decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can any battery be used with an AC or DC coupled system?
Not necessarily. The battery must be compatible with the chosen inverter (a hybrid inverter for DC coupling or a battery inverter for AC coupling). High-quality lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are a popular choice for their excellent safety profile, long cycle life, and reliability in home energy storage systems.
What is a hybrid inverter?
A hybrid inverter is a multi-functional device that can manage power from solar panels, a battery bank, and the utility grid simultaneously. It is the core component of a modern DC-coupled solar-plus-storage system, streamlining the energy flow between all parts of the installation.
Does coupling type affect my ability to go off-grid?
Both AC and DC coupled systems can be configured for off-grid use or to provide backup power during a grid outage. The critical factors are ensuring the inverters and batteries are rated for this purpose and that the entire system is correctly sized to handle your essential loads without support from the grid.
Is one system safer than the other?
Both systems are safe when designed and installed by certified professionals who adhere to all local electrical codes and safety standards, such as those detailed by institutions like the IEC and IEEE mentioned in reports from organizations like IRENA. The safety of a system is determined more by the quality of its components and the installation work rather than the coupling method itself.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.