Fasteners are the components that hold your entire solar energy system together. Yet, they are often overlooked until a problem arises. PV fastener corrosion is a silent threat that can compromise the structural integrity, safety, and performance of your solar array. Addressing your most pressing questions, this page provides clear, actionable insights to protect your investment from the ground up.
What Really Causes Fasteners to Corrode in a Solar Array?
Corrosion isn't a single problem but a result of several factors working together. Understanding these causes is the first step toward effective prevention and ensuring long-term fastener durability for your solar installation.
The Role of Environmental Factors
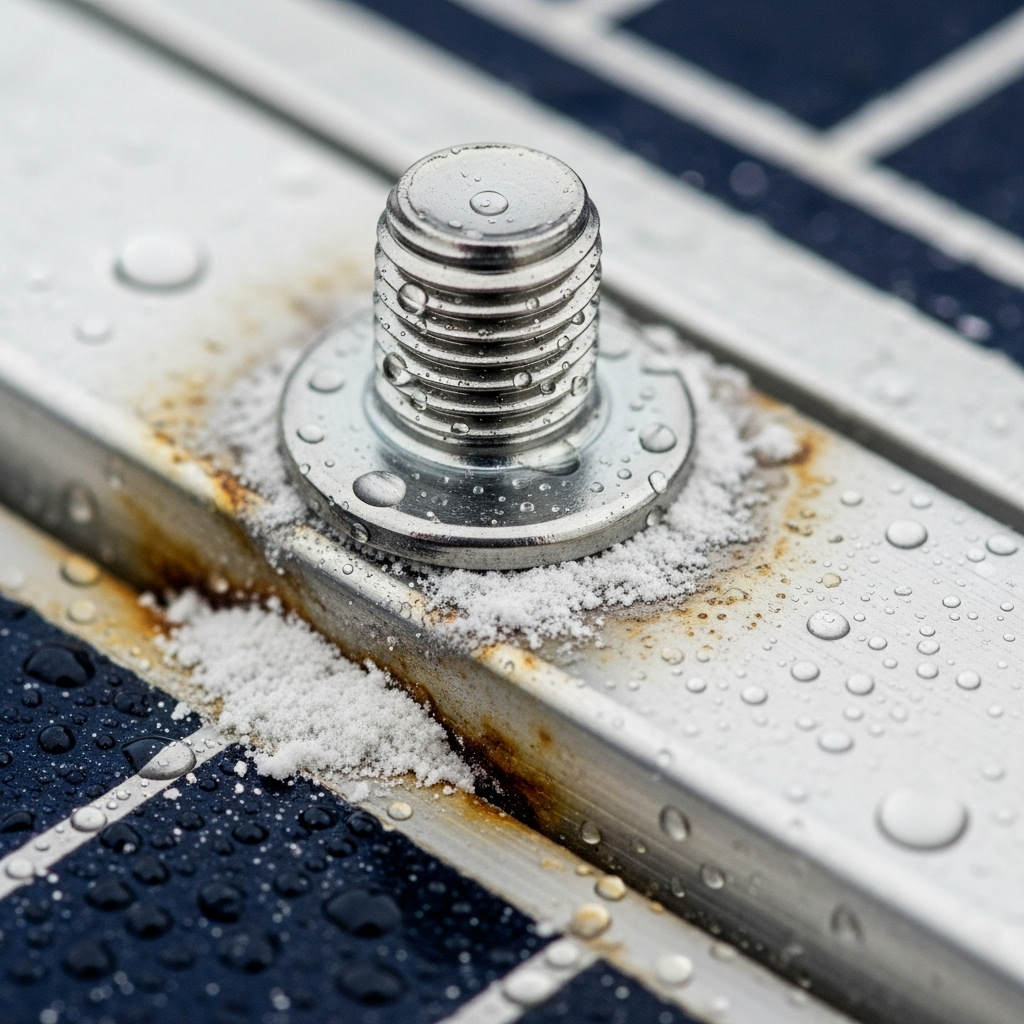
The primary driver of corrosion is exposure to the elements. Moisture, whether from rain, humidity, or dew, creates the electrolyte necessary for corrosion to begin. In coastal areas, salt spray dramatically accelerates this process. Industrial zones with airborne pollutants like sulfur dioxide can also create acidic conditions that attack metal surfaces. Temperature cycles cause materials to expand and contract, which can stress fasteners and crack protective coatings, opening pathways for moisture intrusion.

Understanding Galvanic Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion is a specific electrochemical reaction that occurs when two different metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an electrolyte. In solar arrays, this commonly happens between aluminum mounting racks and stainless steel fasteners. The aluminum becomes the anode and corrodes at an accelerated rate, while the stainless steel (cathode) is protected. Over time, this can weaken the mounting structure around the fastener, leading to a loss of clamping force and potential failure.
Other Corrosion Types to Watch For
Beyond general and galvanic corrosion, other forms can affect PV fasteners. Crevice corrosion can occur in the tight, oxygen-deprived spaces under bolt heads or washers where stagnant moisture accumulates. Stress corrosion cracking is a more insidious issue where a combination of tensile stress and a corrosive environment can cause sudden fastener failure, even if the metal appears intact.
How Can I Identify Early Signs of Fastener Corrosion?
