A home energy storage system (ESS) is a cornerstone of energy independence. Yet, the performance and safety of these powerful systems hinge on managing a single, critical factor: heat. Unchecked, rising temperatures can lead to a dangerous chain reaction known as thermal runaway. Smart ventilation offers an intelligent, automated defense, actively protecting your investment and ensuring your system operates safely and efficiently.
Understanding the Threat: Thermal Runaway in Residential Batteries
Thermal runaway is a process where excessive heat triggers a self-perpetuating cycle of temperature increase. This can compromise the battery's integrity and, in rare cases, lead to fire. While modern lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have a very stable chemistry, understanding the risks is the first step toward effective prevention.
What Triggers This Chain Reaction?
Several factors can initiate the process, including internal short circuits, significant physical damage, or severe overcharging. These events generate heat faster than the battery can dissipate it. As the internal temperature climbs, it accelerates the chemical reactions, producing even more heat. This feedback loop is the core of thermal runaway. Effective thermal management is designed to break this cycle before it can begin.
The Role of Ambient Temperature
The environment surrounding your ESS plays a huge part in its internal temperature. A battery system installed in a hot garage or in direct sunlight is already starting at a thermal disadvantage. Most LiFePO4 batteries perform best between 15°C and 35°C (59°F to 95°F). Operating outside this window not only poses a safety risk but also harms the battery's health and efficiency. As detailed in the ultimate reference on solar storage performance, sustained exposure to high temperatures can permanently reduce a battery's capacity and shorten its operational life.
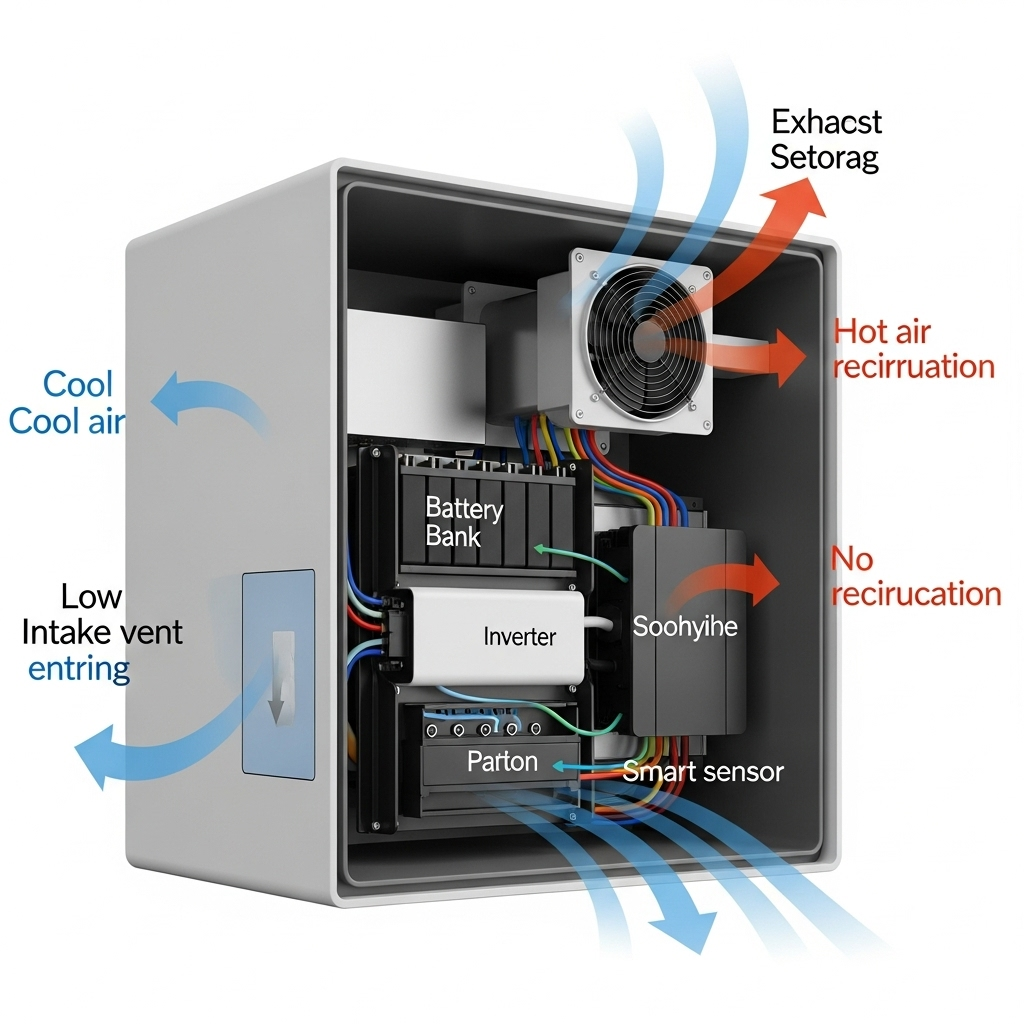
Beyond Basic Vents: The Components of a Smart Ventilation System
A smart ventilation system is more than just a fan in a box. It's a responsive network of components that work together to create the ideal thermal environment for your ESS. It reacts to changing conditions in real-time, providing the precise amount of cooling needed.
