Choosing to adopt solar power is a significant step toward managing your energy future. Once you make that decision, a fundamental question arises: should your system be connected to the utility grid, or should it stand completely on its own? Both grid-tied and off-grid solar systems offer distinct advantages and are designed for different needs and locations. Understanding these differences is the key to selecting a solar power solution that aligns with your goals for cost, reliability, and energy independence.
Understanding Grid-Tied Solar Systems
A grid-tied solar system, as the name suggests, is directly connected to your local utility's power grid. It is the most common type of solar installation for homes and businesses in areas with reliable grid access. This setup allows you to draw power from the grid when your solar panels are not producing enough electricity, such as at night or on overcast days.
How Grid-Tied Systems Work
The mechanics are straightforward. Solar panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. A solar inverter then converts this DC power into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the standard form of power used by household appliances. This AC power is used to run your home. If your panels produce more energy than you consume, the excess power is sent back to the utility grid. Many utility companies offer a program called net metering, where you receive credits for the excess energy you supply, which can offset the cost of the electricity you draw from the grid later.
Advantages of a Grid-Tied Setup
The primary benefit of a grid-tied system is the lower initial investment. Because the utility grid acts as a massive, shared battery, you do not need to purchase a dedicated energy storage system. This significantly reduces the upfront cost and complexity of the installation. The grid provides a reliable backup, ensuring you always have power when you need it. Furthermore, financial incentives like net metering can lead to substantial savings on your electricity bills over time.
Limitations to Consider
The main drawback of a standard grid-tied system is its dependence on the grid. During a power outage, the solar inverter is legally required to shut down automatically. This safety measure prevents the system from sending electricity back to the grid while utility workers are attempting to make repairs. This means that even if the sun is shining, a grid-tied system will not provide you with power during a blackout. Your energy costs are also still tied to the policies and rate structures of your local utility.
Exploring Off-Grid Solar Systems
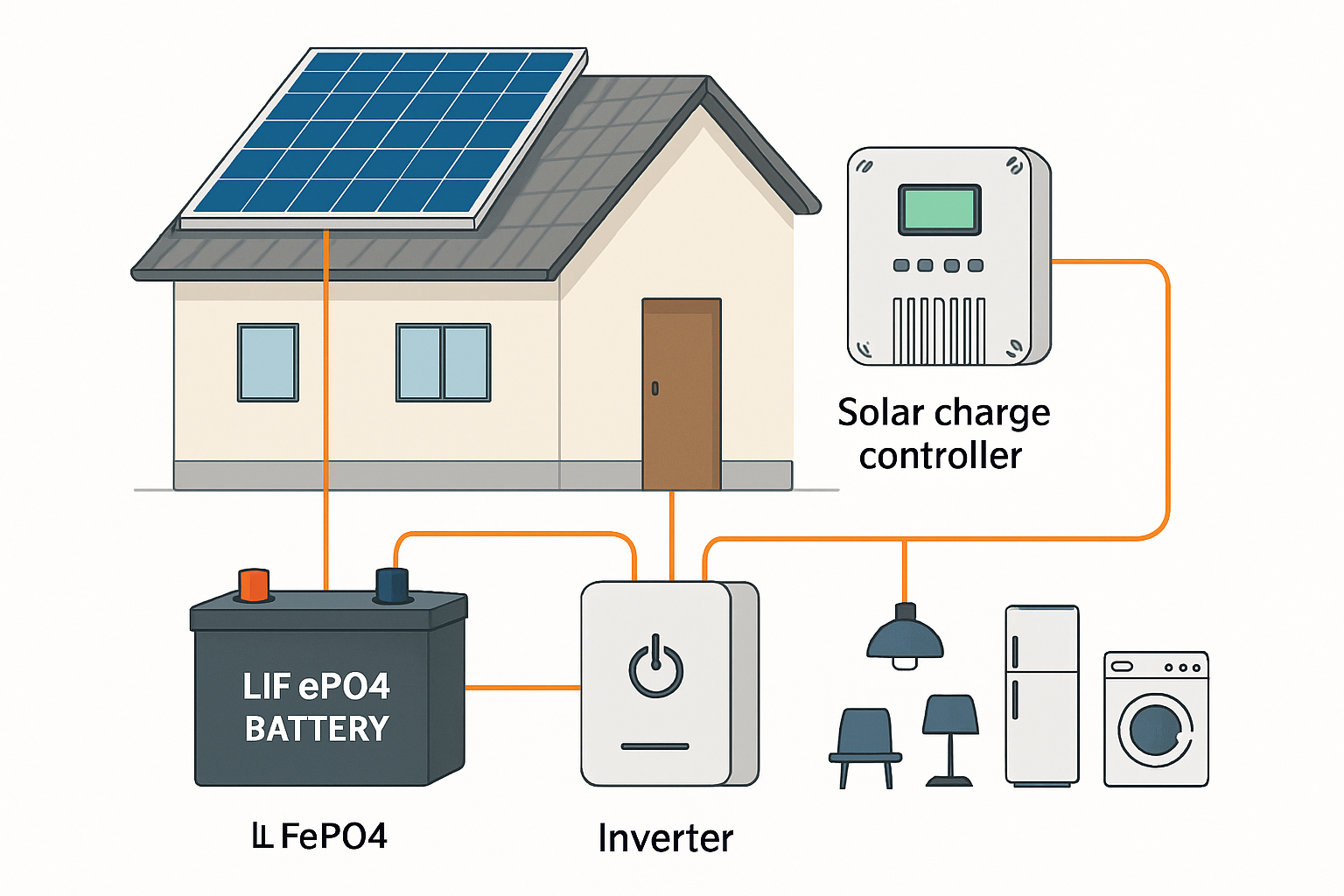
An off-grid solar system is a completely independent power system. It is not connected to the utility grid, giving you full control over your electricity generation and consumption. These systems are ideal for remote properties, cabins, farms, or for anyone seeking complete energy independence and resilience against grid failures.