Regular inspections are critical for catching corrosion before it leads to significant damage. Knowing what to look for allows you to take corrective action early, saving on costly repairs and ensuring the system's safety.
Visual Inspection Checklist
A simple visual check can reveal the first signs of trouble. Look for rust-colored staining on and around steel fasteners, which indicates active oxidation. For aluminum components, check for white, powdery deposits, a tell-tale sign of aluminum oxide. Also, inspect for any pitting, flaking, or bubbling on the surface of coated fasteners, as this suggests the protective layer has been breached. These inspections are especially important after periods of heavy rain or extreme weather.
Tools and Techniques for a Deeper Look
For a more thorough assessment, a few tools can help. A torque wrench can be used to check if fasteners are maintaining their specified clamping force; a fastener that has loosened over time may be a symptom of underlying corrosion. For hard-to-see areas within the racking assembly, a small mirror or a digital borescope can provide a clear view without requiring disassembly.
What Are the Best Strategies for PV System Corrosion Mitigation?
Preventing corrosion is a matter of design, material selection, and proper installation. A proactive approach to PV system corrosion mitigation ensures the system's longevity and reliability from day one. The importance of this field is highlighted by ongoing innovation. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency, corrosion protection is a significant area of patent activity, underscoring the industry's focus on durability. The Offshore wind energy: Patent insight report notes that between 2018 and 2022, 112 new applicants filed patents related to corrosion protection technologies.
Material Selection and Coatings
The first line of defense is choosing the right materials. Stainless steel, particularly grades like 316 (marine grade), offers excellent corrosion resistance but comes at a higher cost. Galvanized steel provides good protection, but the coating can be compromised by scratches during installation. Advanced fastener coatings, such as zinc-flake or ceramic, offer superior protection by creating a durable barrier against the environment.
The Importance of Galvanic Isolation Fasteners
To prevent galvanic corrosion, you must break the electrical circuit between dissimilar metals. This is where galvanic isolation fasteners and components are essential. Using non-conductive polymer washers, sleeves, or pads made from materials like EPDM or nylon creates a physical barrier. This separation stops the electrochemical reaction, protecting the more vulnerable metal (usually the aluminum rack) from accelerated degradation.
Proper Installation and Maintenance Practices
Even the best materials can fail if installed improperly. It is crucial to use a torque wrench to apply the correct amount of force. Overtightening can damage protective coatings and the fastener itself, while under-tightening can allow moisture to penetrate the connection. Additionally, ensuring the racking system is designed for proper water drainage prevents moisture from pooling around fastener locations, reducing the risk of corrosion.
How Does Corrosion Impact Overall System Performance and Safety?
Fastener corrosion is more than a cosmetic issue. It has direct consequences for the safety of the installation and can even have an indirect effect on its energy production and financial return.
Compromised Structural Integrity
The most immediate risk of severe fastener corrosion is structural failure. Weakened or failed fasteners can no longer provide the necessary clamping force to hold solar modules in place. During a high-wind event, this could lead to modules shifting, vibrating, or detaching from the rack entirely. Such a failure poses a significant safety hazard and can cause extensive damage to the system and surrounding property.
The Link Between Corrosion and Energy Output
A well-maintained structure is fundamental to consistent energy generation. Corrosion can compromise the system's electrical grounding paths, which are critical for safety and proper inverter function. While fasteners are not directly involved in electricity production, their failure is part of a larger system health issue. A system suffering from structural neglect is unlikely to receive the attention needed for peak performance. Maintaining every component, from fasteners to batteries, is key to reliability, a principle detailed in the ultimate reference for solar storage performance.
Final Thoughts on Fastener Longevity
Protecting your solar array from corrosion starts with the smallest components. By understanding the causes of PV fastener corrosion, selecting appropriate materials, incorporating galvanic isolation fasteners, and following correct installation procedures, you build a foundation of durability. Regular inspections and proactive maintenance ensure that your solar energy system remains secure, safe, and productive for its entire expected lifespan. Paying attention to these details is a direct investment in your energy independence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I inspect my PV fasteners for corrosion?
For most residential and commercial systems, a thorough visual inspection once a year is sufficient. However, if your system is located in a harsh environment, such as a coastal region with salt spray or an industrial area with chemical pollutants, inspections should be conducted every six months.
Can I replace corroded fasteners myself?
If you have the right tools and technical knowledge, replacing a few corroded fasteners is possible. However, it is critical to use the correct type of replacement fastener and apply the manufacturer-specified torque. For widespread corrosion or if you are unsure, it is always best to consult a qualified solar installer to ensure the system's structural integrity is not compromised.
Are more expensive fasteners always better for corrosion prevention?
Cost often correlates with performance, but the 'best' fastener is the one most appropriate for the specific environment. For example, in a dry, inland climate, a high-quality galvanized fastener may be perfectly adequate. In a coastal or marine setting, investing in marine-grade 316 stainless steel is a wise choice that provides superior long-term protection against salt-induced corrosion.
Does the type of solar panel affect fastener corrosion?
The solar panel itself does not directly cause fastener corrosion. The critical interaction is between the panel's frame, which is typically made of aluminum, and the fasteners used to secure it to the mounting rack. The choice of fastener material must be compatible with the aluminum frame to prevent galvanic corrosion. This is why using galvanic isolation fasteners or washers is a common and effective strategy.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.