The Brains: Smart Controllers and Sensors
At the heart of the system is a controller linked to a series of sensors. Thermistors, a type of temperature sensor, are placed on or near the batteries and within the enclosure to monitor temperatures continuously. The controller processes this data, acting as the decision-making hub. More advanced systems may also incorporate sensors for humidity or airflow to provide a more complete environmental picture.
The Brawn: Variable-Speed Fans and Actuators
Unlike simple on/off fans, variable-speed fans are the muscle of a smart system. They can adjust their speed based on the controller's commands. For minor temperature increases, they might run at a low, quiet speed. During heavy system use or on a hot day, they can ramp up to full power to quickly exhaust excess heat. This dynamic response is far more efficient and quieter than a basic active cooling setup.
The Logic: Setting Up Automated Rules
The intelligence of the system lies in its programming. The controller follows a set of predefined rules to manage the thermal environment. Examples of this logic include:
- If any battery module temperature exceeds 30°C (86°F), set exhaust fans to 50% speed.
- If the enclosure's internal temperature is more than 10°C above the external ambient temperature, increase fan speed by 25%.
- If the external ambient temperature is higher than the battery temperature, keep intake vents closed to prevent drawing hot air into the system.
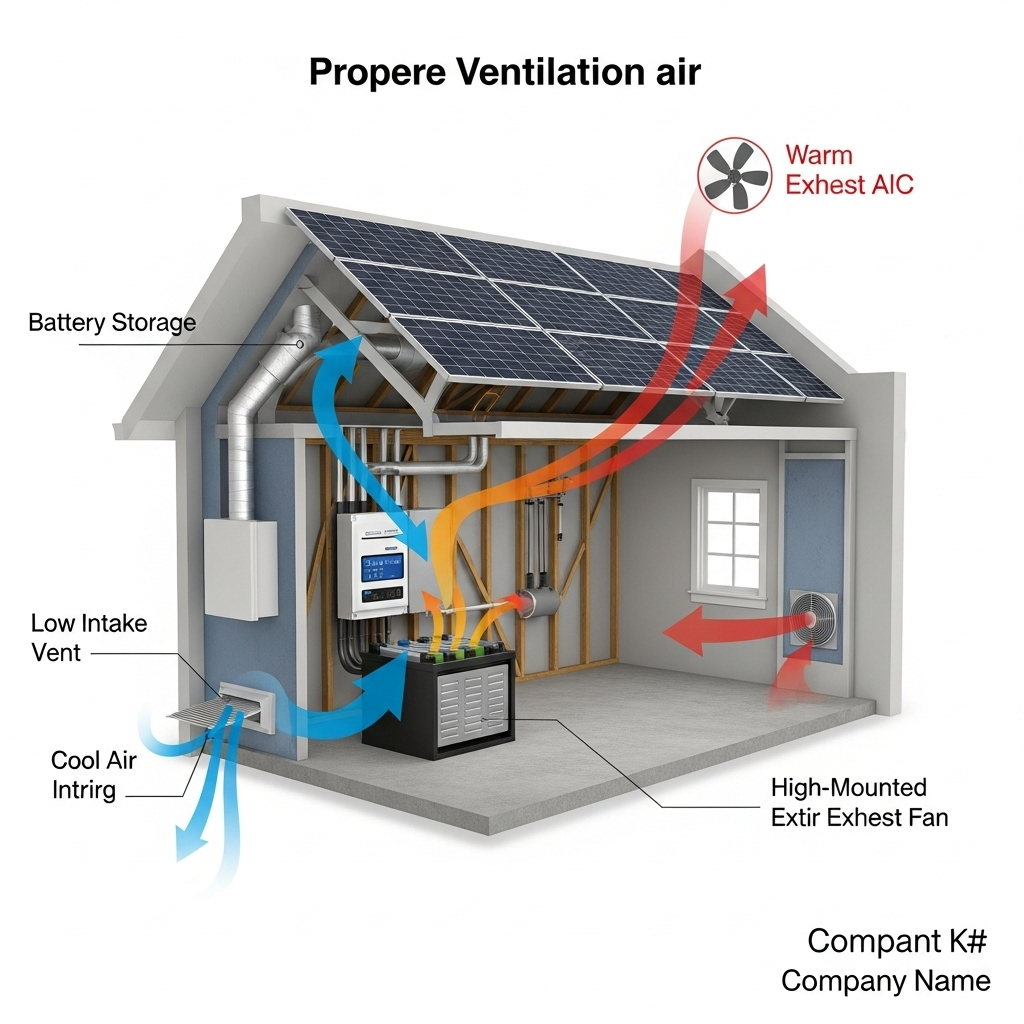
Designing an Effective Smart Ventilation Strategy
A successful smart ventilation system depends on a solid design that considers airflow dynamics, component placement, and the specific heat load of your ESS.