The Core of an Independent Power System
The heart of an off-grid system is its battery bank. Unlike a grid-tied setup, all the energy produced by the solar panels that is not immediately used must be stored for later use. This makes the selection of a high-quality battery crucial for system reliability and longevity. High-performance LiFePO4 (lithium iron phosphate) batteries are a leading choice due to their long cycle life, safety, and efficiency, forming a dependable core for any off-grid solar solution.
Key Components of an Off-Grid System
An off-grid solar system is more complex than its grid-tied counterpart. The essential components include:
- Solar Panels: To capture energy from the sun.
- Charge Controller: To regulate the voltage and current going from the panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging.
- Battery Bank: A scalable array of batteries, such as 12V LiFePO4 battery packs, to store energy.
- Solar Inverter: To convert the stored DC electricity from the batteries into usable AC power.
- Backup Generator (Optional): Often included as a safeguard to charge the batteries during extended periods of poor weather.
Benefits of Energy Independence
The most significant advantage of an off-grid system is immunity to power outages. When the public grid goes down, your lights stay on. This provides an unparalleled level of power security. You also achieve predictable, stable electricity costs, free from the fluctuating rates of utility companies. For properties located far from existing power lines, an off-grid solar system can be more cost-effective than paying for the extension of utility infrastructure.
A Direct Comparison: Key Factors for Your Decision
Choosing between these two solar power solutions requires a careful evaluation of your priorities. The right choice depends on factors like your location, budget, energy needs, and desire for self-sufficiency.
| Feature | Grid-Tied System | Off-Grid System |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower (no batteries required) | Higher (requires batteries, charge controller) |
| Energy Independence | None; dependent on the grid | Complete energy independence |
| Power During Outages | No (shuts down for safety) | Yes (primary benefit) |
| Maintenance | Minimal; mainly panel cleaning | Requires battery monitoring and maintenance |
| Best For | Urban and suburban homes with reliable grid access | Remote properties, cabins, or users seeking total resilience |
Analyzing the Financial Investment
The upfront cost is a major differentiator. Off-grid systems are more expensive due to the necessity of a robust battery bank. However, the cost of solar technology has decreased dramatically. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global weighted average Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) for solar PV fell by 90% between 2010 and 2023. This trend makes both system types more financially accessible than ever before, offering a strong return on investment through long-term energy savings.
Reliability and Power Security
Reliability means different things for each system. A grid-tied system is as reliable as the utility grid it's connected to. However, concerns about grid stability are growing. A recent report from the U.S. Department of Energy highlights that without significant upgrades, the risk of power outages could increase substantially. In contrast, the reliability of an off-grid system is entirely in your hands. It depends on proper system design, the quality of its components—especially the lithium battery storage—and your energy management practices. A well-designed off-grid setup offers superior power security against blackouts.
The Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds?
For those who want the reliability of the grid and the security of backup power, a third option exists: the hybrid solar system. This solution combines elements of both grid-tied and off-grid setups.
What is a Hybrid Solar System?
A hybrid system is a grid-tied system that includes a battery bank for energy storage. Like a standard grid-tied system, it can send excess power back to the grid. However, it can also store that excess energy in batteries. This stored power can be used at night, during peak-rate hours to save money, or most importantly, to provide backup power during a grid outage. This capability is one of the key benefits highlighted by the Department of Energy for homeowners seeking resilience.
Why Choose a Hybrid Solution?
A hybrid solution offers unmatched flexibility. You gain protection from power outages without having to disconnect from the grid entirely. It maximizes your use of the solar energy you generate, further reducing your reliance on your utility. For anyone considering this path, a deep understanding of solar storage performance is essential to designing a system that meets your backup power needs effectively. Hybrid systems represent a future-proof investment, adapting to changing energy needs and utility policies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Property
Ultimately, the ideal solar power solution is the one that best fits your unique circumstances. If you live in an area with a stable grid and your primary goal is to reduce your monthly electricity bill, a grid-tied system is an excellent and cost-effective choice. If you live in a remote location, experience frequent power outages, or place the highest value on complete energy independence, an off-grid system provides the security and self-sufficiency you need. For those who desire the best of both, a hybrid system offers a powerful and flexible compromise, blending grid stability with the peace of mind that comes with battery backup.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a grid-tied system work during a power outage?
Typically, no. For safety reasons, standard grid-tied inverters shut down during an outage to prevent sending power back to the grid where workers may be making repairs. A hybrid system with battery storage is required for backup power.
How large of a battery bank do I need for an off-grid system?
The size depends on your daily energy consumption, the number of days of autonomy you need (for cloudy days), and the depth of discharge of your batteries. A detailed energy audit is the first step. High-performance batteries like a 100Ah lithium battery can be scaled to meet specific needs.
Is going completely off-grid legal?
In most places, yes. However, you must check local building codes and regulations. Some jurisdictions may have specific requirements or restrictions, so it is important to consult with local authorities before disconnecting from the grid.
What is the lifespan of an off-grid solar system?
Solar panels often have warranties of 25 years or more. Inverters typically last 10-15 years. The battery lifespan is a critical factor. Modern lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries can last for thousands of cycles, often exceeding 10 years with proper maintenance, making them a durable core for an independent power system.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.