Calculating Airflow Requirements
Proper airflow is measured in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM). You need enough airflow to remove the waste heat generated by the batteries and inverter. A simplified formula to estimate this is CFM = (Total Heat in Watts) / (Desired Temperature Rise in °F * 1.08). The 'Total Heat' is the energy lost as heat during charging and discharging. A properly sized fan or set of fans is crucial for the system to be effective.
Intake and Exhaust Placement
The layout of your vents is critical. To leverage natural convection, the cool air intake should be positioned low in the enclosure, while the hot air exhaust fan should be placed high. This creates a clear path for air to flow across the components, effectively removing heat. Poor placement can lead to air pockets or recirculation of hot air, defeating the purpose of the ventilation.
The Broader Impact: Smart Thermal Management and Grid Stability
The benefits of intelligent thermal management extend beyond a single home. As more households adopt energy storage, smart systems play a role in creating a more resilient and flexible energy grid.
Enhancing System Longevity and Performance
Ultimately, the primary goal of a smart ventilation system is to protect your investment. By keeping your batteries within their ideal temperature range, you are not just ensuring safety; you are maximizing their lifespan and ensuring you get the performance you paid for, year after year.
The Future of Smart Energy Homes
Smart thermal management is a key component of the modern, connected home. According to the IEA's report on Clean Energy Innovation, deploying smart controls enables households to provide valuable flexibility services that aid in the grid integration of renewable energy. This forward-looking approach is echoed by other institutions. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) notes in its Innovation outlook: Thermal energy storage report that such smart systems are essential for increasing demand-side flexibility and supporting grid stability. The technology to make this happen is becoming more accessible. Research from the IEA's The Power of Transformation report suggests that the cost of adding grid-ready smart functionality to appliances is minimal and likely to become a standard feature over time.
Putting It All Together
Protecting your home energy storage system from thermal runaway is not about hoping for the best; it's about implementing intelligent, proactive measures. A smart ventilation system provides a dynamic and automated solution to thermal management. It goes beyond simple vents and fans, using sensors and logic to maintain optimal conditions, thereby safeguarding your hardware, enhancing performance, and extending the life of your system. While some components are accessible for DIY projects, consulting with a qualified professional is always the best path for designing and installing a system that is both safe and effective.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional engineering, financial, or legal advice. Always consult with certified professionals before designing or installing any energy storage or ventilation system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do all home batteries need ventilation?
Yes, all battery systems generate heat during charging and discharging. While LiFePO4 batteries are known for their safety and stability, proper thermal management through ventilation is a fundamental requirement for ensuring safety, achieving optimal performance, and maximizing the system's lifespan.
What is the difference between active and passive ventilation?
Passive ventilation uses natural convection—the tendency for hot air to rise—to circulate air through vents without mechanical assistance. Active ventilation uses fans to force air movement, providing more powerful and reliable cooling. Smart ventilation is an advanced form of active ventilation that automates fan speed and operation based on real-time data from temperature sensors.
Can I build my own smart ventilation system?
While components like smart controllers, sensors, and fans are available to consumers, creating a safe and effective system requires a solid understanding of airflow principles, electrical wiring, and local safety codes. For most homeowners, using a pre-engineered solution or working with a professional installer is the recommended approach to ensure safety and reliability.
How much noise does a smart ventilation system make?
A major advantage of a smart ventilation system is its low noise profile. Because it employs variable-speed fans, the system typically operates at a low, nearly inaudible speed for routine temperature regulation. The fans only increase to higher, more audible speeds during periods of intense heat, which should be infrequent in a well-designed and properly located ESS.


Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.